The Skin Health Imperative: Navigating the Intersection of Global Burden, Booming Markets, and Technological Innovation in 2026
In 2026, the landscape of skin health presents a compelling and increasingly complex dichotomy. On one hand, the global burden of skin diseases continues its alarming rise, significantly impacting millions worldwide, straining healthcare systems, and diminishing overall quality of life. From pervasive conditions like dermatitis and acne to the escalating incidence of skin cancer – now the world’s most common malignancy – the data underscores that skin health is far more than a cosmetic concern; it is a fundamental aspect of human well-being, productivity, and a critical public health imperative.
Conversely, consumer interest in proactive skin care has never been higher, fueling a booming and innovation-rich industry. Valued at approximately $155 billion in 2023 and projected to exceed $220 billion by 2029, the global skincare market reflects a profound societal shift towards prioritizing dermal wellness. This comprehensive report delves into these converging trends, examining the significant public health challenges posed by dermatological conditions, the exponential growth and evolving dynamics of the global skincare market, and the transformative role of technology and shifting consumer demands in shaping future trajectories.
Key Takeaways
- Skin diseases are a major global health burden, accounting for approximately 44.84 million DALYs (Disability-Adjusted Life Years) worldwide in 2021.
- Skin cancer is the world’s most common malignancy, with over 1.5 million new cases estimated in 2022 and rising incidence rates due to an aging population and insufficient UV protection.
- Despite proven benefits, sun protection adherence remains low, with only 12% of U.S. adults using sunscreen daily in 2025.
- The global skincare market is booming, projected to reach over $220 billion by 2029, driven by increased consumer focus on health and aesthetics.
- Demographic shifts, including an aging population and broader male consumer engagement, are fueling significant growth in anti-aging and general skincare segments.
- Technological innovations like AI-powered diagnostics, personalized product formulations, and smart at-home devices are revolutionizing the skincare industry.
- Consumer demand is shifting towards clean, sustainable, and personalized skincare solutions, with social media playing a powerful role in trend dissemination and brand growth.
1. Executive Summary
The landscape of skin health in 2026 presents a compelling paradox: while the global burden of skin diseases continues to rise, impacting millions and straining healthcare systems, consumer interest in proactive skin care has never been higher, driving a booming, innovation-rich industry. This executive summary provides a high-level overview of the critical findings from our comprehensive research, highlighting the significant public health challenges posed by dermatological conditions, the exponential growth and evolving dynamics of the global skincare market, and the transformative role of technology and shifting consumer demands in shaping future trends. It underscores that skin health is far more than a cosmetic concern; it is a fundamental aspect of overall human well-being, productivity, and an increasingly vital sector of the global economy.
1.1. The Critical Global Burden of Skin Diseases
Skin diseases represent a pervasive and often underestimated public health challenge globally. Unlike many life-threatening conditions, skin ailments rarely garner the same level of attention, yet their collective impact on quality of life, disability, and healthcare resources is profound. As of 2021, skin and subcutaneous diseases accounted for approximately 44.84 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) worldwide[2], a significant increase from an estimated 41.6 million DALYs in 2013[18]. This makes skin conditions one of the leading causes of non-fatal health loss globally, underscoring that maintaining skin health transcends mere aesthetics to become a critical public health imperative[2].
The prevalence of these conditions is striking: three skin diseases rank among the 10 most prevalent diseases worldwide[3]. Conditions such as dermatitis (e.g., eczema), acne, and fungal infections affect hundreds of millions of individuals, leading to chronic discomfort, psychological distress, and, in many cases, lost productivity and increased healthcare expenditure. For instance, dermatitis alone affected around 230 million people in 2019, highlighting the ubiquitous nature of such dermatological issues. While often not life-threatening, the chronic nature and visible manifestations of skin conditions can severely impact mental well-being, social interactions, and professional life, correlating with higher rates of anxiety and depression in affected individuals[20].
1.1.1. The Alarming Rise of Skin Cancer
Among the most serious skin health concerns is cancer, which has become the world’s most common malignancy[10]. In 2021, the total incidence of skin cancer (encompassing both melanoma and non-melanoma types) reached 6.64 million cases globally[5]. This figure reflects a persistent upward trend, with the age-standardized incidence rate increasing by approximately 1.94% annually between 1990 and 2021[6]. Looking specifically at 2022, there were an estimated 1.5 million new skin cancer cases worldwide[4]. Of particular concern is cutaneous melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, which accounted for around 330,000 new cases and nearly 60,000 deaths in 2022 alone[4]. Projections indicate a further 50% increase in annual melanoma cases by 2040, driven by a combination of an aging global population and increased ultraviolet (UV) exposure, unless significant improvements in prevention measures are implemented[11].
Despite the well-documented risks and proven preventative measures, adherence to sun protection guidelines remains insufficient. Research consistently demonstrates that regular daily sunscreen use can reduce the risk of melanoma by roughly 35–40% in young adults[7]. Furthermore, a landmark trial in Queensland showed daily sunscreen use could halve the incidence of squamous-cell carcinoma[15]. Yet, concerning data from 2025 indicates that only 12% of U.S. adults reported using sunscreen daily, while a substantial 28% admitted to never using it[8]. This gap between knowledge and preventative action highlights a critical need for enhanced public awareness campaigns and behavioral changes to mitigate the growing health burden of skin cancer.
1.2. The Skincare Market: A Booming Reflection of Prioritized Skin Health
In stark contrast to the persistent health challenges, the global skincare market is experiencing unprecedented growth, reflecting a significant societal shift towards prioritizing skin health and appearance. Valued at approximately $155 billion in 2023[9], the industry is projected to exceed $220 billion by 2029, demonstrating a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 6%[9]. This expansion far outpaces many other beauty segments, driven by escalating consumer demand for products that support daily care routines, combat aging, and promote overall skin vitality. This surge is underpinned by a “skin-first” mindset, where consumers view skincare as an integral component of holistic health and self-care.
1.2.1. Demographic and Lifestyle Drivers of Market Expansion
Several macro-trends are fueling this market surge. An increasingly aging global population plays a significant role; for example, Asia’s population aged 65 or older is expected to triple from 414 million in 2020 to 1.2 billion by 2060[12]. Longer lifespans, coupled with increased historical and recreational UV exposure, have intensified interest in maintaining youthful and healthy skin. Consequently, the anti-aging product sector alone is projected to almost double, from $55.8 billion in 2023 to $108.5 billion by 2033[13], representing approximately a 6.9% CAGR. Consumers, across all age groups, are proactively investing in preventive measures and advanced care to preserve skin health and appearance.
Furthermore, the skincare demographic is broadening considerably. What was once predominantly a female-centric market now extends significantly to male consumers, with the men’s skincare segment projected to grow at an impressive 10.5% annually, more than doubling from $17.6 billion in 2025 to $37.3 billion by 2035[14]. Younger generations, particularly Generation Z and millennials, are adopting comprehensive skincare routines at earlier ages. Social media platforms like TikTok have become powerful drivers of trends, catapulting niche brands to global prominence—as exemplified by CeraVe, which saw an 82% sales increase after viral recommendations on TikTok[15]. These platforms educate and influence, fostering a more knowledgeable and ingredient-savvy consumer base globally. Emerging markets in Asia, Latin America, and Africa are also experiencing rapid growth, driven by rising disposable incomes and evolving beauty standards.
1.2.2. Regional Dynamics of Skincare Demand
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region stands out as the largest and most dynamic skincare market, holding the highest revenue share as of 2024[19]. Within APAC, countries like South Korea and Japan are innovation powerhouses, driven by a deep-rooted cultural emphasis on elaborate skincare regimens and the continuous evolution of K-beauty and J-beauty trends. This robust market extends to China, where a burgeoning middle class is fueling demand for premium skincare products. While North America and Europe possess substantial markets, their growth rates are comparatively lower, while emerging economies continue to exhibit double-digit growth as consumer awareness and purchasing power rise.
1.3. Technological Innovations and Evolving Consumer Expectations
The skincare industry in 2026 is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological advancements and increasingly sophisticated consumer demands for cleaner, more sustainable, and personalized products.
1.3.1. The Dawn of Tech-Powered Personalization
Breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI), personalized diagnostics, and at-home devices are revolutionizing skincare. Major brands, such as L’Oréal, have introduced AI-powered skin analyzers that scan for parameters like hydration and pigmentation, recommending custom regimens based on individual needs[16]. L’Oréal’s “Perso” device, for example, uses AI to create personalized skincare and cosmetic formulas on demand, even considering local environmental factors[23]. This data-driven approach removes much of the guesswork from selecting products and signifies a shift towards bespoke solutions.
Moreover, the rise of “beauty-tech” includes a proliferation of smart devices for home use. Examples include LED light therapy masks for targeted treatments like acne or collagen stimulation, and microcurrent and radiofrequency (RF) devices designed to tone facial muscles and tighten skin. These gadgets, often Bluetooth-enabled, offer professional-grade results, empowering individuals to monitor and enhance their skin health with precision and convenience. The teledermatology market, valued at approximately $12.7 billion in 2025, is forecast to skyrocket to $57.4 billion by 2035, an almost four-fold increase, driven by AI diagnostics and virtual consultations that expand access to dermatological expertise, particularly in underserved regions[19].
Ingredient innovation also plays a critical role, with advancements like nanoparticle-based sunscreen filters providing superior UV protection without aesthetic drawbacks, and biotechnology leading to ingredients like lab-grown collagen or stem-cell conditioned media. This fusion blurs the lines between cosmetics and medicine, yielding “cosmeceuticals” that deliver clinically tested benefits.
1.3.2. Environmental and Ethical Demands
Modern consumers are demanding more from their skincare products than just efficacy; they seek products that align with their ethical and environmental values. A recent survey found that 63% of consumers consider “clean beauty” (products with safe, natural ingredients) to be very important when making purchasing decisions[17]. This sentiment is coupled with a strong demand for sustainability, with 81% of consumers believing brands should reduce plastic packaging[17]. As a result, companies are adopting eco-friendly formulations, implementing recyclable or refillable packaging options, and ensuring cruelty-free testing practices. Sustainability has transitioned from a niche concern to a mainstream expectation, fundamentally reshaping product development and corporate strategies. Furthermore, concerns about rising pollution and climate factors (e.g., wildfire smoke) are impacting skin health, linking environmental stressors to conditions like eczema flare-ups[16] and driving demand for protective skincare solutions.
1.3.3. The Wellness and Self-Care Nexus
Beyond clinical and environmental aspects, skincare has deeply integrated with the broader wellness and self-care movement. For many, daily skincare routines are a ritualistic form of self-care, contributing to mental well-being and stress relief. The concept of “skinimalism,” advocating for simplified, gentler routines, resonates with consumers seeking efficacy without overwhelming complexity. This framing of skincare as an act of personal investment and holistic well-being further solidifies its importance in consumers’ lives.
1.4. Key Takeaways and Future Outlook
The imperative of maintaining skin health in 2026 is evident through multiple lenses:
- The undeniable and increasing global health burden of skin diseases, including the alarming rise in skin cancer incidence, necessitates greater preventative action and public health awareness.
- The booming skincare market, projected to reach over $220 billion by 2029, signifies consumers’ heightened prioritization of skin health, driven by an aging population, expanded demographics (including men and younger generations), and a “skin-first” mindset.
- Technological innovations like AI-powered diagnostics, personalized formulations, and at-home smart devices are transforming how individuals manage their skin health, making advanced care more accessible and tailored.
- Evolving consumer values are pushing the industry towards cleaner, more sustainable, and inclusive products, demanding transparency and ethical practices from brands.
- The success of public health campaigns, such as Australia’s “Slip-Slop-Slap” initiative, demonstrates that consistent education and accessible preventative measures can significantly reduce the incidence of serious skin conditions like melanoma[15]. The Cork City Council’s free sunscreen dispenser program further exemplifies innovative public health strategies to promote sun safety[26].
In conclusion, the coming years will witness an even greater convergence of medical science, technological innovation, and consumer-driven ethical considerations within the realm of skin health. While the challenges posed by dermatological conditions are significant and growing, the proactive engagement of consumers and the rapid evolution of the skincare industry offer promising pathways for improved public health outcomes and enhanced individual well-being worldwide. The emphasis on prevention, personalized care, and sustainable practices will define the trajectory of skin health and care in 2026 and beyond.
The subsequent sections of this report will delve into each of these areas in greater detail, exploring the individual components of skin health and the latest solutions and strategies for maintaining it.
References
[2] Medscape. (2025, April 21). Skin Diseases Among Top Global Causes of Disability. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/skin-diseases-among-top-global-causes-disability-2025a10009i7#:~:text=Skin%20Diseases%20Among%20Top%20Global,because%20of%20skin%20and%20subcutaneous
[3] HQlo. (n.d.). Factors affecting health-related quality of life in patients with skin disease: cross-sectional results from 8,789 patients with 16 skin diseases. https://hqlo.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12955-020-01542-6#:~:text=Skin%20diseases%20are%20an%20enormous,most%20individuals%20who%20suffer%20from
[4] IARC. (2022). Skin cancer. https://www.iarc.who.int/cancer-type/skin-cancer/#:~:text=more%20than%201,most%20world%20regions%2C%20melanoma%20occurs
[5] Nature. (2025, October). Global trends in melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer, 1990–2021 (GBD Study). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-90485-3#:~:text=year%20covered%2C%20the%20global%20incidence,SDI
[6] Nature. (2025, October). Global trends in melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer, 1990–2021 (GBD Study). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-90485-3#:~:text=significant%20growth%20over%20the%20study,In%202021%2C%20the%20most%20recent
[7] University of Sydney. (2018, July 19). Sunscreen reduces melanoma risk by 40 percent in young people. https://www.sydney.edu.au/news-opinion/news/2018/07/19/sunscreen-reduces-melanoma-risk-by-40-percent-in-young-people.html#:~:text=against%20melanoma%20in%20young%20people,group%20at%20the%20University%20of
[8] CivicScience. (2025). Sunscreen Usage in 2025: Skepticism and Skincare Interest Shift. https://civicscience.com/sunscreen-usage-in-2025-skepticism-and-skincare-interest-shift-usage-and-growth/#:~:text=New%20CivicScience%20data%20finds%20that,percentage%20point%20increase%20over%202024
[9] Business Wire. (2024, December 18). Skincare Market Global Outlook 2024-2029 (Press Release). https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20241218245307/en/Skincare-Market-Global-Outlook-Forecast-2024-2029-Global-Skincare-Market-Projected-to-Reach-USD-220.75-Billion-by-2029—ResearchAndMarkets.com#:~:text=The%20Skincare%20Market%20was%20valued,08
[10] IARC. (n.d.). Skin cancer – Introduction. https://www.iarc.who.int/cancer-type/skin-cancer/#:~:text=Introduction
[11] IARC. (n.d.). Global burden of cutaneous melanoma in 2020 and projections to 2040. https://www.iarc.who.int/infographics/global-burden-of-cutaneous-melanoma-in-2020-and-projections-to-2040/#:~:text=Global%20burden%20of%20cutaneous%20melanoma,per%20year%20will%20increase%20by
[12] Allied Market Research. (2023). Anti-Aging Products Market Outlook 2033. https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/anti-aging-products-market-A06331#:~:text=U,to%20more%20than%20triple%20by
[13] Allied Market Research. (2023). Anti-Aging Products Market Outlook 2033. https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/anti-aging-products-market-A06331#:~:text=The%20global%20anti%20aging%20products,These%20products%20typically%20aim
[14] Future Market Insights. (2025, March). Men’s Skincare Products Market Forecast 2025–2035. https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/mens-skincare-products-market#:~:text=The%20men%E2%80%99s%20skincare%20products%20market,culture%20and%20high%20per%20capita
[15] Vogue Business. (2021). Inside CeraVe’s Marketing Strategy, Post-TikTok Fame. https://www.vogue.com/article/inside-ceraves-marketing-strategy-post-tiktok-fame#:~:text=in%20popularity%3A%C2%A0like,among%20consumers%2C%20Cerave%E2%80%99s%20star%20ascended
[16] Skin Inc. (2025, December 19). Skin Care Innovations and Trends: Transforming Beauty and Health in 2025. https://www.skininc.com/business/trends/article/22957030/future-of-skin-care-innovations-transforming-health#:~:text=Emerging%20AI,driven%C2%A0device%20that%20integrates%C2%A0facial%20scanning%C2%A0and
[17] CleanHub Blog. (2023, December 8). Clean Beauty Consumer Survey — Our Statistical Findings. https://blog.cleanhub.com/clean-beauty-survey-statistics-and-trends#:~:text=%2A%2063,of%20respondents%20are%20satisfied%20with
[18] PMC. (n.d.). Global Skin Disease Morbidity and Mortality: An Update From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5817488/#:~:text=Skin%20and%20subcutaneous%20diseases%20were,age%20DALYs%20for
[19] GlobeNewswire. (n.d.). Skincare Market Outlook & Forecast Report 2024-2029. https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2024/12/11/2995549/28124/en/Skincare-Market-Outlook-Forecast-Report-2024-2029-Shifting-Preference-to-Clean-Beauty-and-Natural-Ingredients.html#:~:text=APAC%20region%20accounted%20for%20the,shape%20demand%20in%20the%20APAC
[20] HQlo. (n.d.). Factors affecting health-related quality of life in patients with skin disease: cross-sectional results from 8,789 patients with 16 skin diseases. https://hqlo.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12955-020-01542-6#:~:text=Skin%20diseases%20are%20an%20enormous,most%20individuals%20who%20suffer%20from
[21] PMC. (n.d.). The Burden of Air Pollution on Skin Health: a Brief Report and Call to Action. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10828340/#:~:text=the%20potential%20impact%20of%20air,together%20to%20improve%20air%20quality
[22] Future Market Insights. (n.d.). Teledermatology Market | Global Market Analysis Report – 2035. https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/teledermatology-market#:~:text=Metric%20%20%7C%20Value%20,USD%2057.4%20billion
[23] L’Oréal. (n.d.). Unveil Perso, The World’s First AI-Powered Device For Skincare And Cosmetics. https://www.loreal.com/en/news/research-innovation/unveil-perso-the-worlds-first-aipowered-device-for-skincare-and-cosmetics/#:~:text=Unveil%20Perso%2C%20The%20World%E2%80%99s%20First,Cosmetics%20A%20highlight%20of%20our
[24] PMC. (n.d.). State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5124531/#:~:text=After%20decades%20of%20prevention%20efforts,potentially
[25] PubMed. (n.d.). The effectiveness of a population-based skin cancer screening program: evidence from Germany. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28353004/#:~:text=robust%20effect%20of%20the%20German,in%20terms%20of%20a%20higher
[26] Cork City Council. (2025, July 23). Cork City Council Launches Free Sunscreen Dispensers in Parks. https://www.corkcity.ie/en/council-services/news-room/latest-news/cork-city-council-and-hse-southwest-launch-free-sunscreen-dispensers-in-city-parks/#:~:text=Cork%20City%20Council%2C%20in%20partnership,the%20risk%20of%20skin%20cancer

2. The Global Burden of Skin Diseases in 2026
In 2026, the global landscape of public health continues to grapple with a significant, often underestimated, challenge: the pervasive and increasing burden of skin diseases. Far from being merely cosmetic concerns, dermatological conditions represent a critical public health issue, impacting millions worldwide, contributing substantially to disability, and straining healthcare systems. The skin, as the body’s largest organ, serves as the primary barrier against environmental aggressors and is a mirror reflecting internal health. When this vital organ is compromised, the implications extend beyond localized discomfort, affecting individuals’ quality of life, mental well-being, and economic productivity. This section will delve into the comprehensive analysis of the increasing health burden posed by skin conditions globally, examining key metrics such as disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), the widespread prevalence of common dermatological issues, and the alarming rise of severe conditions like skin cancer.
