Can You Take Contrave and Qsymia Together: Understanding Drug Interactions
Dr. Matthew Olesiak, MD, is the Chief Medical Director at SANESolution, a renowned wellness technology company dedicated to providing evidence-based solutions for optimal living. Dr. Olesiak earned his medical degree from the prestigious Jagiellonian University Medical College in Kraków, Poland, where he developed a strong foundation in medicine.

Contrave and Qsymia are both weight loss drugs prescribed for chronic weight management in adults struggling with obesity or weight-related conditions. While both medications have shown efficacy in promoting weight loss for compatible individuals, they contain different active ingredients that could interact negatively when taken together.
Clinical trials have shown the safety and effects of these medications, including observed visual field defects, which were found to be reversible after discontinuing the treatment.
In other words, in taking Contrave and Qsymia together, drug interactions can occur. Understanding the drug interactions, possible side effects, and potential risks of combining Contrave and Qsymia is crucial for patients considering these treatments.
Key Takeaways
- Combining Contrave and Qsymia may increase the risk of serious drug interactions, including high blood pressure, seizures, and mood changes.
- Both medications have different active ingredients that can affect the central nervous system, potentially leading to dizziness, blurred vision, and difficulty concentrating.
- Patients should consult their doctor or pharmacist before taking these weight loss drugs to minimize risks and closely monitor side effects.
Comparison of Contrave and Qsymia
| Category | Contrave | Qsymia |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredients | Bupropion, Naltrexone | Phentermine, Topiramate |
| Mechanism of Action | Reduces cravings, alters neural responses to food stimuli | Suppresses appetite, increases satiety |
| Common Side Effects | Dizziness, dry mouth, insomnia, mood changes, increased blood pressure, nausea | Increased heart rate, blurred vision, mood changes, dizziness, insomnia |
| Key Warnings | Not recommended for individuals with seizure disorders, eating disorders, or those on MAOIs | Not recommended for individuals with heart disease, seizures, or substance abuse hist |
What Are Contrave and Qsymia?
Contrave
Contrave is a prescription weight loss drug designed for chronic weight management in certain adults with obesity or overweight individuals who have weight-related conditions such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, or high cholesterol. It combines two active ingredients:
- Bupropion: A medication commonly used to treat depression and aid in smoking cessation. It also acts on the central nervous system, influencing dopamine and norepinephrine levels, which play a role in appetite regulation and mood changes. When used to treat depression, it is important to monitor for suicidal thoughts and behaviors during treatment, especially among young adults.
- Naltrexone: An opioid antagonist often prescribed to help individuals with alcohol or opioid dependence. In the context of weight loss, it affects brain reward pathways, reducing food cravings and reinforcing healthy eating habits.
How Contrave Works
By targeting both hunger signals and food cravings, Contrave helps patients reduce calorie intake while following a reduced-calorie diet and engaging in increased physical activity. Unlike stimulant-based weight loss drugs, it does not directly suppress appetite but instead alters neural responses to food-related stimuli.
Possible Side Effects of Contrave
Like many weight loss medications, taking Contrave may lead to adverse reactions.
Some common Contrave side effects include:
- Dizziness and difficulty concentrating
- Dry mouth and insomnia
- Mood changes, including depression, anxiety, and in rare cases, suicidal thoughts
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate
- Stomach pain, abdominal pain, and nausea
- Constipation: this side effect is so common that it’s often called Contrave constipation.
Do side effects of Contrave go away? You’ll be pleased to know that most of the minor side effects diminish after your body adjusts to the medication.
Patients with eating disorders, seizure disorders, or those taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) should avoid the weight management drug due to increased risks of Contrave drug interactions and severe side effects. Consulting a doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment is essential.
Qsymia
Qsymia is another prescription weight loss drug that combines two active ingredients:
- Phentermine: A stimulant that belongs to the sympathomimetic amine class. It works by increasing norepinephrine release, reducing appetite, and boosting energy levels, making it easier for patients to follow a reduced-calorie diet.
- Topiramate: Originally an anti-seizure medication, it also promotes weight loss by enhancing satiety, making food less appealing, and reducing binge eating behaviors.