2.1 The Escalating Global Impact: Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) and Prevalence
The true measure of a disease’s societal impact extends beyond mortality rates to encompass the years lived with disability and the premature loss of life. Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) serve as a crucial metric for quantifying this burden, combining years of life lost due to premature mortality (YLL) and years lived with disability (YLD) for a particular condition. Analysis of DALY trends reveals a sobering reality for skin diseases.
Historically, skin and subcutaneous diseases have been recognized as significant contributors to non-fatal health loss. As of 2013, skin diseases were identified as the 4th leading cause of non-fatal global health loss[2], a testament to their pervasive impact on quality of life, even if they often do not directly cause death. This position underscored that dermatological conditions are not niche medical issues but rather widespread ailments that profoundly affect daily functioning and well-being. The DALY count associated with these conditions stood at approximately 41.6 million DALYs in 2013[8], a figure that already hinted at the immense scale of the problem.
Fast forward to 2021, and the situation has only intensified. The global burden of skin and subcutaneous diseases has surged, reaching an estimated 44.84 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs)[0]. This increase of over 3 million DALYs in less than a decade signifies a concerning upward trajectory in the global health burden attributed to skin conditions. This growing burden highlights that skin health is not merely a cosmetic concern but a critical public health issue demanding increased attention and resources. The escalating DALYs reflect a multitude of factors, including population growth, aging populations, increased exposure to environmental triggers, and potentially, improved diagnostic capabilities that identify more cases.
Beyond DALYs, the sheer prevalence of skin conditions further solidifies their status as a major global health challenge. Dermatological issues are ubiquitous, affecting individuals across all demographics and regions. Global health studies consistently demonstrate that three skin diseases rank among the 10 most prevalent diseases worldwide[3]. This statistic is particularly striking, indicating that a significant proportion of the global population will, at some point, experience a skin ailment serious enough to warrant inclusion in such a top-ten list. These common conditions, while often not life-threatening, significantly impair quality of life, productivity, and mental well-being.
Consider the following examples outlined in the research:
- Dermatitis (Eczema): In 2019 alone, dermatitis affected approximately 230 million people[10] globally. This chronic inflammatory skin condition manifests with itching, redness, dryness, and sometimes blistering, often leading to significant discomfort, sleep disturbance, and psychological distress.
- Acne: Affecting hundreds of millions, particularly adolescents and young adults, acne can lead to physical scarring and profound psychological impacts, including anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal.
- Fungal Infections: Conditions like athlete’s foot, ringworm, and nail infections are extremely widespread, often causing persistent discomfort and requiring prolonged treatment.
These conditions, while individually often considered “non-serious” by the general public, collectively contribute significantly to the global disease burden. They lead to countless healthcare visits, missed days of work or school, and a diminished quality of life for those afflicted. The chronic nature of many skin diseases means that sufferers live with their symptoms for extended periods, contributing substantially to the YLD component of DALYs.
The increasing prevalence of these conditions suggests a complex interplay of factors:
- Environmental Changes: Rising pollution levels and climate factors, such as smoke from wildfires, have been explicitly linked to flare-ups of conditions like eczema and other skin issues[14]. This highlights the growing vulnerability of skin health to global environmental shifts.
- Lifestyle Factors: Modern lifestyles, including diet, stress levels, and hygiene practices, can influence the onset and severity of many dermatological conditions.
- Diagnostic Improvements: Enhanced diagnostic tools and greater access to healthcare in some regions may also contribute to a higher reported prevalence of skin diseases.
The table below summarizes the key DALY and prevalence data:
| Metric | Value in 2013 | Value in 2021 | Change | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Skin Disease DALYs | ~41.6 million[8] | 44.84 million[0] | +3.24 million DALYs | Substantial increase, highlighting growing burden. |
| Ranking of Skin Diseases (non-fatal health loss) | 4th leading cause[2] | Not explicitly stated for 2021, but burden rose. | N/A | Consistently among top causes of disability. |
| Number of Skin Diseases in Top 10 Most Prevalent Globally | N/A (3 in broader reports)[3] | 3 diseases[3] | Consistent | Ubiquitous nature of dermatological issues. |
| Dermatitis prevalence (2019) | N/A | ~230 million people[10] | N/A | Illustrates the vast number of people affected by common conditions. |
This data unequivocally demonstrates that skin diseases are not to be underestimated. Their widespread nature and significant contribution to global DALYs underscore an urgent need for enhanced awareness, prevention strategies, and accessible treatment options to mitigate their escalating impact on public health in 2026 and beyond.
2.2 The Alarming Rise of Skin Cancer: A Global Epidemic
While many skin conditions are classified as non-fatal contributors to DALYs, skin cancer stands as a stark and growing exception, representing a severe and often deadly dermatological issue. In 2026, skin cancer has cemented its position as the world’s most frequent cancer[11], a designation that underscores the urgent need for widespread prevention and early detection efforts. The statistics are alarming and paint a clear picture of a global health crisis that continues to escalate.
In 2021, the total incidence of skin cancer, encompassing both melanoma and non-melanoma types, reached a staggering 6.64 million cases globally[4]. This figure is not an anomaly but rather part of a long-term upward trend, with the age-standardized incidence rate increasing by approximately 1.94% per year from 1990 to 2021[5]. This steady increase suggests deeply entrenched factors contributing to the rise of this malignancy.
Focusing on the more recent data, the year 2022 saw an estimated over 1.5 million new skin cancer cases worldwide[6]. Within this substantial number, the most dangerous form, cutaneous melanoma, accounted for a significant portion, with approximately 330,000 new melanoma cases and nearly 60,000 melanoma deaths[7] reported in the same year. These figures are not static; projections indicate that annual melanoma cases are expected to increase by 50% by 2040[12] if current trends and prevention measures remain unchanged. This alarming projection highlights the critical need for immediate and effective interventions.
The primary drivers behind this epidemic are well-understood:
- Aging Population: As global populations age, the cumulative lifetime exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation increases, raising the risk of skin cancer. Melanoma, in particular, tends to manifest later in life, making demographic shifts a significant contributing factor.
- Increased UV Exposure: Modern lifestyles, which often include increased recreational sun exposure, tanning bed use, and in some regions, depletion of the ozone layer, contribute directly to higher UV radiation exposure. This is a critical modifiable risk factor.
- Improved Detection Efforts: While a positive development, improved diagnostic technologies and greater awareness among healthcare professionals and the public also lead to a higher number of detected cases. This means some of the “rise” might also be attributed to better identification, but it does not diminish the severity of the underlying trend.
The table below provides a concise overview of the skin cancer burden:
| Skin Cancer Statistics | Value | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total New Skin Cancer Cases | 6.64 million | 2021 | Nature[4] |
| Total New Skin Cancer Cases | ~1.5 million+ | 2022 | IARC WHO[6] |
| Average Annual Increase in Incidence Rate (1990-2021) | ~1.94% | Cumulative | Nature[5] |
| New Melanoma Cases | ~303,000 | 2021 | Nature[10] |
| New Melanoma Cases | ~330,000 | 2022 | IARC WHO[7] |
| Melanoma Deaths | ~60,000 | 2022 | IARC WHO[7] |
| Projected Increase in Annual Melanoma Cases by 2040 | 50% | Projection | IARC WHO[12] |
The seriousness of skin cancer extends beyond these numbers. Melanoma, in particular, is notorious for its aggressive nature and potential for metastasis if not detected and treated early. Non-melanoma skin cancers, while generally less aggressive, can still cause significant disfigurement and health complications, especially if neglected. The treatments for skin cancer, including surgical removal, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, are often invasive, costly, and can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life.
The global community faces a critical juncture in addressing this escalating burden. Without substantial improvements in prevention strategies and public adherence to protective behaviors, the projected increase in melanoma cases will place an even greater strain on healthcare systems worldwide. This makes awareness, education, and accessible sun protection measures critically important in 2026.
2.3 Deficient Prevention Strategies and the Sunscreen Paradox
Despite the well-established and scientifically proven benefits of sun protection in preventing skin cancer, adherence to recommended habits remains remarkably low across many populations. This gap between knowledge and practice represents a significant public health challenge, directly contributing to the rising incidence of skin cancer and highlighting a “sunscreen paradox.”
Years of research have provided unequivocal evidence linking consistent sun protection with a reduced risk of melanoma and other skin cancers. A landmark 2018 Australian study, which followed young adults over time, yielded compelling results: individuals who regularly used sunscreen from childhood demonstrated a 35–40% lower risk of developing melanoma by age 40 compared to those who used sunscreen infrequently[9]. This long-term, observational data speaks volumes about the protective capacity of consistent sunscreen application. Furthermore, a highly respected randomized trial conducted in Queensland, Australia, provided even stronger evidence, showing that daily sunscreen use could effectively halve the incidence of squamous-cell carcinoma[13], a common form of non-melanoma skin cancer. These findings unequivocally cement sunscreen as a powerful, scientifically validated preventive measure.
However, the adoption of these protective behaviors by the general public lags far behind the scientific recommendations. Data from 2025 in the U.S. reveals a concerning trend:
- Only 12% of U.S. adults reported using sunscreen daily[15].
- A substantial 28% of adults indicated they never use sunscreen at all[16].
- The vast majority of individuals reported using sunscreen only “as needed,” which often translates to sporadic use during conscious sun exposure rather than consistent daily application.
Adding to this concern, these figures represent a slight decline in regular daily sunscreen use (down 2 percentage points) compared to the previous year[17]. This downward trend is particularly troubling given the rising skin cancer rates.
This “sunscreen paradox”—where a highly effective preventive tool is widely available but underutilized—is not unique to the U.S. Similar patterns are observed globally. For instance, a Statista survey indicated that over 40% of men in the UK never use sunscreen[18]. This suggests a systemic issue in public health messaging, behavioral change, or overcoming existing barriers to adoption.
Several factors contribute to this persistent gap between knowledge and practice:
- Misconceptions about Sunscreen Safety and Efficacy: Despite scientific consensus, doubts about sunscreen ingredients’ safety or its true effectiveness persist among some segments of the population.
- Skepticism and Disinterest: Some individuals remain skeptical of public health recommendations or simply lack interest in preventative skincare, viewing it as an optional step rather than a health imperative.
- Cost: Quality broad-spectrum sunscreens can be expensive, posing a barrier to consistent daily use for some individuals, particularly in cost-conscious markets.
- Sensory Attributes: Past formulations of sunscreens were often thick, greasy, or left a white cast, deterring daily use. While modern formulations have improved significantly (e.g., nanoparticle-based filters[34]), previous negative experiences can influence current habits.
- Lack of Consistent Messaging: While campaigns exist, they may not always be consistent, engaging, or frequent enough to effect lasting behavioral change.
The consequences of this insufficient adherence are significant, directly correlating with the increasing burden of skin cancer. The continuous upward trend in skin cancer cases, particularly melanoma, underscores the urgent need to bridge this gap.
Nevertheless, there are beacons of hope. Countries like Australia offer a powerful example of how sustained public health campaigns can initiate cultural shifts and improve sun-protective behaviors. Their decades-long “Slip-Slop-Slap” campaign has been instrumental in educating generations about sun safety. While the overall incidence of melanoma remains high, there is evidence that these efforts are yielding results:
- Melanoma incidence rates in Australians under 40 have begun to stabilize or even decline[19].
- Epidemiologists estimate that widespread sunscreen use in Australia has prevented approximately 10–15% of potential skin cancer cases in that population[20].
This demonstrated success in Australia provides a crucial blueprint for other nations. It confirms that consistent, long-term public health education, coupled with accessible prevention tools, can indeed “bend the curve” of skin cancer incidence over time. In 2026, similar diligent prevention efforts are critical globally to counteract the rising burden of this devastating disease.
2.4 The Interconnectedness of Skin Health and Overall Well-being
The impact of skin diseases extends far beyond the physical manifestations on the epidermal layer. In 2026, there is a growing recognition that skin health is intrinsically linked to overall physical, mental, and social well-being. Neglecting skin conditions can create a cascade of negative effects that impair quality of life, affect psychological health, and even signal broader systemic health issues.
2.4.1 Physical, Mental, and Social Impacts
Chronic skin conditions, even those not considered life-threatening, can profoundly diminish an individual’s quality of life. The research highlights several facets of this impact:
- Physical Discomfort: Many skin conditions are characterized by relentless itching (pruritus), pain, burning, scaliness, and discomfort. Conditions like severe eczema, psoriasis, or chronic urticaria can disrupt sleep, interfere with daily activities, and reduce physical functioning. For instance, severe eczema flares can be debilitating, requiring significant management and causing considerable distress.
- Psychological Distress: The visible nature of skin conditions, particularly on exposed areas like the face, can lead to significant psychological and emotional burden. Studies have explicitly linked severe acne and psoriasis with higher rates of anxiety and depression[23]. The emotional toll can be immense, leading to feelings of self-consciousness, embarrassment, low self-esteem, and social withdrawal. These psychological comorbidities are often under-diagnosed and under-treated, further exacerbating the patent’s suffering.
- Social Embarrassment and Discrimination: Because skin issues are visible, individuals may face social stigma, rejection, or even discrimination. This can impact their personal relationships, career opportunities, and overall social engagement. Children with visible skin conditions, for example, may experience bullying, while adults might face challenges in professional settings.
- Economic Burden: Beyond the personal toll, skin diseases impose a substantial economic burden on healthcare systems and economies. They necessitate millions of healthcare visits annually, including consultations with general practitioners and dermatologists, prescription medications, and various treatments. Illness-related absenteeism from work or school, such as days lost due to severe eczema flares or painful shingles, contributes to lost productivity and economic costs. The DALY metric, which accounts for years lived with disability, aptly captures this productivity loss.
In essence, the skin, being the most visible organ, plays a crucial role in self-perception and social interaction. When its health is compromised, it directly impacts an individual’s confidence, self-worth, and ability to participate fully in society. As the research insight succinctly puts it, “healthy skin is integral to overall well-being, and neglecting it can carry significant personal and economic consequences.”
2.4.2 Skin as a Gateway to Other Health Problems
The skin is not merely an external covering; it is the body’s largest organ, averaging around 2 square meters, and serves as the body’s first line of defense against pathogens, UV radiation, and environmental toxins. When the integrity of this barrier is compromised, it can open the door to more serious systemic health issues.
- Infection Risk: Broken skin, whether from chronic ulcers, wounds, or severe dermatitis (e.g., scratching due to eczema), creates entry points for bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This can lead to localized infections, cellulitis, or even more serious systemic infections, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
- Systemic Inflammation: Chronic inflammatory skin conditions are increasingly recognized as having systemic implications. For example, persistent inflammation associated with psoriasis has been linked to a higher risk of developing other serious conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and inflammatory bowel disease. This highlights that skin inflammation is not always isolated but can be a manifestation of broader systemic dysregulation.
- Progression to Cancer: UV damage accumulated in the skin is the primary cause of skin cancer. What might begin as seemingly innocuous sun spots or moles, if neglected, can progress into life-threatening malignancies like melanoma. The importance of monitoring skin changes and seeking early diagnosis cannot be overstated in this context.
Thus, maintaining skin integrity and promptly treating dermatological conditions is critical for preventing more serious “downstream” health issues. Health experts are increasingly emphasizing routine skin checks and integrated skin care as fundamental components of preventive health, much like dental hygiene or nutritional guidance.
2.4.3 Global Inequities in Skin Health
The burden of skin diseases is not distributed equally across the globe; significant disparities exist, often reflecting broader socioeconomic and healthcare access inequalities.
- Geographic Disparities: Developing countries frequently face a higher prevalence of certain infectious skin diseases, such as fungal infections or historically, leprosy, due to factors like crowded living conditions, inadequate sanitation, and limited access to clean water. These regions often lack sufficient dermatological infrastructure and trained specialists.
- Healthcare Access: Even within developed countries, underserved communities or rural areas may experience worse patient outcomes. For instance, melanoma mortality rates can be higher in rural areas because of delayed diagnoses, where access to dermatologists for screening and early intervention is limited.
- Environmental Factors: Residents in polluted urban centers might experience worse outcomes for conditions like eczema, as environmental pollutants act as triggers for inflammatory skin responses. The research notes that rising pollution and climate factors like wildfire smoke are linked to eczema flare-ups[14], indicating an environmental justice component to skin health.
- Cultural Stigma: Culturally, stigma surrounding visible skin diseases can prevent individuals from seeking timely medical help, further exacerbating conditions and leading to more severe outcomes. This delays diagnosis and treatment, impacting long-term prognosis.
Addressing these nuances requires a multi-faceted approach. It’s not just about developing effective products; it also necessitates global efforts in education, improving access to dermatological specialists (potentially via teledermatology, as discussed later), and implementing public health initiatives specifically tailored to the diverse needs and cultural contexts of different populations. Recognizing and addressing these inequities is a crucial step towards reducing the global burden of skin diseases.