How Qsymia Works
Qsymia affects multiple pathways, leading to a dual-action approach to weight loss:
- Phentermine’s stimulant effects reduce hunger and increase metabolism.
- Topiramate’s neurological impact helps patients feel fuller sooner and for longer periods.
Because phentermine topiramate influences both brain chemistry and metabolic function, Qsymia is considered one of the more effective weight loss drugs for chronic weight management for compatible individuals.
However, it requires careful monitoring due to potential drug interactions and side effects.
Possible Side Effects of Qsymia
Patients taking Qsymia may experience various side effects, including:
- Increased heart rate and high blood pressure
- Blurred vision, eye pain, and difficulty operating hazardous machinery
- Abdominal pain and stomach pain
- Mood changes, including depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts
- Dizziness, insomnia, and dry mouth
Due to its stimulant component, Qsymia is not recommended for individuals with a history of heart disease, seizures, or substance abuse. Patients should work closely with their doctor to determine the recommended dose and assess any adverse reactions.
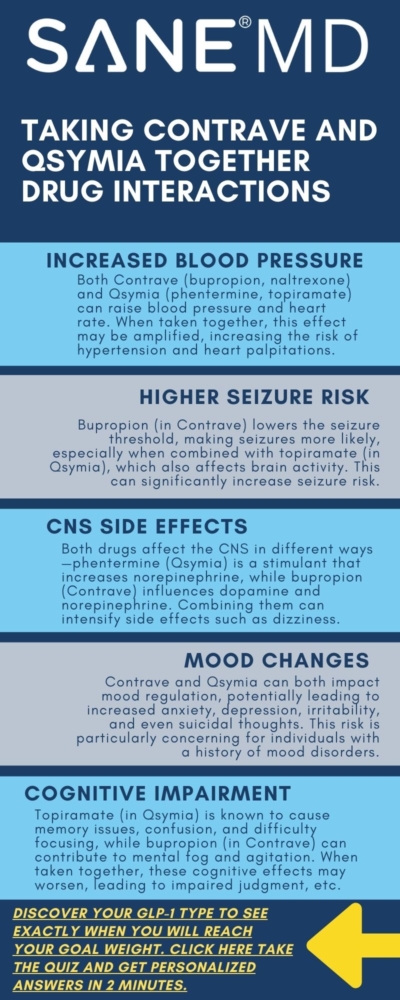
Can You Take Contrave and Qsymia Together?
While both Qsymia and Contrave treatment are used for weight loss, taking them together can increase the risk of severe drug interactions.

These medications work on different pathways but share overlapping side effects, potentially leading to:
- Increased blood pressure and heart disease risks
- Mood changes, including depression, suicidal thoughts, and anxiety
- Risk of seizures, especially in patients with a history of epilepsy
- Dizziness, blurred vision, and difficulty concentrating, increasing the risk when operating hazardous machinery
How These Medications Interact
When considering Contrave and Qsymia together, it is essential to understand how their active ingredients interact within the body.
Since both medications influence different physiological pathways, they can create compounding effects that may lead to significant health risks.
These interactions primarily affect three major areas: cardiovascular health, the central nervous system (CNS), and the risk of seizures. Patients who have pre-existing conditions related to high blood pressure, heart disease, depression, or neurological disorders should be especially cautious.
Consulting a doctor before combining these weight loss drugs is crucial to minimize the risk of severe adverse reactions.
Effects on Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
One of the most concerning risks of combining Contrave treatment with phentermine topiramate in Qsymia is the impact on blood pressure and heart rate.
Both medications can stimulate the cardiovascular system, leading to:
- Increased blood pressure, which can elevate the risk of hypertension
- Chest pain, potentially signaling underlying heart disease
- Increased heart rate, which may contribute to cardiovascular complications
Patients with high blood pressure, heart disease, or those taking beta-blockers should avoid taking these medications together, as the combination may increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events.
Close monitoring of blood pressure and heart function is essential for anyone taking Contrave and Qsymia simultaneously.