2.5 The Booming Skincare Industry: A Reflection of Shifting Priorities
The global skincare industry is undergoing a period of unprecedented growth, transforming into a multi-billion-dollar enterprise that reflects a fundamental shift in consumer priorities towards health, wellness, and self-care. This robust expansion signals a widespread recognition of the importance of maintaining skin health, moving beyond purely aesthetic concerns to emphasize proactive care and preventative measures.
2.5.1 Market Size and Growth Trajectory
The financial figures underscore the industry’s dynamism:
- In 2023, the global skincare products market was valued at approximately $154.9 billion USD[21].
- Projections indicate a significant surge, with the market expected to reach $220.8 billion by 2029[22]. This represents a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.1%[22].
This growth rate consistently outpaces many other segments within the broader beauty industry, including color cosmetics. Notably, the skincare sector demonstrated resilience even during the COVID-19 pandemic, as consumers confined to home redirected discretionary spending from makeup to skincare products, embracing “pampering” routines and focusing on “Zoom-ready” skin. This trend suggests that skincare has become a non-discretionary item for many, indicating its entrenched position in daily consumer habits. This strong financial outlook has attracted significant investment, with venture capitalists and large conglomerates increasingly funding skincare startups and acquiring established brands, recognizing it as a high-growth, resilient sector.
2.5.2 Key Drivers: Demographics and Awareness
Several critical factors are fueling this boom:
- Aging Populations: A significant driver is global demographics. Populations are aging rapidly; by 2030, an estimated one in six people globally will be over 60, and this demographic is actively seeking products to maintain youthful-looking skin and address age-related skin concerns[24]. This phenomenon contributes massively to the anti-aging product segment, further detailed below.
- Rising Consumer Awareness: There’s a heightened public awareness of skin health, largely amplified by social media, online communities, and accessible dermatological content. Consumers in 2026 are more educated about ingredients, product efficacy, and the importance of preventive care. They perceive skincare as an investment in long-term health, confidence, and well-being, rather than mere vanity. This “skin-first” mindset has led to more consistent spending on quality products and routine maintenance.
- Younger Generations: Millennials and Gen Z are initiating skincare routines at increasingly younger ages, often in their teens or early twenties. Their focus is heavily on prevention, incorporating daily SPF and antioxidant serums as foundational steps in their routines. Social media platforms, particularly TikTok, play a pivotal role in disseminating skincare knowledge and driving product trends among these younger, digitally-native consumers.
2.5.3 Segmentation and Emerging Trends
Within the vast skincare market, specific segments are experiencing particularly rapid growth and innovation:
- Anti-aging Products: This is one of the largest and most dynamic segments. Valued at approximately $55.8 billion in 2023, the global anti-aging products market (including creams, serums, etc.) is forecast to nearly double, reaching $108.5 billion by 2033[26]. This remarkable growth (approximately 6.9% CAGR) is directly linked to demographic shifts and a proactive consumer mindset seeking to stave off visible signs of aging. Ingredients like retinoids, collagen, hyaluronic acid, and antioxidants are in high demand.
- Sun Care (SPF Products): Driven by increasing awareness about skin cancer prevention, the sun care segment is also flourishing, with projections estimating it will reach over $14 billion by mid-decade. Daily SPF moisturizers have become a staple for many informed consumers.
- “Clinical” or “Doctor-Branded” Skincare: This category bridges the gap between cosmetic and pharmaceutical products, offering formulations developed by dermatologists or backed by clinical research, often with higher concentrations of active ingredients.
- Nutricosmetics/Skin Supplements: The “beauty-from-within” trend has boosted the popularity of ingestible supplements like collagen peptides, vitamins, and probiotics, aiming to improve skin health internally.
- Men’s Skincare: Historically neglected, the men’s skincare market is experiencing explosive growth. Projected to grow from $17.6 billion in 2025 to $37.3 billion by 2035, with a robust 10.5% CAGR[27], this segment reflects evolving societal norms around male grooming. Men are increasingly adopting basic skincare routines, including cleansers, moisturizers, and sunscreens.
2.5.4 Regional Dynamics
The growth and trends within the skincare market are not uniform globally.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) Dominance: The APAC region is currently the world’s largest skincare market, accounting for the highest revenue share[29]. Countries like South Korea and Japan are innovation hubs, with their K-beauty and J-beauty trends (e.g., 10-step routines, essences, sheet masks, snail mucin creams) profoundly influencing global skincare practices. China, with its booming middle class, is also a major growth engine, driving demand for premium products.
- Western Markets: While significant, North American and European markets exhibit lower growth rates compared to APAC. However, they lead in trends like “clean beauty” and high-tech skincare devices.
- Emerging Markets: Countries in India, Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa are experiencing double-digit growth as consumer income rises and awareness of skincare benefits increases. However, products often need to be tailored to local preferences, such as demand for skin-lightening creams in some Asian countries, contrasting with self-tanners in the West.
2.5.5 Opportunities and Challenges for Businesses
The vibrant skincare market of 2026 presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges for businesses. Opportunities lie in identifying new niches (e.g., teen acne kits, probiotic skincare), expanding into untapped geographies, and leveraging technological advancements for product development and personalization. Conversely, the market is characterized by fierce competition. Large conglomerates are actively acquiring successful indie brands to expand their portfolios, as demonstrated by Estée Lauder’s acquisition of Dr. Jart+ from Korea.
However, the barrier to entry has simultaneously lowered due to contract manufacturers and the power of social media, enabling influencer-founded brands to emerge rapidly. This intensifies competition and empowers consumers. In 2026, consumers are more discerning than ever: they demand transparency, research ingredients extensively, and can quickly amplify or discredit product claims online. To thrive, skincare companies must balance continuous innovation with authenticity, ethical practices, and sustainable sourcing, aligning with the values of increasingly savvy customers. The evolution of the skincare industry stands as a robust indicator of the global populace’s heightened appreciation for skin health as a cornerstone of overall well-being.
2.6 Preventive Skincare: A Paradigm Shift in Public Health and Lifestyle
The conversation around skin health has evolved significantly over the past decade, moving from a reactive “treat the problem” approach to a proactive “prevent the problem” paradigm. In 2026, preventive skincare has been firmly established as a critical component of both public health initiatives and individual lifestyle choices, driven by a deeper understanding of long-term health outcomes and an increased public appreciation for holistic well-being.
2.6.1 From Treatment to Preventative Action
Dermatologists and public health experts are increasingly emphasizing daily habits as the frontline defense against skin problems. The focus is on maintaining the skin barrier and preventing issues like dryness, premature aging, and, most critically, skin cancer. Key recommendations include:
- Daily Sun Protection: The cornerstone of preventive skincare is consistent protection against UV radiation. This involves applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day, irrespective of weather conditions, to mitigate cumulative UV damage. Furthermore, wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses, and actively seeking shade, are critical. The dangers of artificial tanning, particularly through tanning beds, are also strongly discouraged.
- Regular Cleansing and Moisturizing: Basic skincare practices like gentle cleansing and consistent moisturizing are crucial for maintaining the skin’s barrier function, preventing dryness, and supporting overall skin health. These routines help ward off common irritations and maintain skin resilience.
This preventive ethos is particularly embraced by younger consumers who view early skincare practices as a long-term investment in their future skin health. They understand that decisions made in their 20s will significantly impact their skin’s appearance and health in their 40s and beyond.
2.6.2 Public Health Campaigns and Education
Governments and health organizations worldwide have recognized the power of public health messaging in driving behavioral change regarding skin health.
- Australia’s “Slip-Slop-Slap” Campaign: Initiated in 1981, Australia’s iconic “Slip-Slop-Slap” campaign (slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen, slap on a hat) is a globally recognized success story. Decades of consistent messaging have instilled sun-safe habits in generations, leading to a demonstrable cultural shift. The campaign has been credited with a decline in melanoma incidence among younger age groups[19], making it a model for effective long-term public health communication.
- Global Awareness Days: Organizations globally mark initiatives like World Skin Health Day (July 8) to raise awareness about various skin diseases, promote early detection, and educate the public on effective skincare practices.
These initiatives, often amplified by celebrity influencers and expert dermatologists on social media, have collectively made the general public in 2026 more knowledgeable and proactive about skin health than ever before.
2.6.3 Early Detection and Screening
Beyond daily prevention, the concept of early detection forms another critical pillar of preventive skincare.
- Skin Cancer Screening: Regular self-exams for new or changing moles and professional skin screenings are strongly promoted by dermatologists. Some regions are exploring broader population-level screenings; Germany implemented a national skin cancer screening program in 2008, which has been shown to increase early diagnoses[38].
- Early Intervention for Common Conditions: For conditions like acne and eczema, early intervention is emphasized to prevent chronic issues and long-term consequences. Treating teenage acne promptly can prevent scarring and mitigate the negative self-esteem impacts often associated with severe breakouts. Similarly, using prescription creams at the first sign of psoriasis can avert a full-blown flare-up.
This proactive mindset ensures minor skin issues are addressed before they escalate, reducing the severity and complexity of future treatments.
2.6.4 Lifestyle Links and Holistic Care
Modern preventive skincare takes a holistic view, acknowledging that external skin health is influenced by internal well-being and lifestyle choices.
- Diet, Sleep, and Stress Management: Growing evidence strongly links lifestyle factors such as diet, sleep quality, and stress levels to various skin conditions. Dermatologists in 2026 often take a holistic approach, advising patients on nutrition (e.g., diets low in sugar, rich in antioxidants), emphasizing adequate sleep, and strategies for stress reduction.
- Environmental Factors: The impact of rising pollution and climate factors, such as wildfire smoke, on skin conditions like eczema flare-ups is increasingly recognized[14]. This leads to increased demand for protective routines, such as antioxidant creams and anti-pollution formulations.
- Skin as Self-Care: The act of maintaining a skincare routine has become intertwined with the broader “wellness” movement. Many consumers view their daily skincare regimen as a ritualistic form of self-care, contributing to mental well-being and stress relief. This is reflected in marketing that frames skincare as an act of self-love and a means to “take care of your whole self.”
This comprehensive approach reflects that healthy skin is an outcome of a healthy lifestyle, integrating topical treatments with broader health and wellness practices.
2.6.5 Concrete Examples of Success
The effectiveness of preventive efforts is evidenced by notable successes:
- Australia’s Melanoma Stabilization: As mentioned, Australia’s long-term sun safety campaigns have led to the stabilization and even decline of melanoma rates in younger populations[19].
- Free Sunscreen Dispensers: Initiatives like the one in Cork City, Ireland, in 2025, which installed free SPF 50 sunscreen dispensers in public parks, exemplify a community-level commitment to making sun protection accessible and convenient[42]. Similar programs have been implemented in cities like Boston and New York.
- Policy Changes for Sunscreen Access: In the U.S., states have progressively implemented policies that allow students to carry sunscreen at school without a doctor’s note, addressing previous regulatory hurdles that hampered access to sun protection for minors.
These examples vividly illustrate that investment in preventive skincare, whether through public awareness campaigns, accessible resources, or policy changes, pays significant dividends in reducing the burden of skin diseases and improving public health outcomes in the long run. The shift towards prevention is undeniable and will continue to shape skin health practices in the coming years.
2.7 The Future of Skin Health: Technology, Sustainability, and Inclusivity
The dynamic landscape of skin health in 2026 is continuously shaped by rapid advancements in technology, growing ethical considerations, and an expanding understanding of consumer diversity. These interconnected trends are revolutionizing how people approach skincare, how products are developed, and how dermatology is practiced, moving towards a future that is more personalized, sustainable, and inclusive.
2.7.1 Technology-Powered Personalization and Access
Technology is profoundly transforming skincare through innovation a variety of applications:
- AI-Driven Skin Analysis: Artificial intelligence is making personalized skincare a reality. Brands and dermatological clinics are deploying AI skin diagnostic tools that can analyze selfies or imaging scans to assess various skin parameters such as moisture levels, wrinkles, dark spots, and even the severity of conditions like acne. For example, L’Oréal’s MODIFACE technology and new AI-driven devices can scan a user’s face and provide tailored product recommendations within minutes[30], factoring in local environmental data like weather and pollution. This data-driven approach removes much of the guesswork from selecting appropriate skincare products.
- Customized Formulations: Building on AI diagnostics, companies are now offering bespoke skincare formulations. Devices like L’Oréal’s Perso, unveiled in 2020, can dispense freshly mixed, personalized creams and serums based on an individual’s unique skin profile and daily environmental conditions[31]. Similarly, many brands offer online quizzes or virtual consultations that lead to custom-blended products, ensuring optimal ingredient concentrations (e.g., Vitamin C, hyaluronic acid, niacinamide). This shift from mass-produced products to individually tailored regimens enhances efficacy and consumer satisfaction.
- High-Tech At-Home Devices: The market is saturated with advanced beauty-tech gadgets designed for home use. These include LED light therapy masks (using blue light for acne, red for collagen stimulation), microcurrent and radiofrequency (RF) devices for facial toning and skin tightening, and even smart micro-needling tools that guide users through treatments[32]. Enabled by Bluetooth connectivity and user-friendly apps, these devices make professional-grade treatments more accessible and integrate skincare routines with digital tracking.
- Nanotechnology and Advanced Ingredients: Breakthroughs in material science are enhancing product performance. Nanoparticle-based sunscreen filters offer superior UV protection without the traditional white cast or greasiness[34], significantly improving user compliance. Encapsulated active ingredients like retinol and vitamins ensure targeted delivery and reduced irritation. The burgeoning field of “cosmeceuticals” blurs the line between cosmetics and medicine, with products delivering clinically tested benefits for specific skin concerns.
- Teledermatology and Remote Care: The adoption of teledermatology has surged, particularly post-pandemic, becoming a standard mode of access for dermatological expertise. The teledermatology market, valued at $12.7 billion in 2025, is projected to reach $57.4 billion by 2035, reflecting a staggering 16% annual growth rate[35]. Patients can now consult dermatologists via video calls or by sending high-resolution images, making routine check-ups and prescription refills more convenient and improving access for underserved populations. AI also plays a supportive role, assisting dermatologists in analyzing mole images for early cancer detection and triaging cases.
These technological advancements are making skincare more precise, effective, and accessible, empowering individuals to take a more informed and proactive role in managing their skin health.
2.7.2 Evolving Consumer Demands: Clean, Sustainable, and Ethical Skincare
Modern consumers are increasingly sophisticated and ethically-minded, driving significant shifts in product development and brand practices.
- Clean and Transparent Beauty: Ingredient-consciousness is paramount. A 2023 survey found that 63% of consumers consider “clean beauty” (non-toxic ingredients) very important in their purchasing decisions[36]. This demand has led to a proliferation of “free-from” claims (e.g., paraben-free, sulfate-free) and a strong emphasis on transparency. Brands are increasingly publishing comprehensive ingredient glossaries, avoiding proprietary “mystery blends,” and backing claims with scientific evidence. This fosters trust and loyalty in a market where consumers are scrutinizing formulations more than ever. Regulators, particularly in regions like the EU, are also strengthening standards for product safety and claims accuracy.
- Sustainability and Eco-Consciousness: Environmental impact is a major concern. Approximately 81% of consumers believe beauty brands should reduce plastic packaging[37], and 70% actively research a brand’s eco-credentials before buying. This has spurred innovations in sustainable packaging (recycled, refillable, biodegradable) and formulations (waterless products, solid formats). “Cruelty-free” certification is a baseline expectation, and there’s a growing preference for vegan ingredients and formulations. Companies are increasingly aligning their practices with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals, committing to reduced carbon footprints and ethical sourcing (e.g., fair-trade ingredients).
2.7.3 Inclusivity and Diversity
The skincare industry is moving towards a more inclusive and diverse representation of its consumer base:
- Formulations for All Skin Tones and Types: Brands are now designing products with a broader range of complexions in mind, ensuring sunscreens don’t leave a white cast on darker skin tones and that tinted products offer a comprehensive shade range. There’s also increased focus on conditions disproportionately affecting specific demographic groups, such as hyperpigmentation in skin of color or hormonal acne.
- Gender Inclusivity: Skincare is no longer a female-centric domain. The men’s skincare segment is growing at ~10.5% annually[28], with products rebranded in gender-neutral or male-friendly packaging. Targeted products address specific male concerns like razor bumps or beard care.
- Representation in Marketing: Advertising campaigns increasingly feature diverse age groups, genders, ethnicities, and body types, reflecting the varied audience for skincare products.
This push for inclusivity reflects a societal shift towards equitable representation and the recognition that everyone, regardless of background, deserves effective and tailored skincare solutions.
2.7.4 The Influence of Social Media and the “Wellness” Angle
Social media continues to play a monumental role in shaping skincare trends and consumer behavior:
- Empowered Consumers: Platforms like TikTok and YouTube have given rise to “Skinfluencers” and dermatologists who educate millions, fostering a highly ingredient-savvy consumer base. Viral trends can dramatically impact a brand’s success; for example, CeraVe’s sales surged 82% in 2020 due to TikTok endorsements[39]. Conversely, negative online sentiment can quickly damage a brand’s reputation.
- Skincare as Self-Care: The act of engaging in a skincare routine has merged with broader wellness and self-care movements. Brands market products with calming sensorial experiences and promote routines as therapeutic rituals that enhance mental well-being and stress relief. Concepts like “skinimalism” (skin minimalism) advocate simpler, gentler routines, resonating with those seeking effective care without overwhelming complexity. This framing positions skincare as an essential component of holistic self-care, a personal investment in health and emotional balance.
These evolving consumer demands and technological integrations highlight a future where skincare is not merely a product application but a data-driven, ethically-conscious, and deeply personalized journey towards holistic well-being.
The global burden of skin diseases in 2026 presents a multifaceted challenge, yet it also underscores a monumental opportunity inherent in the burgeoning skincare industry and innovative public health strategies. The alarming DALY figures, the escalating incidence of skin cancer, and the persistent gap in preventative behaviors starkly highlight the need for continued, intensified efforts in education, prevention, and accessible care. Simultaneously, the booming, technologically advanced, and ethically-driven skincare market indicates a powerful consumer-led shift towards recognizing skin health as fundamental to overall well-being. The intersection of these trends points towards a future where diligent, proactive skin care is not only medically advised but culturally expected.
The next section will delve deeper into the burgeoning skincare market, analyzing its growth drivers, key segments, and the impact of consumer preferences on product innovation and brand strategies.
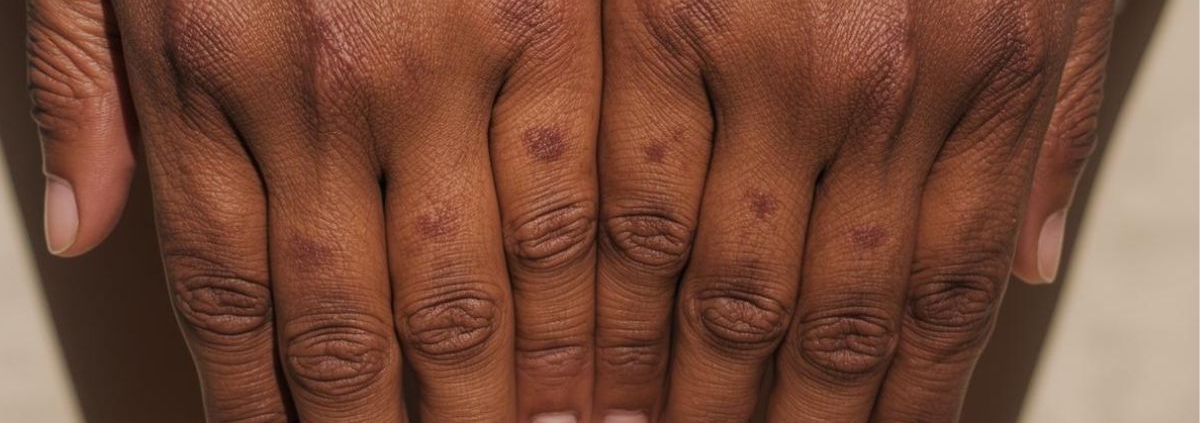
3. Rising Incidence of Skin Cancer and Insufficient Prevention
The skin, often overlooked as merely a cosmetic feature, is in fact the body’s largest organ and a critical component of overall health. Its primary role as a protective barrier shields the internal organs from environmental aggressors, pathogens, and harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. However, despite its vital functions, awareness and consistent engagement in preventive skin health practices remain a significant public health challenge in 2026. This is particularly concerning given the alarming and sustained increase in skin cancer incidence rates worldwide, juxtaposed with insufficient adoption of proven prevention strategies. The global burden of skin diseases, including the most serious forms of skin cancer, highlights a critical gap between scientific knowledge of effective prevention and widespread public adherence, necessitating a deep dive into the epidemiological trends, challenges, and successful intervention models.
The escalating prevalence of skin cancer, both melanoma and non-melanoma types, presents a profound concern for global health systems. As of 2022, skin cancers collectively represent the world’s most frequent malignancy, demonstrating a clear and worrying upward trajectory over recent decades [10]. This rise is not just an abstract statistical increase; it translates into millions of new diagnoses annually, imposing considerable strain on healthcare resources, significant DALYs (Disability-Adjusted Life Years), and, tragically, tens of thousands of deaths. Yet, effective prevention—chief among them, consistent sun protection practices—remains critically underutilized by the general population. This section will meticulously examine the current landscape of skin cancer incidence, analyze the contributing factors to its increase, scrutinize the persistent challenges in promoting public sun safety, and highlight successful public health efforts that offer a blueprint for mitigating this growing health crisis.
3.1 The Alarming Global Rise of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is no longer a rare disease but a pervasive and growing health threat. It encompasses several forms, primarily basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), collectively known as non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSC), and the far more aggressive and potentially lethal cutaneous melanoma. The epidemiological data from the past three decades paints a stark picture of increasing incidence across all forms of skin cancer.
3.1.1 Overview of Skin Cancer Incidence and Mortality
The sheer scale of skin cancer poses a major global health burden. In 2021 alone, the total number of new skin cancer cases—combining melanoma and non-melanoma types—reached an astonishing 6.64 million globally [7]. This figure reflects a steady, long-term upward trend, with the age-standardized incidence rate increasing by approximately 1.94% per year between 1990 and 2021 [8]. This consistent annual rise underscores the urgent need for enhanced preventive measures and public awareness.
Breaking down these figures further, melanoma, while less common than NMSC, is responsible for the vast majority of skin cancer deaths due to its aggressive metastatic potential. In 2021, approximately 303,000 new cases of melanoma were diagnosed worldwide [9]. The year 2022 saw an estimated 330,000 new melanoma cases and nearly 60,000 melanoma deaths globally [12]. These numbers are projected to continue their upward climb, with annual melanoma cases expected to increase by 50% by 2040 if existing prevention measures do not significantly improve [13]. This substantial projected increase is attributed to a combination of demographic shifts, such as an aging global population, and prevailing behavioral factors, particularly persistent patterns of inadequate sun protection.
Non-melanoma skin cancers, including BCC and SCC, are far more prevalent, accounting for over 5 million cases in 2021. While generally less lethal than melanoma, NMSCs still contribute significantly to morbidity, disfigurement, and healthcare costs due to their high incidence and the need for surgical removal and follow-up care.
The table below summarizes the key skin cancer statistics:
| Cancer Type/Category | Metric | Value | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Skin Cancers (Melanoma & Non-Melanoma) | New Cases (Global) | 6.64 million | 2021 | Scientific Reports (Nature) [7] |
| All Skin Cancers (Melanoma & Non-Melanoma) | Annual Incidence Rate Increase | ~1.94% (since 1990) | 1990-2021 | Scientific Reports (Nature) [8] |
| Melanoma | New Cases (Global) | ~303,000 | 2021 | Scientific Reports (Nature) [9] |
| Melanoma | New Cases (Global) | ~330,000 | 2022 | IARC (WHO) [12] |
| Melanoma | Deaths (Global) | ~60,000 | 2022 | IARC (WHO) [12] |
| Melanoma | Projected Increase by 2040 | 50% | 2040 | IARC (WHO) [13] |
3.1.2 Underlying Drivers of Increasing Incidence
The persistent rise in skin cancer cases is multifactorial, rooted in demographic shifts, environmental changes, and specific human behaviors:
* **Aging Population:** Globally, populations are aging, particularly in developed nations. Skin cancer incidence increases with age due to cumulative lifetime UV exposure. As the proportion of older adults grows, so too does the pool of individuals with accumulated sun damage, leading to higher rates of diagnosis [?]. For example, over 414 million people in Asia were aged 65 or older in 2020, a number projected to triple to 1.2 billion by 2060 [?]. This demographic trend alone ensures a sustained increase in age-related skin conditions, including cancer.
* **Increased UV Exposure:**
* **Lifestyle Changes:** The advent of affordable international travel, a cultural emphasis on tanning as a beauty ideal (despite mounting evidence of its harms), and increased time spent outdoors for recreation have collectively led to greater intermittent and recreational sun exposure, particularly intense exposures during vacations.
* **Tanning Beds:** Despite widespread warnings, indoor tanning remains a significant risk factor, especially among younger demographics. Tanning beds emit UV radiation up to 10-15 times higher than midday sun, significantly increasing the risk of melanoma and NMSC.
* **Ozone Depletion:** While global efforts have mitigated ozone layer depletion, historical reductions in atmospheric ozone led to increased ground-level UV radiation, contributing to the rise in skin cancer cases, particularly in regions like Australia and New Zealand.
* **Improved Detection and Reporting:** Advances in medical technology and public health campaigns have led to earlier detection and more thorough reporting of skin cancers. Increased awareness among healthcare professionals and the public, coupled with better diagnostic tools, means more cases are being identified that might have previously gone undiagnosed or been misclassified. While this does not directly represent an increase in *actual* cases, it contributes to the observed increase in *diagnosed* incidence rates.
* **Genetic Susceptibility:** Certain genetic predispositions, particularly in individuals with fair skin, light eye and hair color, and a high number of moles, increase susceptibility to UV damage and skin cancer. The demographic groups historically susceptible to skin cancer (e.g., Caucasians) have also experienced increasing life expectancies and sun exposure habits.
3.2 The Paradox of Prevention: Insufficient Sun Protection Habits
Despite overwhelming scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of sun protection in preventing skin cancer, public adherence to these practices remains woefully inadequate. This disparity between knowledge and action represents a critical public health failure that contributes directly to the rising cancer burden.
3.2.1 Proven Benefits of Sun Protection
The effectiveness of sun protection, particularly regular sunscreen use, in reducing skin cancer risk is well-established through rigorous scientific studies.
* **Melanoma Risk Reduction:** A landmark 2018 Australian study conducted on young adults provided compelling evidence, demonstrating that individuals who consistently used sunscreen from childhood experienced a **35–40% lower risk of developing melanoma by age 40** compared to those who used it infrequently [14]. This is a substantial reduction for the deadliest form of skin cancer.
* **Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer Prevention:** Beyond melanoma, daily sunscreen use has been shown to be effective against NMSCs. A seminal randomized controlled trial conducted in Queensland, Australia, revealed that regular daily application of sunscreen could halve the incidence of squamous cell carcinoma [15]. This demonstrates broad-spectrum protection against both major categories of skin cancer.
These findings affirm that interventions as simple and accessible as sunscreen application can significantly alter the trajectory of skin cancer risk.
3.2.2 The Gap Between Knowledge and Practice
Despite these robust findings, public engagement with daily sun protection remains strikingly low. Data from 2025 in the U.S. illustrates this persistent gap:
* **Low Daily Sunscreen Use:** Only **12% of U.S. adults reported using sunscreen daily** [16]. This figure is particularly concerning given expert recommendations for daily, year-round sunscreen use, even on cloudy days or during incidental outdoor exposure.
* **Significant Non-Adherence:** A substantial portion of the adult population, **28%, stated that they never use sunscreen at all** [16]. This outright avoidance leaves a significant segment of the population completely unprotected from UV damage.
* **Declining Trends:** The percentage of U.S. adults using sunscreen daily actually showed a slight **decline of 2 percentage points from the prior year** [17]. This worrying trend suggests that instead of improving, sun protection habits may be regressing in some populations.
* **Gender Disparities:** Similar patterns of low adherence are observed globally, with notable gender differences. For instance, a Statista survey highlighted that over **40% of men in the UK *never* use sunscreen** [18], indicating a significant segment of the male population that foregoes this essential protection.
These statistics reveal a profound challenge: convincing individuals to consistently adopt preventive behaviors. Possible reasons for this adherence gap include:
* **Misconceptions and Skepticism:** Some individuals harbor doubts about sunscreen efficacy or express concerns about potential chemical ingredients, often fueled by misinformation online.
* **Cost and Accessibility:** The perceived cost of sunscreen, especially for daily, broad-specturm products, can be a barrier for some populations.
* **Aesthetic Concerns:** Traditional sunscreens often left a white cast, were greasy, or felt heavy, deterring consistent use. While modern formulations have improved significantly, these past experiences can linger.
* **Lack of Perceived Risk:** Many people underestimate the cumulative effects of daily sun exposure or believe that skin cancer only affects others, particularly those with fair skin or a history of sunburns.
* **Behavioral Inertia:** Instilling new daily routines can be challenging, particularly for a perceived latent threat like sun damage rather than an immediate one.
3.2.3 The Role of Public Health Campaigns and Education
Against this backdrop, public health initiatives play a crucial role in shifting societal norms and improving preventive behaviors. One of the most successful examples comes from Australia.
* **Australia’s “Slip-Slop-Slap” Campaign:** Launched in 1981, Australia’s iconic “Slip-Slop-Slap” campaign (slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen, slap on a hat) aimed to combat the nation’s exceptionally high skin cancer rates [46]. This multi-decade public health effort, which later expanded to include “Seek” shade and “Slide” on sunglasses, embedded sun-safety practices into the national culture.
* **Tangible Results:** After nearly 40 years of consistent public health messaging, the campaign has yielded significant, measurable results. Epidemiological data indicates that melanoma incidence rates in Australians under the age of 40 have begun to **stabilize or even decline** [19]. Experts estimate that widespread sunscreen use and other sun-smart behaviors in Australia have **prevented approximately 10–15% of potential skin cancer cases** in that population [20]. This demonstrates that sustained, well-communicated prevention programs can effectively “bend the curve” of skin cancer incidence over time, fundamentally altering public health outcomes.
* **Global Inspiration:** The Australian model serves as a powerful precedent for other countries grappling with rising skin cancer rates, highlighting the importance of long-term commitment, clear messaging, and integrated public education across various societal touchpoints, including schools, workplaces, and media.
3.3 New Approaches to Sun Protection and Adherence
Recognizing the persistent challenges in sun protection, innovative approaches are emerging in 2026 to enhance adherence and make sun safety more accessible and appealing.
3.3.1 Technological Advancements in Sunscreen Formulation
One significant area of innovation involves improving the sensorial qualities and efficacy of sunscreens themselves, directly addressing common barriers to use.
* **Nanoparticle-Based Sunscreen Filters:** Scientists are developing sophisticated **nanoparticle-based sunscreen filters** that offer superior UV protection while eliminating the traditional drawbacks of older formulations. These modern sunscreens are designed to be clear, non-greasy, and lightweight, avoiding the dreaded white cast that often deterred individuals with darker skin tones or those seeking an invisible finish [38]. By making sunscreen more cosmetically elegant, brands hope to boost daily compliance, which is critical for effective long-term protection.
* **Encapsulation Technologies:** Advanced encapsulation techniques are being used to stabilize active sunscreen ingredients and other beneficial compounds (like antioxidants) within formulations, enhancing their photostability and preventing degradation, thereby improving sustained efficacy throughout the day.
3.3.2 Public Infrastructure and Accessibility Initiatives
Beyond individual product choices, some communities and health organizations are taking proactive steps to integrate sun protection into public spaces, making it a collective responsibility.
* **Free Sunscreen Dispensers in Public Parks:** In a forward-thinking initiative, **Cork City Council in Ireland**, in partnership with health authorities, launched a pilot program in the summer of 2025 to install **free, touch-free SPF 50 sunscreen dispensers in popular public parks** [42]. This simple, yet impactful, program was implemented in response to rising skin cancer rates in Ireland and aimed to make sun protection readily available to park visitors at no cost.
* **Positive Reception and Expansion:** Early reports indicated significant uptake, with families and individuals actively utilizing the dispensers during sunny periods. This initiative, costing only a few thousand euros, demonstrated that low-cost, high-impact public health interventions can effectively encourage sun-safe behaviors. Such programs represent a growing trend towards viewing sun protection as a public amenity, akin to providing clean water or shaded resting areas, and are inspiring other municipalities to consider similar endeavors [49].
3.3.3 Digital Tools and AI for Personalized Prevention
The integration of technology, particularly AI and digital platforms, is transforming how individuals can monitor their sun exposure and personalize their prevention strategies.
* **UV Index Apps and Wearables:** Smartphone applications that provide real-time UV index updates and personalized sun protection recommendations based on location and skin type are becoming more sophisticated. Wearable devices that track UV exposure can alert users when they’ve reached their daily limit or when reapplication of sunscreen is due.
* **Teledermatology for Early Detection:** While primarily focused on diagnosis, the rapid growth of teledermatology, with the market projected to reach **$57.4 billion by 2035** (a four-fold increase from 2025) [23], contributes to prevention by facilitating early detection of suspicious lesions. Virtual consultations make it easier for individuals, especially in underserved areas, to get moles or skin changes checked by a dermatologist, thereby preventing progression to advanced stages of cancer.
3.4 Addressing Broader Skin Disease Burden and Public Health Implications
While skin cancer remains a paramount concern, it is essential to contextualize it within the broader landscape of skin diseases, which collectively impose a massive health burden worldwide. Understanding this larger picture reinforces the importance of skin health as a critical, often underestimated, public health issue.
3.4.1 The Pervasive Burden of Skin Diseases
Skin diseases are not merely cosmetic nuisances; they represent a major global health challenge, leading to substantial disability and impaired quality of life.
* **Significant DALYs:** As of 2021, skin and subcutaneous diseases were responsible for approximately **44.84 million Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) globally** [1]. This represents an increase from around 41.6 million DALYs in 2013 [2], indicating a worsening trend. DALYs measure the years of healthy life lost due to illness, disability, or early death, underscoring that skin conditions significantly contribute to global health loss, even if they are not typically fatal. In 2013, skin diseases were ranked as the **fouth leading cause of non-fatal global health loss** [3], an astonishing statistic that highlights their widespread impact.
* **High Prevalence:** Many skin conditions are among the most common ailments worldwide. In fact, global health studies indicate that **three skin diseases are among the ten most prevalent diseases globally** [6]. Conditions such as dermatitis (eczema), which affected roughly 230 million people in 2019, acne, and fungal infections, impact hundreds of millions, often leading to chronic discomfort, psychological distress, and reduced productivity.
3.4.2 Skin Health as a Broader Public Health Imperative
The interconnectedness of skin health with overall well-being necessitates a comprehensive public health approach.
* **Beyond Cosmetic Concerns:** Skin conditions are frequently associated with significant physical and psychological consequences. Chronic itching, pain, and visible lesions can lead to severe distress, anxiety, depression, and social stigma [29]. This often results in lost workdays, reduced quality of life, and substantial healthcare expenditures.
* **Gateway to Other Health Problems:** The skin acts as the body’s primary defense. When its integrity is compromised, it can open the door to other health issues. For example, breaches in the skin barrier from chronic ulcers, severe eczema, or wounds can facilitate infections. Persistent inflammation seen in conditions like psoriasis is increasingly linked to systemic comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease and arthritis. Therefore, maintaining skin integrity and treating conditions early can prevent a cascade of more serious health complications.
* **Environmental Factors:** Rising pollution and climate-related factors, such as smoke from wildfires, are increasingly linked to exacerbations of inflammatory skin conditions like eczema [12]. This connection highlights the need for public health strategies that consider environmental influences on skin health.
3.5 Transition to the Next Section
The escalating incidence of skin cancer and the broader burden of skin diseases underscore the critical importance of effective prevention. While public health campaigns have demonstrated success in shifting behaviors, the persistent gap in widespread adoption of sun protection highlights the need for continued innovation, education, and accessible solutions in 2026. The next section will delve into the societal perception of skin health, examining how cultural norms, media influence, and economic factors are shaping consumer attitudes and behaviors toward skincare, and how these forces can be leveraged to promote better skin health outcomes.