Impact on the Central Nervous System
Both bupropion (from Contrave) and phentermine (from Qsymia) target the central nervous system, which can lead to neurological side effects when combined.
The simultaneous stimulation of the CNS may result in:
- Insomnia, making it difficult to fall or stay asleep
- Dizziness, which can impair physical activity and increase risks when operating hazardous machinery
- Mood changes, including increased anxiety, irritability, and depression
- Suicidal thoughts, particularly in patients with a history of mental health conditions
- Difficulty concentrating, which may affect work and daily activities
Because these drugs both affect neurotransmitter levels, they may also increase the risk of blurred vision and eye pain, further impacting day-to-day function.
If a patient experiences any of these symptoms, they should contact their doctor immediately.
Risk of Seizures
Combining Contrave and Qsymia may significantly increase the risk of seizures, especially in individuals with a personal or family history of epilepsy.
The following factors contribute to this increased risk:
- Bupropion in Contrave lowers the seizure threshold, making seizures more likely
- Phentermine topiramate in Qsymia also affects brain activity, which may compound the risk of seizures
- Patients using other drugs that influence neural function (such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications) may be at even greater risk
Those who have experienced seizures in the past should not take Contrave treatment and Qsymia together unless specifically approved and closely monitored by a doctor.
Possible Side Effects of Taking Contrave and Qsymia Together
The combined use of Contrave and Qsymia may lead to numerous adverse reactions.
Some of the most common side effects include:
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate, elevating the risk of heart disease
- Seizures, particularly in individuals with a history of neurological conditions
- Mood changes, including depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts
- Dizziness and blurred vision, which may interfere with daily activities
- Dry mouth and stomach pain, common among weight loss drugs
- Abdominal pain and joint pain, which may indicate an allergic reaction
- Eye pain and unusual changes in vision, potentially signaling a serious adverse reaction
Since these side effects can be severe, patients should carefully monitor their health and report any unusual symptoms to their doctor.
Proper medical supervision and periodic health checkups are essential when taking these medications for chronic weight management.
Contraindications and Warnings
When considering Contrave and Qsymia together, it is crucial to understand that not all patients are suitable candidates for these medications. Certain pre-existing medical conditions and other drugs can lead to severe adverse reactions, increasing the risk of heart complications, seizures, and mood changes.
Some individuals may face increased risks of high blood pressure, liver damage, or neurological issues when using these weight loss drugs.
Before starting treatment, patients should consult their doctor or pharmacist to assess whether these medications are safe for their specific health profile.
Below are the key groups of patients who should avoid taking Contrave and Qsymia together due to heightened health risks.
Who Should Avoid Taking These Drugs Together?
Patients with High Blood Pressure or Heart Disease
Since both Contrave and Qsymia can increase blood pressure and heart rate, individuals with hypertension or a history of heart disease should avoid combining these medications.
Taking Contrave and Qsymia together may elevate the risk of:
- Chest pain and heart palpitations
- Increased heart rate, which may worsen cardiovascular conditions
- High blood pressure, leading to a greater risk of stroke or heart attack
Patients with a history of heart disease should work closely with their doctor to determine safer alternatives for chronic weight management.
Individuals with a History of Seizures
People with a history of epilepsy or those at risk for seizures should avoid Contrave treatment, especially when combined with phentermine topiramate in Qsymia. Bupropion, one of the active ingredients in Contrave, is known to lower the seizure threshold, increasing the risk of seizures.
Additionally, topiramate in Qsymia can also impact neurological function, compounding the potential for seizure activity.
If a patient has previously experienced seizures, their doctor should explore alternative weight loss drugs that do not interfere with neurological stability.
Those Diagnosed with Eating Disorders (Such as Anorexia or Bulimia)
Patients with a history of eating disorders, particularly anorexia nervosa or bulimia nervosa, should not take Contrave. This is because bupropion has been shown to increase the risk of seizures in individuals with a history of disordered eating behaviors.
Additionally, using phentermine topiramate in Qsymia may suppress appetite to a dangerous extent, leading to malnutrition or worsening of disordered eating patterns.