References
[10] International Agency for Research on Cancer. Skin cancer – IARC. (2022). Available at: https://www.iarc.who.int/cancer-type/skin-cancer/#:~:text=Introduction
[7] Scientific Reports (Nature). Global trends in melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer, 1990–2021 (GBD Study). (Oct 2025). Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-90485-3#:~:text=year%20covered%2C%20the%20global%20incidence,SDI
[8] Scientific Reports (Nature). Global, regional, and national trends in the burden of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer: insights from the global burden of disease study 1990–2021. (Oct 2025). Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-90485-3#:~:text=significant%20growth%20over%20the%20study,In%202021%2C%20the%20most%20recent
[9] Scientific Reports (Nature). Global, regional, and national trends in the burden of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer: insights from the global burden of disease study 1990–2021. (Oct 2025). Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-90485-3#:~:text=variation%20in%20incidence%20and%20DALYs,63%20per%20100%2C000%20population%29%20for
[12] International Agency for Research on Cancer. Skin cancer – IARC. (2022). Available at: https://www.iarc.who.int/cancer-type/skin-cancer/#:~:text=more%20than%201,most%20world%20regions%2C%20melanoma%20occurs
[13] International Agency for Research on Cancer. Global burden of cutaneous melanoma in 2020 and projections to 2040. (2022). Available at: https://www.iarc.who.int/infographics/global-burden-of-cutaneous-melanoma-in-2020-and-projections-to-2040/#:~:text=Global%20burden%20of%20cutaneous%20melanoma,per%20year%20will%20increase%20by
[?] Allied Market Research. Anti-Aging Products Market Size & Share, Trends | Forecast 2033. (2023). Available at: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/anti-aging-products-market-A06331#:~:text=U,to%20more%20than%20triple%20by
[14] University of Sydney (News). Sunscreen reduces melanoma risk by 40 percent in young people. (July 19, 2018). Available at: https://www.sydney.edu.au/news-opinion/news/2018/07/19/sunscreen-reduces-melanoma-risk-by-40-percent-in-young-people.html#:~:text=against%20melanoma%20in%20young%20people,group%20at%20the%20University%20of
[15] PubMed. Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up. (2011). Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21135266/#:~:text=PubMed%20pubmed,We%20evaluated
[16] CivicScience. Sunscreen Usage in 2025: Skepticism and Skincare Interest Shift. (2025). Available at: https://civicscience.com/sunscreen-usage-in-2025-skepticism-and-skincare-interest-shift-usage-and-growth/#:~:text=New%20CivicScience%20data%20finds%20that,percentage%20point%20increase%20over%202024
[17] CivicScience. Sunscreen Usage in 2025: Skepticism and Skincare Interest Shift. (2025). Available at: https://civicscience.com/sunscreen-usage-in-2025-skepticism-and-skincare-interest-shift-usage-and-growth/#:~:text=only%20wear%20sunscreen%20%E2%80%98as%20needed,percentage%20point%20increase%20over%202024
[18] Statista. U.S.: attitudes towards sunscreen by gender 2024. (2024). Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1482308/us-consumers-who-never-use-sunscreen-by-gender/#:~:text=U,Share%20of
[46] State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now – PMC. (2016). Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5124531/#:~:text=After%20decades%20of%20prevention%20efforts,potentially
[19] State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now – PMC. (2016). Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5124531/#:~:text=After%20decades%20of%20prevention%20efforts,potentially
[20] State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now – PMC. (2016). Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5124531/#:~:text=After%20decades%20of%20prevention%20efforts,potentially
[38] Skin Inc. Skin Care Innovations and Trends: Transforming Beauty and Health in 2025. (Dec 19, 2025). Available at: https://www.skininc.com/business/trends/article/22957030/future-of-skin-care-innovations-transforming-health#:~:text=match%20at%20L55%20For%20example%2C,compliance%2C%20crucial%20for%C2%A0effective%20sun%C2%A0protection%20and%C2%A0skin
[42] Cork City Council (News). Cork City Council Launches Free Sunscreen Dispensers in Parks. (July 23, 2025). Available at: https://www.corkcity.ie/en/council-services/news-room/latest-news/cork-city-council-and-hse-southwest-launch-free-sunscreen-dispensers-in-city-parks/#:~:text=Cork%20City%20Council%2C%20in%20partnership,the%20risk%20of%20skin%20cancer
[49] Cork City Council (News). Cork City Council Launches Free Sunscreen Dispensers in Parks. (July 23, 2025). Available at: https://www.corkcity.ie/en/council-services/news-room/latest-news/cork-city-council-and-hse-southwest-launch-free-sunscreen-dispensers-in-city-parks/#:~:text=Cork%20City%20Council%2C%20in%20partnership,the%20risk%20of%20skin%20cancer
[23] Future Market Insights. Teledermatology Market | Global Market Analysis Report – 2035. (Mar 2025). Available at: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/teledermatology-market#:~:text=Metric%20%20%7C%20Value%20,USD%2057.4%20billion
[1] Medscape. Skin Diseases Among Top Global Causes of Disability. (Apr 21, 2025). Available at: https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/skin-diseases-among%C2%A0top%C2%A0global%C2%A0causes%C2%A0of%C2%A0disability-2025a10009i7#:~:text=Skin%20Diseases%20Among%20Top%20Global,because%20of%20skin%20and%20subcutaneous
[2] Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. The Lancet. (2015). 386(9995):743-800. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5817488/#:~:text=Skin%20and%20subcutaneous%20diseases%20were,age%20DALY for
[3] Global Burden of Skin Disease Representation in the Literature: Bibliometric Analysis – PMC. (2020). Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10334954/#:~:text=The%202013%20Global%20Burden%20of,the%20representation%20of%20dermatologic%20conditions
[6] Health and Quality of Life Outcomes. Factors affecting health-related quality of life in patients with skin disease: cross-sectional results from 8,789 patients with 16 skin diseases. (2020). Available at: https://hqlo.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12955-020-01542-6#:~:text=Skin%20diseases%20are%20an%20enormous,most%20individuals%20who%20suffer%20from
[29] Health and Quality of Life Outcomes. Factors affecting health-related quality of life in patients with skin disease: cross-sectional results from 8,789 patients with 16 skin diseases. (2020). Available at: https://hqlo.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12955-020-01542-6#:~:text=Skin%20diseases%20are%20an%20enormous,most%20individuals%20who%20suffer%20from
[12] The Burden of Air Pollution on Skin Health: a Brief Report and Call to Action – PMC. (2024). Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10828340/#:~:text=match%20at%20L145%20starkly%20demonstrated,aged%20%E2%89%A5%2065%20years%20were

4. The Booming Global Skincare Market
The global skincare market is experiencing an unprecedented surge, transforming from a subset of the broader beauty industry into a powerhouse sector driven by a confluence of demographic shifts, evolving consumer priorities, and technological innovation. In 2023, the industry was valued at approximately **$155 billion USD** and is projected to burgeon to over **$220 billion by 2029**, demonstrating a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about **6.1%** [8]. This rapid expansion signifies more than just a passing trend; it reflects a fundamental shift in how consumers perceive and interact with their skin health. No longer viewed as merely cosmetic, skincare has ascended to a critical component of overall well-being and preventive healthcare. This section delves into the multifaceted dynamics fueling this booming market, analyzing its current landscape, future projections, and the key drivers shaping its trajectory in 2026 and beyond. From addressing the concerns of aging populations to catering to a new generation of ingredient-savvy consumers, the skincare industry is adapting at a fast pace, underpinned by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on ethical and sustainable practices.
The Skincare Market’s Unprecedented Growth and Valuation
The robust growth of the skincare market speaks volumes about its increasing importance in global consumer habits. While the broader beauty industry often sees ebbs and flows tied to economic cycles, the skincare segment has proven remarkably resilient, even thriving during periods of uncertainty such as the recent global pandemic. During lockdowns, for instance, consumers shifted spending from color cosmetics, which saw reduced demand due to mask-wearing and social distancing, towards skincare products. This pivot underscored a deeper commitment to fundamental skin health and self-care, a phenomenon sometimes dubbed the “skin-first” mindset. The valuation of the global skincare products market at **$154.9 billion USD in 2023** [8] is not merely an impressive figure; it represents widespread investment by individuals into their physical appearance and health. The forecast to reach **$220.8 billion by 2029** [8] highlights a strong expectation of continued consumer demand, signaling sustained confidence in the sector’s long-term viability. This consistent and significant growth trajectory far outpaces many other beauty segments, positioning skincare as a key growth engine within the personal care industry.
The drivers behind this substantial market expansion are diverse and interconnected:
* **Rising Consumer Spending in Emerging Markets:** A burgeoning middle class in regions like Asia, Latin America, and Africa is fueling increased disposable income, leading to higher spending on personal care products. As economic prosperity grows, so does the aspiration for better self-care and presentation, making skincare an essential component of modern lifestyle upgrades.
* **Expansion of Online Retail:** E-commerce has democratized access to a vast array of skincare products, from niche independent brands to established global players. Online platforms offer convenience, competitive pricing, and a wealth of information through reviews and product descriptions, making it easier for consumers to explore and purchase.
* **Heightened Awareness of Skin Health:** Public education campaigns, dermatologist outreach, and the pervasive influence of social media have significantly amplified awareness about the importance of skin health, not just for aesthetic reasons but also for overall well-being. This awareness translates directly into a proactive approach to skincare routines.
The skincare segment now commands a substantial share of the overall beauty industry, and its continued expansion is a testament to its intrinsic value in consumers’ daily lives.
Key Drivers of Market Expansion
The rapid growth observed in the global skincare market is propelled by several interlocking factors, which collectively foster a dynamic and ever-evolving industry landscape. These drivers reflect deep-seated changes in global demographics, consumer psychology, and technological capabilities.
Aging Populations and the Anti-Aging Segment
One of the most significant demographic forces shaping the skincare market is the global phenomenon of population aging. As life expectancies increase worldwide, a larger proportion of the global population is entering older age brackets. For instance, in Asia alone, the population aged 65 or older, which stood at **414 million in 2020**, is projected to **triple to 1.2 billion by 2060** [9]. This demographic shift directly translates into a heightened demand for products that promise to maintain youthful appearance and mitigate the visible signs of aging.
The anti-aging products market stands as a colossal and fast-growing segment within skincare. Valued at approximately **$55.8 billion in 2023**, this specific market is forecast to nearly double to **$108.5 billion by 2033** [10], representing a substantial **6.9% CAGR**. This tremendous growth is not solely driven by older generations seeking to reverse aging; increasingly, younger consumers are adopting anti-aging routines earlier as a preventive measure. This proactive mindset, often influenced by social media and educational content, emphasizes starting early with ingredients like retinol, collagen, and various antioxidants to delay the onset of wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. The desire to maintain healthy, resilient skin for longer periods is a powerful economic motivator, prompting consistent investment across various age groups.
Heightened Consumer Awareness and “Skin-First” Mentality
Beyond demographics, a profound shift in consumer awareness is playing a pivotal role. The internet and social media have democratized information about skincare ingredients, routines, and skin health issues. Consumers are now more educated, savvy, and discerning than ever before. This heightened awareness has cultivated a “skin-first” mentality, where individuals prioritize the health and integrity of their skin as a foundation for overall beauty and well-being.
* Education Through Digital Platforms: Platforms like TikTok and YouTube feature “skinfluencers” and dermatologists who break down complex dermatological concepts into digestible content. This access to expert and peer-generated information empowers consumers to make informed choices, fostering a demand for effective, science-backed products.
* Self-Care as a Priority: Skincare routines are increasingly viewed as an integral part of self-care and mental wellness. The act of engaging in a daily regimen or targeted treatments provides a moment of personal pampering, contributing to stress relief and a sense of control over one’s appearance.
* Preventive Mindset: There’s a growing understanding that consistent daily care and preventative measures, such as broad-spectrum sunscreen application, are crucial for long-term skin health. This has led to a greater willingness to invest in higher-quality, active ingredients and regimens rather than reactive treatments.
This evolution in consumer mindset has transformed skincare from a luxurious indulgence into an everyday necessity for many, consolidating its position as a key element of modern health and beauty upkeep.
Evolving Demographics: Men, Gen Z, and Global Markets
The burgeoning skincare market is also characterized by a significant broadening of its demographic appeal. Historically, skincare was predominantly marketed towards women in Western countries. However, 2026 sees a much more inclusive landscape, with increasing engagement from men, younger generations across the globe, and rapidly expanding markets in emerging economies.
The Rise of Men’s Skincare
The men’s skincare segment is one of the fastest-growing niches within the industry. It is projected to more than double from **$17.6 billion in 2025 to $37.3 billion by 2035** [11], reflecting an impressive **10.5% annual growth rate**. This shift can be attributed to several factors:
* **Changing Societal Norms:** There’s a growing acceptance and even encouragement for men to invest in their appearance and grooming. The stigma once associated with men using skincare products is rapidly eroding.
* **Targeted Product Development:** Brands are increasingly developing products specifically tailored to men’s skin concerns, such as oiliness, razor burn, and anti-aging. These products are often presented in packaging that appeals to a male aesthetic, and marketing campaigns emphasize efficacy and practicality.
* **Influence of Celebrity and Social Media:** Male celebrities and influencers openly discussing their grooming routines have normalized skincare for a wider male audience, promoting the idea that healthy skin is a sign of good self-care and professionalism.
* **Basic Hygiene and Protection:** Beyond aesthetics, men are also recognizing the importance of fundamental skin health, leading to increased usage of basic products like facial cleansers, moisturizers, and crucially, sunscreen. As of 2025, only **12% of U.S. adults** used sunscreen daily, with **28% never using it** [6], highlighting a significant knowledge-practice gap which the growing men’s segment can help address. For instance, data indicates that over **40% of men in the UK never use sunscreen** [6], showcasing untapped potential for comprehensive skin health education and product penetration in this demographic.
Gen Z and the Early Adoption of Skincare Routines
Generation Z (born roughly between 1997 and 2012) and younger millennials are starting their skincare journeys earlier than previous generations, often in their early teens. This demographic is characterized by:
* **High Digital Literacy:** Gen Z consumes vast amounts of content on social media, where skincare tips, product reviews, and routines are widely shared. This exposure fosters early adoption and a more sophisticated understanding of ingredients and product benefits.
* **Emphasis on Prevention:** Influenced by online educators and a general wellness trend, these younger consumers prioritize preventive skincare, understanding that addressing concerns like sun damage and acne early can yield long-term benefits.
* **Ingredient Awareness:** This generation is particularly ingredient-savvy, often researching product formulations and seeking out “clean” or “active” ingredients. The viral success of brands like CeraVe, whose sales jumped **82% in the first nine months of 2020** [14] after gaining traction on TikTok, exemplifies their influence and preference for transparent, effective, and often affordable solutions.
Expansion in Global Markets
The global footprint of the skincare market is expanding dramatically beyond traditional Western strongholds, with the **Asia-Pacific (APAC) region leading the charge**. APAC currently accounts for the highest revenue share in the global skincare market [9].
* **Cultural Drivers in Asia:** Countries like South Korea and Japan have long-standing cultural traditions that emphasize meticulous skincare, driving innovation and demand. K-beauty and J-beauty trends, renowned for elaborate multi-step routines and innovative ingredients (e.g., sheet masks, fermented essences), continue to exert global influence.
* **Booming Middle Class in China:** China’s rapidly expanding middle class represents a massive consumer base with increasing purchasing power, fueling demand for both mass-market and premium skincare products.
* **Emerging Markets:** India, Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa are experiencing double-digit growth rates as consumer awareness of skin health rises alongside economic development. Beauty standards are evolving, and access to a broader range of products is improving in these regions.
This demographic diversification means that skincare brands must adopt inclusive strategies, offering solutions that cater to a wide array of skin tones, types, and cultural preferences.
Technological Innovation and Personalization
Technology is rapidly transforming the skincare landscape, moving it towards hyper-personalization, data-driven diagnostics, and accessible at-home treatments. These innovations are not only enhancing product efficacy but also revolutionizing how consumers interact with skincare.
AI-Driven Skin Analysis and Personalized Formulations
Artificial intelligence (AI) is at the forefront of this technological revolution. Brands and dermatological clinics are deploying advanced AI tools that can meticulously analyze an individual’s skin condition:
* **Diagnostic Precision:** AI-powered devices or smartphone applications can scan facial images to assess hydration levels, identify wrinkles, dark spots, acne severity, and other specific concerns. L’Oréal, for instance, has launched AI-powered skin analyzers that scan for hydration, pigmentation, and other markers to recommend custom regimens [15]. Its MODIFACE technology offers real-time, data-driven recommendations.
* **Tailored Solutions:** This detailed analysis enables the creation of truly customized skincare products. Companies are developing “bespoke” moisturizers and serums where machines can dispense personalized concentrations of active ingredients (like Vitamin C, hyaluronic acid, or niacinamide) based on the user’s unique skin profile and even environmental factors like local weather or pollution. L’Oréal’s *Perso* device, unveiled at CES 2020, exemplifies this by mixing fresh, personalized skincare doses on demand [17].
* **Enhanced Efficacy and Satisfaction:** By removing the guesswork from product selection, AI-driven personalization promises to increase the efficacy of skincare routines and
improve consumer satisfaction, making expert-level advice more accessible.
High-Tech Gadgets and At-Home Devices
The market for beauty-tech devices for home use is flourishing, bringing professional-grade treatments into the comfort of one’s home:
* **LED Light Therapy Masks:** Once exclusive to salons and dermatologists, LED masks are now widely available for consumers. These devices utilize specific wavelengths of light—blue light for treating acne, red light to stimulate collagen production—to address various skin concerns over time [18].
* **Microcurrent and Radiofrequency (RF) Devices:** These tools allow users to perform facial toning, muscle stimulation, and skin tightening at home, mimicking results typically achieved in medical spas.
* **Smart Micro-needling Tools:** Integrating with mobile apps, these devices guide users through treatments and track progress, optimizing results and minimizing risks.
* **Wearable Sensors:** Emerging technologies include wearable sensors that can monitor skin parameters like hydration and UV exposure, providing real-time data to help users adjust their routines and protect their skin more effectively.
These gadgets represent a significant investment for enthusiasts seeking professional results without frequent clinic visits, highlighting the consumer’s growing desire for control and precision in their skincare journey.
Advanced Ingredients and Nanotechnology
Innovation is also deeply embedded in the very formulations of skincare products:
* **Nanoparticle-Based Sunscreens:** Scientists are developing nanoparticle-based sunscreen filters that offer superior UV protection without the traditional white cast or greasiness, which traditionally hindered daily compliance [19]. This makes daily SPF application more appealing and practical, especially for diverse skin tones.
* **Encapsulated Actives:** Advanced delivery systems, such as encapsulated retinol and vitamins in nano-carriers, improve ingredient penetration into the skin, maximizing anti-aging and corrective benefits while minimizing irritation.
* **Biotechnology Crossover:** The line between cosmetics and medicine continues to blur with the advent of cosmeceuticals. Lab-grown collagen, stem-cell conditioned media, and other bio-engineered ingredients are being incorporated into creams to boost skin repair and rejuvenation. Concepts like “DNA-personalized” skincare, though in early stages, promise products tailored precisely to an individual’s genetic predispositions for skin health.
Teledermatology and Remote Care
Beyond products and devices, technology is revolutionizing access to dermatological expertise. Teledermatology, which saw an explosion in use during the COVID-19 pandemic, has become a standard offering.
* **Virtual Consultations:** Patients can now consult dermatologists via video calls or dedicated apps, often by sending high-resolution images of concerns like rashes, moles, or acne in advance. The teledermatology market, valued at approximately **$12.7 billion in 2025**, is forecast to soar to **$57.4 billion by 2035** [12], reflecting a remarkable **16% annual growth**.
* **Accessibility:** This virtual approach dramatically improves access, particularly for patients in rural or underserved areas, reducing geographical barriers to specialist care.
* **AI-Assisted Diagnostics:** AI algorithms are increasingly assisting dermatologists in tasks like analyzing mole images for early skin cancer detection or triaging cases to ensure urgent conditions receive prompt attention. Future applications include AI predicting flare-ups of conditions like eczema based on environmental data, allowing for preemptive care.
These technological advancements collectively underscore a significant shift towards more precise, personalized, and accessible skincare, marking a new era of data-driven skin health management in 2026.
Preventive Skincare: A Public Health Imperative and Lifestyle Trend
The growing recognition of skin health’s intrinsic link to overall well-being has propelled preventive skincare into a major public health imperative and a lifestyle trend in 2026. This shift emphasizes proactive measures to maintain skin integrity and prevent diseases rather than solely reacting to existing conditions.
From Treatment to Prevention
There is a palpable movement away from a purely reactive approach to skincare towards one rooted in prevention. Dermatologists and health organizations increasingly advocate for daily routines that cleanse, moisturize, and critically, protect the skin from environmental aggressors.
* **Sun Protection as Foundation:** Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least **SPF 30 daily** [5], regardless of weather conditions, has become a cornerstone of preventive care. This is crucial for mitigating UV damage, which accumulates over time and is a primary cause of premature aging and skin cancer. Studies demonstrate that consistent sunscreen use can reduce melanoma risk by **35-40%** in young adults [4]. Despite this, only **12% of U.S. adults used sunscreen daily in 2025**, with **28% never using it** [6], highlighting a significant need for continued education and behavioral change.
* **Maintaining the Skin Barrier:** Regular cleansing and moisturizing are essential for maintaining the skin’s natural barrier function, which protects against irritants, pollutants, and pathogens. Disrupted barrier function can lead to dryness, sensitivity, and exacerbate conditions like eczema.
* **Antioxidant Integration:** The use of antioxidant-rich serums and creams is gaining traction as a preventive measure against oxidative stress caused by pollution and other environmental factors.
This preventive ethos is particularly embraced by younger generations who view skincare as a long-term investment in their future health and appearance.
Public Health Campaigns and Education
Many nations and health organizations have recognized the importance of skin health through targeted public health campaigns.
* **Australia’s “Slip-Slop-Slap”:** Australia’s iconic “Slip-Slop-Slap” campaign, launched in 1981, has become a global model for public health messaging. This initiative, encouraging wearing protective clothing (“slip”), applying sunscreen (“slop”), and wearing a hat (“slap”), has been instrumental in cultural change. After four decades of sustained effort, there is evidence of stabilization or even a decline in melanoma incidence rates among Australians under 40 [7]. Experts estimate that widespread sunscreen use in Australia has prevented approximately **10-15% of potential skin cancer cases** [7] in its population.
* **Global Awareness Days:** Events like World Skin Health Day (July 8) further amplify awareness about skin diseases and the importance of skincare through global dermatological initiatives.
* **Innovative Public Access:** Initiatives such as **Cork City Council’s free sunscreen dispensers** in public parks in 2025 demonstrate proactive measures to reduce barriers to sun protection [21]. Such efforts show that simple, accessible solutions can have a meaningful impact on community health, potentially inspiring similar programs worldwide.
These campaigns underscore that consistent, clear public health messaging can significantly impact population-level skin health outcomes.
Early Detection and Screening Methods
Another critical facet of preventive skincare is the emphasis on early detection of skin conditions, especially skin cancer.
* **Self-Exams and Professional Screenings:** Individuals are encouraged to conduct regular self-examinations for new or changing moles, and dermatologists advocate for routine professional skin checks.
* **Population Screening Programs:** Some regions, like Germany, have implemented national skin cancer screening programs, which have been shown to increase early diagnoses [23].
* **Early Intervention for Chronic Conditions:** For conditions like acne and eczema, early intervention can prevent more severe outcomes, such as scarring or chronic inflammation. Timely treatment of adolescent acne, for example, can avert the physical and psychological scars (e.g., higher rates of anxiety and depression [3]) often associated with severe cases.
The overarching principle is that proactive monitoring and timely action can prevent minor skin issues from escalating into more significant health problems.
Holistic Lifestyle Links to Skin Health
Preventive skincare increasingly integrates with broader wellness trends, recognizing the interconnectedness of skin health with lifestyle choices.
* **Diet and Nutrition:** There is growing evidence of the profound impact of diet on skin conditions, with many dermatologists recommending anti-inflammatory diets, rich in antioxidants, and low in refined sugars for conditions like acne and rosacea.
* **Stress Management and Sleep:** Stress can trigger or exacerbate various skin conditions, from acne to eczema. Likewise, adequate sleep is crucial for skin repair and regeneration. Therefore, stress reduction techniques and healthy sleep hygiene are often incorporated into holistic skincare advice.
* **Environmental Factors:** The impact of environmental factors, such as pollution and climate change, on skin health is also gaining recognition. Rising pollution levels and smoke from wildfires are now linked to flare-ups of eczema and other skin issues [16], prompting demand for protective routines and “pollution shields.”
* **Self-Care Rituals:** Skincare routines are increasingly embraced as mindful self-care rituals, contributing to mental well-being and stress relief. This “skincare as wellness” narrative positions the daily routine as an act of self-love and self-preservation.
The integration of these lifestyle factors into skincare emphasizes that healthy skin is an outcome of a healthy lifestyle, positioning skincare as an essential component of overall health management.
Evolving Consumer Demands: Clean, Sustainable, and Inclusive Skincare
The modern skincare consumer in 2026 is highly informed, ethically conscious, and increasingly diverse. These evolving demands are fundamentally reshaping product development, marketing strategies, and corporate responsibility within the industry.
The Imperative of “Clean” and Transparent Beauty
Consumer skepticism towards synthetic ingredients and a desire for safer, more natural formulations have fueled the “clean beauty” movement.
* **Ingredient Consciousness:** A recent global survey found that **63% of consumers consider “clean beauty” (safe, natural ingredients) to be very important** when making purchasing decisions [13]. This translates into a strong preference for products free from parabens, phthalates, sulfates, and other perceived harmful chemicals.
* **Demand for Transparency:** Consumers expect full ingredient lists and demand to know the purpose of each component in a product. Brands are responding by providing comprehensive ingredient glossaries and avoiding proprietary “mystery blends.” This transparency fosters trust and allows informed purchase decisions.
* **Regulatory Scrutiny:** The growing demand for clean beauty is also influencing regulatory bodies. Regions like the European Union have stringent cosmetic regulations, and there is increasing pressure on agencies like the U.S. FDA to create clearer definitions and standards for “clean” claims, ensuring products genuinely meet consumer expectations for safety and naturalness.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Environmental consciousness and ethical practices are no longer niche concerns but mainstream expectations from skincare brands.
* **Reduced Plastic Packaging:** A significant **81% of consumers believe beauty brands should reduce plastic packaging** [13]. This has spurred innovation in sustainable packaging, including biodegradable materials, refillable containers, and concentrated or solid formulations (e.g., bar cleansers) to minimize waste.
* **Cruelty-Free and Vegan:** “Cruelty-free” certification (no animal testing) is a baseline expectation in many markets, and demand for vegan formulations (free from animal-derived ingredients) is rapidly growing.
* **Corporate Responsibility:** Brands are increasingly publishing sustainability reports, setting ambitious environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals, and demonstrating commitments to ethical sourcing, fair trade practices, and supporting the communities involved in ingredient production.
Brands that actively demonstrate a commitment to planetary and social well-being are gaining a significant competitive advantage and building stronger loyalty with ethically-minded consumers.
Inclusivity and Diversity in Skincare
The skincare industry is moving towards a more inclusive model, recognizing the diverse needs of all skin types and tones globally.
* **Formulating for All Skin Tones:** Brands are actively developing products that address concerns across various skin tones, such as sunscreens that eliminate white cast on darker skin, and tinted moisturizers available in extensive shade ranges. More attention is being paid to common conditions in skin of color, such as hyperpigmentation.
* **Gender-Neutral Products:** The growth of men’s skincare (projected to reach **$37.3 billion by 2035** [11]) and the broader normalization of grooming for all genders leads to blurred lines between traditional gendered products. Many brands are adopting gender-neutral packaging and marketing.
* **Diverse Marketing:** Advertising campaigns are featuring a wider array of ages, genders, ethnicities, and body types, reflecting the true diversity of the global consumer base and promoting a more aspirational and relatable image of beauty.
* **Addressing Specific Needs:** Formulas are increasingly designed to cater to specific concerns that vary across demographics, such as razor bumps in men with curly hair or hormonal acne experienced by women.
This inclusive approach reflects a broader societal push for representation and ensures that skincare solutions are accessible and effective for everyone.
Social Media and the Empowered Consumer
Social media is not just a marketing channel; it’s a dynamic ecosystem where skincare trends are born, products are reviewed, and consumer opinions are amplified.
* **Peer Influence and Virality:** Platforms like TikTok provide powerful platforms for “skinfluencers” and dermatologists to share authentic product reviews and routines. The phenomenon of CeraVe, which saw its sales surge by **82% in the first nine months of 2020** [14] after gaining viral traction on TikTok, underscores the profound impact of digital word-of-mouth.
* **Educated and Demanding Consumers:** This constant flow of information creates an incredibly knowledgeable consumer base. They are more likely to scrutinize product claims, research ingredients, and hold brands accountable for their promises.
* **Two-Way Communication:** Brands are compelled to engage actively with online communities, respond to feedback, and even co-create products with influencers.
* **Combatting Misinformation:** While social media empowers consumers, it also presents challenges, as misinformation can spread rapidly. Dermatologists and reputable brands often engage in online dialogue to debunk myths and provide evidence-based advice, guiding consumers away from potentially harmful practices.
In 2026, the empowered consumer, armed with vast digital information and a strong voice, demands authenticity, efficacy, and ethical conduct from skincare brands, compelling the industry to elevate its standards across the board.
Conclusion of Market Dynamics
The global skincare market’s trajectory reflects a profound evolution in consumer priorities, driven by a blend of health consciousness, technological innovation, and ethical considerations. The rapid growth from **$155 billion in 2023 to a projected $220.8 billion by 2029** [8] is not merely economic expansion but a testament to how deeply integrated skin health has become with modern well-being. From navigating the complexities of aging populations and rising skin cancer rates to empowering a new generation of educated and diverse consumers, the industry is poised for continued transformation. As we move forward, successful brands will be those that skillfully blend scientific rigor with ethical practices, personalization with inclusivity, and digital engagement with tangible results.
The next section will delve into “Consumer Behavior and Awareness,” exploring how these market dynamics translate into individual choices and daily routines, further detailing the shift towards proactive and informed skin health management.
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Skin cancer – IARC. 2022. Available from: https://www.iarc.who.int/cancer-type/skin-cancer/> [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Medscape. Skin Diseases Among Top Global Causes of Disability. 2025. Available from: https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/1000997 [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- BioMed Central. Factors affecting health-related quality of life in patients with skin disease: cross-sectional results from 8,789 patients with 16 skin diseases | Health and Quality of Life Outcomes | Full Text. 2020. Available from: https://hqlo.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12955-020-01542-6 [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- University of Sydney (News). Sunscreen reduces melanoma risk by 40 percent in young people. 2018. Available from: https://www.sydney.edu.au/news-opinion/news/2018/07/19/sunscreen-reduces-melanoma-risk-by-40-percent-in-young-people.html [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- CivicScience. Sunscreen Usage in 2025: Skepticism and Skincare Interest Shift Usage and Growth. 2025. Available from: https://civicscience.com/sunscreen-usage-in-2025-skepticism-and-skincare-interest-shift-usage-and-growth/ [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Statista. U.S.: attitudes towards sunscreen by gender 2024| Statista. Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1482308/us-consumers-who-never-use-sunscreen-by-gender/ [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- PMC. State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now – PMC. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5124531/ [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Business Wire. Skincare Market Global Outlook & Forecast 2024-2029: Global Skincare Market Projected to Reach USD 220.75 Billion by 2029 – ResearchAndMarkets.com. 2024. Available from: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20241218245307/en/ [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Allied Market Research. Anti Aging Products Market Size & Share, Trends | Forecast 2033. 2023. Available from: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/anti-aging-products-market-A06331 [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Newswire. Skincare Market Outlook & Forecast Report 2024-2029 -. 2024. Available from: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2024/12/11/2995549/28124/en/Skincare-Market-Outlook-Forecast-Report-2024-2029-Shifting-Preference-to-Clean-Beauty-and-Natural-Ingredients.html [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Future Market Insights. Men’s Skincare Products Market Forecast 2025–2035. 2025. Available from: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/mens-skincare-products-market [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Future Market Insights. Teledermatology Market | Global Market Analysis Report – 2035. Available from: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/teledermatology-market [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- CleanHub Blog. Clean Beauty Consumer Survey — Our Statistical Findings. 2023. Available from: https://blog.cleanhub.com/clean-beauty-survey-statistics-and-trends [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Vogue Business. Inside CeraVe’s Marketing Strategy, Post-TikTok Fame. 2021. Available from: https://www.vogue.com/article/inside-ceraves-marketing-strategy-post-tiktok-fame [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Skin Inc.. Future of Skin Care: Innovations Transforming Health. 2025. Available from: https://www.skininc.com/business/trends/article/22957030/future-of-skin-care-innovations-transforming-health [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- PMC. The Burden of Air Pollution on Skin Health: a Brief Report and Call to Action – PMC. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10828340/ [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- L’Oréal. Unveil Perso, The World’s First AI-Powered Device For Skincare And Cosmetics. Available from: https://www.loreal.com/en/news/research-innovation/unveil-perso-the-worlds-first-aipowered-device-for-skincare-and-cosmetics/ [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Skin Inc.. Future of Skin Care: Innovations Transforming Health | Skin Inc. 2025. Available from: https://www.skininc.com/business/trends/article/22957030/future-of-skin-care-innovations-transforming-health [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Skin Inc.. Future of Skin Care: Innovations Transforming Health | Skin Inc. 2025. Available from: https://www.skininc.com/business/trends/article/22957030/future-of-skin-care-innovations-transforming-health [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- PMC. Global burden of skin and subcutaneous diseases: an update from the GBD 2021 study. 2025. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/bjd/article/192/6/1136/8110998 [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- Cork City Council (News). Cork City Council Launches Free Sunscreen Dispensers in Parks. 2025. Available from: https://www.corkcity.ie/en/council-services/news-room/latest-news/cork-city-council-and-hse-southwest-launch-free-sunscreen-dispensers-in-city-parks/ [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- PMC. Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up – PubMed. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21135266/ [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
- PubMed. The effectiveness of a population-based skin cancer screening program: evidence from Germany – PubMed. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28353004/ [Accessed 18 Dec 2024].
5. Technological Innovations and Personalization in Skincare
The landscape of skincare in 2026 is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by an accelerating pace of technological innovation. No longer confined to traditional creams and lotions, skin health management is becoming increasingly sophisticated, leveraging breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI), advanced diagnostic tools, cutting-edge at-home devices, and nanotechnology. This technological revolution is ushering in an era of unprecedented personalization, making skincare solutions more precise, effective, and accessible than ever before. The days of one-size-fits-all products are rapidly fading, replaced by data-driven approaches that cater to individual needs, environmental factors, and even genetic predispositions. This section will delve into how these technological advancements are reshaping the skincare industry, empowering consumers, and improving dermatological care, signaling a future where maintaining optimal skin health is both more proactive and deeply individualized.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Skin Analysis and Personalization
Artificial intelligence stands at the forefront of the technological revolution in skincare, enabling levels of personalization previously unattainable. AI-powered diagnostic tools are fundamentally changing how skin conditions are assessed and how product recommendations are made. These systems can process vast amounts of visual data, identifying subtle nuances and patterns that might escape the human eye, thereby offering highly accurate and tailored insights into an individual’s skin health.
AI-Driven Skin Diagnostic Tools
The core application of AI in skincare diagnostics involves sophisticated image analysis. Consumers and professionals alike can utilize devices or applications that capture high-resolution images of the skin. These images are then analyzed by AI algorithms to assess various parameters critical to skin health. Key metrics typically include hydration levels, the presence and severity of wrinkles, pigmentation irregularities (such as dark spots), and the characteristics of conditions like acne. Major brands and dermatology clinics are rapidly deploying these AI solutions. For instance, L’Oréal, a leader in the beauty industry, has developed AI-driven devices and technologies like MODIFACE that can scan a user’s face and provide tailored product recommendations within minutes[11]. Such systems go beyond a superficial evaluation, delving into objective, quantifiable data points to construct a comprehensive skin profile.