For those with eating disorders, a doctor should be consulted for alternative treatments that support chronic weight management without increasing health risks.
Patients Currently Taking Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of antidepressant medications that interact dangerously with Contrave and Qsymia. Patients taking MAOIs, such as phenelzine or tranylcypromine, should avoid these weight loss drugs because the combination can cause:
- Dangerous spikes in blood pressure (hypertensive crisis)
- Severe mood changes, including increased risk of suicidal thoughts
- Increased heart rate, leading to cardiovascular complications
Patients should wait at least 14 days after stopping MAOIs before starting treatment with Contrave or Qsymia to prevent adverse reactions.
Those with Liver Damage or Severe Kidney Disease
Both Contrave and Qsymia are metabolized through the liver and kidneys, meaning patients with liver damage or severe kidney disease may be at increased risk of toxicity or impaired drug clearance.
These individuals may experience:
- Worsening liver function, increasing the risk of liver damage
- Reduced kidney function, leading to potential drug accumulation in the body
- Heightened side effects, including abdominal pain, joint pain, and blurred vision
Patients with liver disease or severe kidney impairment should speak with their doctor to find safer options for chronic weight management.
Final Considerations
For patients with any of the conditions above, the combination of Contrave and Qsymia may pose serious health risks.
A doctor should assess each individual’s medical history before prescribing weight loss drugs and consider alternative treatment plans that minimize drug interactions and adverse reactions.
Recommended Dose and Safety Precautions
Proper Dosage
Patients should follow the recommended dose for each medication and avoid self-medicating or combining low-dose forms without medical supervision.
Monitoring for Adverse Reactions
Patients should watch for adverse reactions, including chest pain, difficulty concentrating, blurred vision, and mood changes. If any of these occur, they should contact their doctor immediately.
Interactions with Other Drugs
When considering weight loss drugs like Contrave and Qsymia, it’s crucial to be aware of potential interactions with other medications. These interactions can lead to serious adverse reactions, including high blood pressure, seizures, and mood changes. Here are some key drug interactions to be mindful of:
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Combining Contrave with MAOIs can result in dangerous spikes in blood pressure, seizures, and severe mood changes. Patients should wait at least 14 days after stopping MAOIs before starting Contrave.
- Other Antidepressants: Taking Contrave with other antidepressants can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by high fever, agitation, and rapid heart rate.
- Antipsychotics: Combining Contrave with antipsychotic medications can heighten the risk of seizures and other adverse reactions, making it essential to consult a doctor before combining these drugs.
- Beta-Blockers: Using Contrave alongside beta-blockers can lead to increased blood pressure and other cardiovascular issues, necessitating close monitoring by a healthcare provider.
- Antiarrhythmics: The combination of Contrave with antiarrhythmic drugs can elevate the risk of seizures and other serious side effects.
- Ticlopidine and Clopidogrel: These medications, when taken with Contrave, can increase the risk of bleeding, requiring careful medical supervision.
- Ritonavir and Lopinavir: Combining these antiviral drugs with Contrave can lead to elevated blood pressure and cardiovascular complications.
- Efavirenz: This medication can increase the risk of seizures and other adverse reactions when taken with Contrave.
- Theophylline: The risk of seizures and other adverse reactions is heightened when Contrave is combined with theophylline.
- Corticosteroids: Using corticosteroids with Contrave can lead to increased blood pressure and other cardiovascular problems.
- Levodopa and Amantadine: These medications can increase the risk of seizures and other adverse reactions when taken with Contrave.
- Alcohol: Combining alcohol with Contrave can exacerbate high blood pressure, seizures, and other adverse reactions, making it important to avoid alcohol while on this medication.
Understanding these interactions is vital for safe and effective chronic weight management. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting or combining weight loss drugs with other medications.
Alternative Weight Loss Treatments
For those who cannot take Contrave or Qsymia due to interactions with other medications, there are several alternative weight loss treatments available. These options can help you achieve your weight loss goals while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): Originally used to treat type 2 diabetes, Liraglutide has been shown to aid in weight loss by regulating appetite and food intake.