The process often involves:
- Image Capture: Users take selfies or utilize specialized imaging devices that capture their facial skin under various lighting conditions.
- Data Analysis: AI algorithms process these images to detect and quantify features such as:
- Wrinkle Depth and Quantity: Identifying fine lines and deeper wrinkles to assess skin aging.
- Pigmentation Analysis: Detecting sunspots, melasma, and other irregularities, quantifying their size and intensity.
- Pore Size and Count: Indicating skin texture and potential for congestion.
- Hydration Levels (indirectly): Often inferred from skin texture, fine lines, and reflective properties. Some devices combine imaging with bio-impedance measurements.
- Acne Severity: Counting lesions, assessing inflammation, and classifying breakout types.
- Environmental Consideration: Advanced AI systems can integrate real-time environmental data, such as local weather conditions (humidity, UV index) and pollution levels, into their analysis. This allows for dynamic adjustments to skincare recommendations, ensuring products are suitable for current external stressors. For example, a system might recommend a heavier moisturizer on a cold, dry day or increased antioxidant protection when pollution levels are high.
The primary benefit of these AI diagnostic tools is their ability to reduce guesswork. Consumers, often overwhelmed by the sheer volume of skincare products available, can receive guidance that is backed by data specific to their skin. This leads to more effective routines and reduced wasted expenditure on unsuitable products. By 2026, many consumers access virtual skin assessments through mobile applications or in-store kiosks, democratizing access to what was once considered expert-level dermatological advice[11].
Customized Product Formulations
Building on AI-driven diagnostics, the industry is witnessing a significant shift towards customized skincare formulations. This personalization extends beyond simple product recommendations to the actual creation of bespoke products tailored to an individual’s precise skin needs. The concept involves blending active ingredients in specific concentrations based on the diagnostic results.
Examples of customized product formulation include:
- “Bespoke” Moisturizers and Serums: Specialized machines can dispense face creams and serums with personalized concentrations of active ingredients. For example, based on an AI analysis showing low hydration and early signs of aging, a machine might blend a moisturizer with a higher percentage of hyaluronic acid and a specific concentration of a peptide for collagen stimulation.
- L’Oréal’s Perso Device: At the CES tech show in 2020, L’Oréal introduced Perso, an at-home device that represents a significant leap in personalized skincare. This smartphone-sized gadget uses AI and skin scanning to create custom formulas on demand. After a user takes a selfie, the AI analyzes factors such as wrinkles, dark spots, and moisture. The device then dispenses a freshly mixed dose of skincare (e.g., a day moisturizer or serum) tailored to the user’s immediate needs, even considering daily environmental factors like local weather or pollution. While still in early rollout by 2025, Perso exemplifies the merging of technology and personalized beauty, with L’Oréal reporting that AI-driven services boost customer satisfaction and online sales conversions[49], [50].
- Online Quizzes and Genetic Testing: Some brands utilize online quizzes or even at-home genetic test kits to gather data. Based on these inputs, custom-blended products are designed and shipped directly to the consumer. While genetic testing for skincare is an early-stage concept, it holds the promise of tailoring products based on an individual’s inherited predispositions to specific skin concerns.
This trend moves skincare from a mass-market approach to an individually tailored regimen, significantly enhancing product efficacy and consumer satisfaction. The ability to receive a product “made just for me” resonates strongly with consumers, fostering a sense of individualized care and optimized results.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools and At-Home Skincare Devices
Beyond AI for product personalization, the skincare ecosystem in 2026 is enriched by a proliferation of advanced non-invasive diagnostic tools and sophisticated at-home devices. These innovations empower consumers to monitor their skin health, apply treatments, and obtain professional-grade results from the comfort of their homes, thereby bridging the gap between clinical dermatology and daily self-care.
Sophisticated At-Home Devices
The market is burgeoning with high-tech gadgets that bring once-exclusive dermatology clinic treatments to the consumer level:
- LED Light Therapy Masks: These masks, previously confined to med-spas and dermatologists’ offices, are now widely available for home use. They utilize specific wavelengths of light to target various skin concerns. For example, blue light is commonly used to treat acne by eliminating bacteria, while red light is known for its collagen-stimulating properties, helping to reduce wrinkles and improve overall skin texture. Smart LED therapy devices can even emit specific light combinations tailored to personal needs and track usage via companion apps[30].
- Microcurrent and Radiofrequency (RF) Devices: These handheld devices allow users to perform facial toning and skin-tightening treatments at home. Microcurrent technology sends low-level electrical currents to stimulate facial muscles, providing a lifting and contouring effect. RF devices use energy to heat the deeper layers of the skin, promoting collagen production and skin tightening. These devices offer a non-invasive alternative to more intensive procedures, mimicking the results of professional treatments over time.
- Smart Micro-Needling Tools: Micro-needling, which involves creating microscopic punctures in the skin to stimulate collagen and enhance product absorption, is also being adapted for home use. Smart micro-needling tools often come with integrated apps that guide the user through the process, ensure proper technique, and track progress, making the procedure safer and more effective for home users[30].
- Wearable Sensors: Emerging wearable sensors can continuously monitor skin parameters throughout the day. These can track hydration levels, UV exposure, and even changes in skin temperature or pH. Such data allows for dynamic adjustments to skincare routines, providing alerts when the skin is dehydrated or when sun protection is required, enabling a truly proactive approach to skin health.
These devices, often Bluetooth-enabled and integrated with smartphone applications, gamify and optimize skincare routines. While they represent a significant investment for some, their popularity is growing among enthusiasts seeking professional-grade results without the frequent visits to a clinic.
Nanotechnology and Advanced Ingredient Delivery
Innovation in skincare also extends to the very molecular structure of active ingredients, with nanotechnology playing a crucial role in enhancing their efficacy and user experience. Nanotechnology involves manipulating materials at the atomic or molecular scale, typically between 1 to 100 nanometers, to create novel properties or functionalities.
- Nanoparticle-Based Sunscreen Filters: A notable application is in sunscreen formulations. Traditional mineral sunscreens (zinc oxide, titanium dioxide) can often leave a visible white cast and feel heavy or greasy, which contributes to poor user compliance. Nanoparticle versions of these filters, however, provide high UV protection without these aesthetic drawbacks. Their smaller size allows them to be more transparent and spreadable on the skin, significantly improving cosmetic elegance, which is crucial for encouraging daily use and adherence to sun protection habits. This refinement helps address the issue of insufficient sun protection habits, as better-feeling products increase the likelihood of regular application[31].
- Encapsulated Active Ingredients: Many potent skincare ingredients, such as retinoids (Vitamin A derivatives like retinol) and certain vitamins (e.g., Vitamin C), are notoriously unstable when exposed to light or air, and can also be irritating to the skin. Nanotechnology addresses this through encapsulation. Encapsulated retinol or vitamins are encased in tiny protective shells (nano-carriers) that shield them from degradation and ensure a more controlled, gradual release into the skin. This improves ingredient stability, increases penetration into the deeper layers of the epidermis, and reduces the likelihood of irritation, leading to better anti-aging results and improved tolerance.
- Biotechnology Crossover: The lines between cosmetics and medicine are blurring, leading to the rise of “cosmeceuticals”—products that combine cosmetic benefits with medicinal or drug-like advantages. This includes biotechnologically derived ingredients such as lab-grown collagen, which aims to replenish the skin’s natural support structure, or stem-cell conditioned media, which contains growth factors and signaling molecules intended to boost skin repair and regeneration. These advanced ingredients are designed to deliver clinically tested benefits for specific skin issues like hyperpigmentation, rosacea, and aging. “DNA-personalized” skincare, which uses at-home genetic test kits to recommend products based on an individual’s genetic predispositions, is an emerging concept within this domain, although still in its early stages of development.
These advancements in nanotechnology and biotechnology ensure that active ingredients are delivered more efficiently and effectively, maximizing their benefits while minimizing potential side effects, thus elevating the performance of modern skincare products.
Teledermatology and Enhanced Accessibility to Care
The accessibility of dermatological expertise has been dramatically expanded by technological innovations, particularly through teledermatology. This shift, accelerated by global health changes, has made professional skin care advice and treatment more convenient and available to a broader population.
Explosion of Teledermatology Services
Teledermatology, which involves the use of telecommunication technologies to provide dermatological care from a distance, experienced an exponential surge during the COVID-19 pandemic and has since become a standard option for many patients. The global teledermatology market, valued at approximately $12.7 billion in 2025, is projected to soar to $57.4 billion by 2035, representing a significant four-fold increase and roughly 16% annual growth[19]. This accelerated adoption reflects both patient preference for convenience and the health system’s capacity to deliver remote care efficiently.
The operational models of teledermatology services typically include:
- Video Consultations: Patients can schedule live video calls with dermatologists, discussing their concerns and showing affected skin areas in real-time.
- Store-and-Forward Dermatology: This popular model involves patients or primary care providers capturing high-resolution images or videos of skin issues, along with relevant medical history, and securely transmitting them to a dermatologist for review and diagnosis at a later time. This asynchronous method allows specialists to manage a higher volume of cases and offers flexibility for both parties.
- Mobile Applications: Numerous apps now facilitate direct communication between patients and dermatologists, allowing for easy photo submission, secure messaging, and prescription management.
The benefits of teledermatology are substantial, especially in terms of accessibility. It effectively surmounts geographical barriers, providing expert dermatological care to individuals in rural or underserved areas where in-person specialists are scarce. It also improves convenience for those with mobility issues, busy schedules, or the inability to travel, thereby broadening access to crucial skin health services (e.g., checking suspicious moles, managing chronic conditions like acne or eczema, and getting prescription refills).
AI Assistance for Dermatologists and Predictive Capabilities
While empowering patients, technology also significantly augments the capabilities of dermatologists, particularly through AI integration:
- AI in Lesion Analysis: Artificial intelligence algorithms are increasingly assisting dermatologists in analyzing images of moles and other suspicious skin lesions. These AI tools demonstrate high sensitivity in detecting characteristics indicative of skin cancer, acting as a valuable second opinion or a preliminary screening tool. They can help triage cases, ensuring that potentially urgent conditions are flagged for immediate review by a human specialist.
- Predictive Analytics for Flare-Ups: An exciting frontier in teledermatology and AI is the development of predictive analytics. Imagine an app that can integrate various data points—such as a patient’s historical skin condition data, local environmental factors (weather, pollen counts, pollution levels), and even personal stress indicators (via wearables)—to predict an impending flare-up of chronic conditions like eczema or rosacea. Such a system could then proactively alert the patient, suggesting preventive measures like preemptive moisturizing, adjusting medication, or avoiding specific triggers. This shifts the paradigm from reactive treatment to proactive management, significantly improving quality of life and potentially reducing the severity of episodes.
The integration of technology, particularly AI, transforms teledermatology into a powerful tool for extending the reach and enhancing the precision of skin care, making expert guidance more available and treatment more timely. The future will see an increasingly synergistic relationship between human medical expertise and advanced technological support, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and facilitating preventative care strategies.
The Interplay of Technology and Consumer Behavior
The rapid technological advancements in skincare are not occurring in isolation; they are deeply intertwined with evolving consumer demands and behaviors. The empowered consumer of 2026 is more informed, tech-savvy, and expects personalized, effective, and convenient solutions, pushing the industry to innovate at an unprecedented pace. This dynamic relationship shapes product development, marketing strategies, and the overall trajectory of the skincare market.
Consumer Expectations for Personalization and Efficacy
Modern consumers harbor high expectations regarding the personalization and efficacy of their skincare. This demand is a direct response to the availability of advanced diagnostics and customizable product offerings:
- Increased Sophistication: Gone are the days when a generic “anti-aging cream” sufficed. Consumers now expect products to be tailored to their specific skin type, concerns (e.g., hyperpigmentation, sensitivity, acne), and even lifestyle and environmental factors.
- Data-Driven Decisions: With tools like AI skin analyzers, consumers are accustomed to receiving data-driven insights about their skin. This shifts their purchasing behavior from relying solely on broad claims to seeking products recommended based on their individual skin profile. The “made just for me” appeal of personalized products, such as those formulated by L’Oréal’s Perso device, demonstrates the strong consumer draw towards unique and targeted solutions[29].
- Desire for Tangible Results: As technology enables more precise product formulations and treatments, consumers anticipate more noticeable and measurable results. They are less willing to invest in products that do not demonstrate clear benefits tailored to their diagnosed needs.
This pursuit of optimal efficacy drives innovation, as brands must continuously develop more advanced formulations and delivery systems to meet these heightened expectations.
The Influence of Digital Connectivity and Social Media
Digital platforms and social media play a pivotal role in shaping consumer perceptions, disseminating information (and misinformation), and driving trends in the skincare industry. The empowered consumer leverages these platforms for research, recommendations, and sharing experiences:
- “Skinfluencers” and Dermatologists Online: Social media personalities, often referred to as “skinfluencers,” and dermatologists who engage online (often called “dermfluencers”) have become influential voices. They review products, share routines, and educate followers, impacting purchasing decisions. For instance, the rise of CeraVe to global prominence is a classic example: sales surged by 82% in the first nine months of 2020 after influencers and dermatologists praised its affordable, science-backed formulas on platforms like TikTok and YouTube[15]. The brand struggled to meet demand, underscoring the immense power of digital word-of-mouth.
- User-Generated Content and Community Feedback: Consumers actively share their “before and after” photos, product reviews, and “skin journey” narratives across platforms. Hashtags like #SkinCareRoutine with billions of views on TikTok showcase the pervasive interest and the community-driven aspect of skincare[15]. This democratization of information means consumers are more knowledgeable about ingredients and efficacy.
- Transparency and Authenticity: This high level of digital engagement fosters a demand for transparency from brands. Consumers expect detailed information about ingredients, ethical sourcing, and scientific backing for product claims. Brands that are open and authentic in their communication tend to build stronger loyalty. Conversely, misinformation can also spread rapidly, requiring dermatologists and brands to actively debunk myths and provide accurate scientific guidance.
Social media has transformed skincare into a dynamic, interactive space where consumers are both learners and educators, demanding higher standards and influencing product life cycles.
Accessibility through Teledermatology
Teledermatology, while a technological innovation in itself, also addresses a significant consumer demand for convenience and accessibility in healthcare:
- Overcoming Geographic Barriers: For individuals in remote areas or those with limited access to specialized medical facilities, teledermatology offers a lifeline. The ability to consult a dermatologist via video call or by sending high-resolution images eliminates the need for travel, extensive wait times, and logistical challenges.
- Reduced Barrier to Entry: For routine check-ups, prescription refills, or initial assessments of non-urgent skin concerns, virtual consultations are more convenient and often quicker to arrange than in-person appointments. This increased ease of access means more people are likely to seek professional advice earlier, potentially preventing minor issues from escalating.
- Integration with Daily Life: The seamless integration of teledermatology services via mobile apps or online platforms into daily life means that skin health management can become a more embedded and less disruptive activity, aligning with modern consumer preferences for on-demand services.
The synergy between technological innovations and evolving consumer demands is creating a skincare ecosystem that is more responsive, personalized, and consumer-centric. As technology continues to advance, the industry will likely see further convergence of diagnostic accuracy, customized solutions, and seamless access, fundamentally reshaping how individuals approach and maintain their skin health.
Challenges and Future Directions
While technological innovations are rapidly transforming skincare, their widespread adoption and continued evolution present certain challenges and clear future directions for the industry and consumers alike.
Challenges in Adoption and Regulation
- Cost and Accessibility: Many advanced at-home devices and personalized formulations, particularly those involving AI and biotechnology, come with a high price tag. This can create a disparity in access, where sophisticated skincare solutions are primarily available to affluent consumers. Bridging this gap will require innovation in manufacturing to reduce costs and business models that make these technologies more affordable or widely available through healthcare systems or accessible retail channels.
- Regulatory Frameworks: The rapid pace of innovation often outstrips the development of regulatory frameworks. As skincare products become more technologically advanced, blurring the lines between cosmetics and medical devices or pharmaceuticals, there is a growing need for clear guidelines on efficacy claims, safety standards, and data privacy. For instance, the safety and labelling of nanoparticle ingredients, or the accuracy and clinical validity of AI diagnostic tools, may require specific regulatory oversight.
- Data Privacy and Security: AI skin analysis and personalized formulations rely heavily on collecting and processing sensitive personal data, including facial images and health information. Ensuring robust data privacy and cybersecurity measures is paramount to build consumer trust and prevent misuse of this information.
- Misinformation and Overwhelm: While social media empowers consumers, it also proliferates misinformation. The sheer volume of new products, devices, and ingredients, coupled with diverse (and sometimes conflicting) advice online, can overwhelm consumers. The industry needs to focus on clear, scientifically backed communication to help consumers navigate this complex landscape.
Future Directions and Opportunities
- Enhanced Integration and Ecosystems: The future will likely see greater integration of diverse skincare technologies into holistic ecosystems. Imagine a wearable sensor that continuously monitors skin hydration and UV exposure, syncing data with an AI-powered app that then signals an at-home device to dispense a custom blended serum and advises on dietary adjustments for optimal skin health. This seamless data flow and interconnectedness will offer truly dynamic and responsive skin care.
- Preventative and Predictive Health: The shift from reactive treatment to proactive prevention will intensify. AI’s predictive capabilities, especially in teledermatology, will be honed to forecast skin issues based on a multitude of factors (genetics, environment, lifestyle), allowing for early intervention and minimizing the severity of conditions. This aligns with a broader trend in healthcare towards personalized preventative medicine.
- Sustainable Technology: As consumer demand for sustainability grows (with 81% of consumers wanting brands to reduce plastic packaging[14]), future technological innovations will also need to align with eco-conscious principles. This includes developing energy-efficient devices, utilizing biodegradable materials for device components, and ensuring the environmental footprint of customized systems is minimized.
- Accessibility through Public Health Initiatives: Emulating successful public health campaigns like Australia’s “Slip-Slop-Slap” program[48], future innovations may integrate into broader public health initiatives. For example, AI-powered skin analysis tools could be deployed in pharmacies or community centers, and teledermatology could be further subsidized or integrated into national healthcare systems to ensure equitable access. Initiatives like Cork City’s free sunscreen dispensers highlight how simple, accessible solutions contribute to public skin health[51].