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): Another medication initially developed for type 2 diabetes, Semaglutide helps with weight loss by mimicking a hormone that targets areas of the brain involved in appetite regulation.
- Phentermine/Topiramate (Qsymia): While Qsymia may not be suitable for everyone due to potential interactions, it remains an effective option for some patients under careful medical supervision.
- Orlistat (Alli, Xenical): This medication works by reducing the absorption of fat in the digestive system, helping patients lose weight when combined with a reduced-calorie diet.
- Bariatric Surgery: For those with severe obesity, bariatric surgery can be a highly effective option. This surgical procedure reduces the size of the stomach, limiting food intake and promoting significant weight loss.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthier lifestyle is a cornerstone of weight loss. This includes following a reduced-calorie diet, increasing physical activity, and making sustainable changes to eating habits.
It’s essential to discuss these alternative treatments with your doctor to understand the potential risks and benefits. Your healthcare provider can help you determine the best weight loss strategy tailored to your individual health needs and medical history.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
As patients explore weight loss medications like Contrave and Qsymia, many have concerns about potential drug interactions and safety risks.
Below are answers to some of the most common questions regarding the use of Contrave treatment, phentermine-topiramate, and other medications.
Understanding these interactions is essential for chronic weight management and minimizing potential side effects.
1. Can you take Qsymia and Contrave together?
It is not recommended to take Qsymia and Contrave together due to their overlapping effects on blood pressure, heart rate, and the central nervous system. Both medications influence appetite suppression and cravings through different mechanisms, but when combined, they can increase the risk of severe side effects, such as high blood pressure, seizures, mood changes, and suicidal thoughts.
Additionally, both drugs can cause dizziness, blurred vision, and difficulty concentrating, making it dangerous to engage in activities like operating hazardous machinery.
Patients considering combining these drugs should consult their doctor immediately to discuss safer alternatives.
2. Can I take topiramate and Contrave together?
Taking topiramate (an ingredient in Qsymia) and Contrave together is generally not advised unless under strict medical supervision. Topiramate is known to affect cognitive function, which, when combined with bupropion in Contrave, could increase the risk of difficulty concentrating, dizziness, and mood changes.
Additionally, both medications have been linked to increased blood pressure and seizures, particularly in patients with pre-existing neurological conditions. If a doctor prescribes both medications, they may start with a low dose and closely monitor for adverse reactions.
3. Can you take phentermine and Contrave together?
Combining phentermine (the stimulant in Qsymia) with Contrave is generally not recommended due to its effects on the central nervous system and cardiovascular system.
Phentermine increases heart rate and blood pressure, which, when taken alongside bupropion and naltrexone in Contrave, could significantly increase the risk of chest pain, hypertension, and seizures. Furthermore, both drugs can contribute to insomnia, anxiety, and mood changes, potentially leading to suicidal thoughts in vulnerable patients.
Those interested in using both medications should consult a doctor to explore safer chronic weight management options.
4. What medications should not be taken with Contrave?
Several other medications can negatively interact with Contrave, leading to potentially serious adverse reactions.
Patients should avoid taking Contrave with:
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) – Can lead to dangerous spikes in blood pressure and severe drug interactions.
- Opioid medications – Since Contrave contains naltrexone (an opioid antagonist), it can block the effects of opioids and trigger withdrawal symptoms.
- Beta-blockers and blood pressure medications – Combining these drugs may lead to increased blood pressure or reduced effectiveness of blood pressure control.
- Seizure medications – Since bupropion lowers the seizure threshold, it should not be taken with drugs like phenytoin or carbamazepine, which also affect neurological stability.
- Alcohol – Consuming alcohol while taking Contrave can worsen dizziness, depression, and mood changes, increasing the risk of suicidal thoughts.
To prevent severe interactions, patients should discuss their current medications with a doctor or pharmacist before starting Contrave treatment.
Conclusion
Taking Contrave and Qsymia together is not typically recommended due to increased risks of high blood pressure, seizures, and drug interactions. Patients should discuss their weight loss options with a doctor or pharmacist before combining these medications.
Proper medical supervision and lifestyle changes are key to safe and effective chronic weight management.