The technological landscape of skincare in 2026 is one of immense potential, promising a future where personalized, proactive, and accessible solutions empower individuals to achieve and maintain optimal skin health. Addressing the accompanying challenges through thoughtful regulation, ethical AI development, and equitable access strategies will be crucial to realizing this vision.
The next section of this report will explore environmental and wellness trends, examining how external factors and holistic lifestyle choices further influence skin health practices and consumer behavior.

6. Evolving Consumer Demands: Clean, Sustainable, and Inclusive Skincare
In 2026, the landscape of the skincare industry is fundamentally shaped by a dynamic interplay of shifting consumer values and priorities. No longer content with mere promises of efficacy, today’s consumers demand products that align with a broader ethical and environmental consciousness. This evolution has catalyzed a significant movement towards “clean beauty,” prioritizing formulations free from controversial ingredients, and an unwavering commitment to sustainability, encompassing everything from packaging to ethical sourcing. Simultaneously, the demographic boundaries of skincare engagement are expanding remarkably, drawing in previously underserved or overlooked segments such as men and a highly informed Gen Z. This section delves into these pivotal shifts, analyzing their drivers, impact on the market, and implications for the future of skin health and product development. The growth of the global skincare market, valued around $155 billion in 2023 and projected to exceed $220 billion by 2029 (a Compound Annual Growth Rate of approximately 6%)[8], is a testament to this increasing consumer prioritization of skin health, which extends beyond conventional beauty to encompass broader well-being[8].
This profound transformation is not merely a fleeting trend but a foundational recalibration of consumer expectations. Modern shoppers approach their purchasing decisions with an unprecedented level of scrutiny, armed with information readily available through digital platforms. They scrutinize ingredient lists, research brand values, and seek products that reflect their personal ethos. This informed and empowered consumer base is compelling the industry to innovate not just in product performance, but in corporate responsibility and transparency. The implications are far-reaching, from ingredient sourcing and manufacturing processes to marketing strategies and brand narratives. Understanding these evolving demands is critical for any entity operating within or adjacent to the skincare ecosystem in 2026, as they dictate market success, drive innovation, and ultimately influence global skin health outcomes.
6.1 The Ascendance of Clean and Transparent Beauty
The concept of “clean beauty” has moved from a niche concern to a dominant force in the skincare market by 2026, reflecting a profound shift in consumer perception regarding product safety and ingredient integrity. Consumers are increasingly wary of synthetic chemicals, artificial fragrances, and dubious additives, opting instead for formulations perceived as safer and more natural. A late-2023 global survey emphatically illustrates this trend, reporting that **63% of respondents consider “clean beauty” – defined as products with safe, natural ingredients – to be either “extremely important” or “very important”** when making cosmetics purchasing decisions[13]. This sentiment is not confined to a single demographic; it permeates various age groups and markets, underscoring a collective desire for greater transparency and reassurance about what is being applied to the skin.
This heightened ingredient consciousness has directly translated into market demands for products formulated without certain contentious components. The ubiquitous “free-from” labels are a clear indicator of this trend, with consumers actively seeking products advertised as paraben-free, sulfate-free, phthalate-free, and fragrance-free. The concerns extend beyond immediate skin reactions to potential long-term health implications, even if scientific consensus on some ingredients is still evolving. As a result, brands are compelled to actively reformulate their product lines, replacing traditional ingredients with alternatives that meet consumer expectations for cleanliness. For instance, the demand for mineral sunscreens (zinc oxide, titanium dioxide) has surged due to concerns over chemical UV filters, even as innovations in nanoparticle-based chemical filters aim to mitigate white cast and enhance user compliance[51].
Beyond ingredient exclusion, the clean beauty movement champions unparalleled transparency. Consumers in 2026 are not satisfied with vague claims; they demand a clear understanding of every component in their skincare products and the role it plays. This has led many brands to publish comprehensive ingredient glossaries on their websites, meticulously explaining the function and sourcing of each ingredient. The days of proprietary, undisclosed “mystery blends” are rapidly fading, as trust is increasingly earned through clarity and openness. Brands that readily disclose their formulation philosophy, sourcing practices, and the scientific rationale behind their ingredient choices are building stronger, more loyal customer bases. The power of digital platforms, especially social media, means that any perceived lack of transparency or misleading claims can be quickly exposed, leading to significant brand damage. This dynamic holds companies accountable, effectively elevating the overall standard of honesty and ethical marketing within the industry.
Regulatory bodies are also beginning to catch up to these evolving consumer demands. While regions like the European Union have historically maintained stricter regulations on cosmetic ingredients, there is growing pressure in other markets, such as the United States, for the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to establish clearer definitions and stricter oversight for “clean” and “natural” claims. This regulatory push is a direct response to consumer advocacy and the proliferation of sometimes ambiguous marketing terminology. The future of clean beauty in 2026 will likely see a convergence of consumer-driven demand for transparency with more formalized industry standards and governmental regulations, further solidifying its presence as a core tenet of modern skincare.
6.2 The Imperative of Sustainability and Ethical Practices
The commitment to sustainability in skincare is no longer an optional add-on but a fundamental pillar of brand identity and consumer expectation in 2026. This encompasses a broad spectrum of practices, from eco-friendly formulations and responsible sourcing to environmentally conscious packaging and ethical manufacturing. The late-2023 global survey highlighted this urgency, revealing that an overwhelming **81% of consumers believe that beauty brands should actively work to reduce plastic packaging**[13]. This statistic underscores a clear consumer mandate for environmental stewardship, compelling companies to rethink their entire supply chain and product lifecycle.
One of the most visible manifestations of this trend is the revolution in skincare packaging. The industry, historically reliant on single-use plastics, is rapidly transitioning towards more sustainable alternatives. Innovations include:
- Recyclable Materials: Increased use of glass, aluminum, and post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics for product containers.
- Refill Systems: The introduction of refillable packaging for popular products, allowing consumers to purchase concentrate or cartridges to replenish their existing containers, thereby reducing waste.
- Concentrates and Solid Formats: Development of highly concentrated formulas or solid formats (e.g., bar cleansers, shampoo bars) that require minimal packaging and offer a reduced carbon footprint during transport.
- Biodegradable Solutions: Exploration of biomaterials and biodegradable plastics as alternatives to conventional plastics.
These initiatives not only respond to consumer demands but also represent a critical step towards mitigating the beauty industry’s significant environmental impact.
Beyond packaging, ethical sourcing of ingredients has become a paramount concern. Consumers are increasingly interested in the origin of raw materials and the social and environmental practices of suppliers. This includes:
- Fair Trade: Sourcing ingredients from communities that adhere to fair labor practices and provide equitable compensation for their work, such as shea butter cooperatives in West Africa.
- Sustainable Cultivation: Ensuring that botanical ingredients are cultivated using methods that do not deplete natural resources or harm biodiversity.
- Cruelty-Free and Vegan: The “cruelty-free” standard (no animal testing) is now a baseline expectation in many markets, often accompanied by a preference for vegan formulations, free from animal-derived ingredients.
These considerations reflect a holistic view of sustainability, recognizing the interconnectedness of environmental and social responsibility.
Corporate responsibility extends to broader environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals. Many large conglomerates and indie brands alike are publishing detailed sustainability reports, outlining their commitments to reducing carbon emissions, minimizing water usage, and achieving circular economy principles. Pledges to use a certain percentage of recycled materials or achieve carbon neutrality by specific dates are becoming normalized, indicating a long-term strategic commitment to sustainability.
The economic implications of this shift are considerable. Brands that successfully integrate sustainable and ethical practices into their core operations are gaining a competitive edge, attracting environmentally conscious consumers, and potentially securing investments from ESG-focused funds. Conversely, companies failing to adapt risk alienating a significant portion of the market. The sustainability imperative in skincare in 2026 is driving widespread innovation, fostering greater transparency, and fundamentally reshaping how products are developed, manufactured, and marketed. It represents a powerful demonstration of how consumer preferences can compel an industry towards more responsible and conscientious practices.
6.3 Broadening Skincare Demographics: Men, Gen Z, and Global Markets
The traditional confines of the skincare market, once predominantly focused on women in Western markets, have dramatically expanded by 2026 to embrace a far more inclusive and diverse demographic. This expansion is driven by evolving societal norms, increased awareness of skin health across all segments, and the powerful influence of digital media.
6.3.1 The Rise of Men’s Skincare
One of the most significant shifts is the mainstreaming of men’s skincare. Historically, men’s routines were limited to basic washing and shaving products, often viewed with skepticism or perceived as a feminine pursuit. However, this perception has undergone a profound transformation. The global **men’s skincare products market is projected to grow robustly, from $17.6 billion in 2025 to $37.3 billion by 2035**, reflecting an impressive **Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 10.5%**[11].
Several factors contribute to this exponential growth:
- Increased Grooming Awareness: Modern men are more invested in their personal appearance and overall well-being. Grooming is no longer stigmatized but seen as an integral part of self-care and professional presentation.
- Targeted Product Development: Brands are launching specific product lines tailored to men’s skin concerns, which can differ due to factors like facial hair, thicker skin, and hormonal differences. This includes products for razor bumps, anti-aging solutions, and sun protection adapted for men.
- Changing Marketing Strategies: Skincare advertising for men has evolved, portraying routines as masculine, practical, and a form of self-investment rather than vanity.
- Influence of Social Media: Male influencers, celebrities, and even dermatologists on platforms like TikTok and Instagram are openly discussing and recommending skincare routines, normalizing their use for a male audience.
Surveys indicate that men are increasingly incorporating foundational skincare products such as facial cleansers, moisturizers, and sunscreen into their daily routines. This represents a substantial new customer base for the industry, emphasizing that skin health is a universal concern irrespective of gender.
6.3.2 Gen Z: The Skincare Savants
The younger generations, particularly Gen Z and millennials, are fundamentally reshaping skincare consumption. These cohorts are starting their skincare routines at an earlier age, often in their teens or early twenties, driven by a strong focus on prevention and health. This contrasts with previous generations who typically approached skincare reactively, primarily for anti-aging concerns later in life.
Gen Z is distinguished by its digital nativity and reliance on social media for information and trend discovery. Platforms like TikTok have become powerful conduits for skincare education and product endorsement. For instance, the largely unknown brand **CeraVe saw its sales jump by 82% year-over-year in the first nine months of 2020** after dermatologists and influencers on TikTok praised its affordable, science-backed formulations[14]. This phenomenon illustrates several key characteristics of Gen Z consumers:
- Ingredient Savviness: They are educated about active ingredients (e.g., retinol, hyaluronic acid, niacinamide) and seek products with proven efficacy.
- Value and Authenticity: While interested in effective ingredients, they prioritize value for money and authentic recommendations over celebrity endorsements or lavish marketing.
- Community-Driven Trends: Social media fosters communities where skincare routines, product reviews, and “skin journeys” are shared and discussed, rapidly propagating trends and boosting demand.
- Proactive Prevention: Rather than waiting for signs of aging or damage, Gen Z actively invests in preventive measures, including daily SPF and antioxidant serums, viewing skincare as a long-term health investment.
This proactive and digitally informed consumption behavior has a ripple effect throughout the market, pushing brands towards transparency, science-backed claims, and relatable marketing.
6.3.3 Expanding Global Markets
Skincare’s reach is also broadening geographically, with rapid growth observed in emerging markets across Asia, Latin America, and Africa. While the Asia-Pacific region already leads the global skincare market, accounting for the highest revenue share as of 2024[9], its growth continues unabated, particularly in countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations where a rising middle class has increasing disposable income for personal care.
Specific regional influences are noteworthy:
- K-Beauty and J-Beauty Dominance: South Korea and Japan continue to be innovation hubs, with their multi-step routines, unique formulations (e.g., essences, fermented ingredients), and emphasis on healthy, glowing skin influencing global trends.
- Diverse Needs: As the market globalizes, there’s a growing need for products that cater to a wider array of skin tones and types. This includes ensuring sunscreens don’t leave a white cast on darker skin, and addressing conditions like hyperpigmentation which are more prevalent in skin of color.
- Local Adaptations: Brands are increasingly adapting their offerings to local preferences and cultural beauty standards, such as developing skin-lightening products for certain Asian markets or formulations suitable for humid climates.
This globalization signifies that the importance of skincare is universally recognized, transcending cultural boundaries, even if specific product demands are locally nuanced. The industry is responding by fostering greater inclusivity in research, product development, and marketing campaigns, reflecting a true “skincare for all” approach.
6.4 Consumer Engagement and the “Self-Care” Narrative
The relationship between consumers and their skincare routines has deepened, extending beyond functional benefits to encompass mental well-being and self-care. In 2026, skincare is increasingly framed as a ritualistic act of self-love and mindfulness, tapping into the broader wellness movement.
Many individuals view their morning and evening skincare routines as dedicated moments for relaxation and introspection. Brands have intelligently capitalized on this by emphasizing sensory experiences – luxurious textures, calming scents, and affirmations of self-worth. The concept of “skinimalism,” or skincare minimalism, has also gained traction, advocating for simplified routines with fewer, yet highly effective, products. This serves as an antidote to overwhelming multi-step routines, promoting a sense of ease and preventing skin overload.
Research suggests that chronic skin conditions, such as acne and psoriasis, can significantly impact mental health, leading to anxiety and depression[23]. Conversely, nurturing one’s skin can contribute to a sense of control and boost confidence, reinforcing the emotional benefits of consistent skincare. By positioning skincare as an integral component of a holistic well-being strategy, brands connect with consumers on a deeper, more personal level. This narrative aligns with the post-pandemic emphasis on looking after one’s overall health, where even seemingly small acts like applying a moisturizer or sunscreen become part of a larger commitment to oneself.
The shift towards these evolving consumer demands—cleanliness, sustainability, inclusivity, and self-care—is not merely about market trends; it reflects a fundamental redefinition of what “health” and “beauty” mean in the 21st century. It underscores a more conscious, responsible, and personalized approach to skin health, compelling the industry to continually adapt and innovate.
Next, we will transition into a discussion of section 7, which will explore the pivotal role of technology and innovation in transforming skincare, examining breakthroughs in AI, personalized diagnostics, and smart devices that are making skincare more tailored and data-driven.
7. Preventive Skincare: Public Health and Lifestyle Integration
In 2026, the landscape of skin health is unequivocally shifting from a reactive model of treatment to a proactive paradigm centered on prevention. This profound transformation is driven by a confluence of factors: the escalating global burden of skin diseases, the growing recognition of skin’s integral role in overall health, and a heightened public awareness fueled by both public health initiatives and digital information dissemination. The increasing emphasis on preventive skincare is not merely a cosmetic concern but has emerged as a critical public health objective, integrating lifestyle factors for holistic wellness and leveraging technological advancements for early detection and personalized care.
The sheer scale of skin-related health issues underscores the urgency of this shift. Skin diseases accounted for an astronomical 44.84 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) globally in 2021[1], a significant rise from approximately 41.6 million DALYs in 2013[2]. This makes skin conditions one of the leading causes of non-fatal health loss worldwide[3], asserting that skin health is far more than an aesthetic consideration; it is a fundamental component of public health. Indeed, three skin diseases rank among the ten most prevalent diseases globally[4], illustrating the ubiquitous nature of dermatological concerns. Conditions such as dermatitis, acne, and fungal infections collectively affect hundreds of millions, substantially impacting quality of life and productivity, even if they are not typically life-threatening. The most alarming trend, however, is the relentless rise of skin cancer, which is now the world’s most frequent cancer. In 2021, the total incidence of skin cancer (melanoma and non-melanoma) reached 6.64 million cases globally[5], exhibiting an average annual increase of approximately 1.9% since 1990[6]. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) estimated over 1.5 million new skin cancer cases in 2022, including about 330,000 new melanoma cases and approximately 60,000 melanoma-related deaths in the same year[7]. These sobering statistics highlight the imperative for greater preventive action and the integration of comprehensive skincare strategies into public health frameworks and individual lifestyles.
### 7.1 The Evolving Public Health Landscape of Skin Health
The re-evaluation of skin health as a public health priority is a defining characteristic of 2026. This paradigm shift acknowledges that skin conditions are not isolated ailments but rather interconnected with broader societal health and economic well-being.
7.1.1 Recognizing the Burden: Beyond Cosmetic Concerns
For too long, skin issues were often relegated to the realm of cosmetic or superficial problems. However, data from global burden of disease studies have forcefully challenged this perception. The 44.84 million DALYs attributed to skin and subcutaneous diseases in 2021 alone are a stark indicator that these conditions significantly impair daily functioning, cause discomfort, and reduce overall well-being on a massive scale[1]. This statistic alone presents a compelling argument for greater investment in skin health prevention and management. The increase from 41.6 million DALYs in 2013 to 44.84 million in 2021 demonstrates an intensifying burden over a relatively short period[2].
Moreover, the fact that three skin diseases are among the top ten most prevalent diseases globally further cements their status as a major public health concern[4]. These are not rare conditions affecting a small subset of the population; rather, they are pervasive, impacting vast numbers of individuals across all demographics. Dermatitis, for instance, affected an estimated 230 million people in 2019, with acne and fungal infections also being widespread. While often non-fatal, the chronicity and visibility of these conditions can lead to considerable physical discomfort, psychological distress, and social stigma. Studies have linked chronic skin conditions like severe acne and psoriasis to higher rates of anxiety and depression[21], underscoring the deep impact on mental health and quality of life. From a public health perspective, such widespread conditions place substantial strain on healthcare systems, leading to millions of doctor visits annually and significant productivity losses due to days off work.
7.1.2 Skin Cancer: A Preventable Epidemic
The alarming rise in skin cancer incidence serves as the most potent call to action for preventive skincare. With 6.64 million total skin cancer cases worldwide in 2021[5], and an estimated 1.5 million new cases globally in 2022, including 330,000 new melanoma cases and 60,000 melanoma deaths[7], skin cancer is an undisputed public health crisis. This trend is driven by an aging global population and increased recreational UV exposure over decades, posing a significant challenge that primarily demands preventive strategies. Projections indicate that annual melanoma cases could increase by 50% by 2040 without substantial improvements in prevention measures[10].
Despite the clear benefits of sun protection, adherence remains woefully inadequate. Research indicates that consistent, daily sunscreen usage can reduce melanoma risk by approximately 35-40% in young adults[11]. However, in the U.S. in 2025, only 12% of adults reported using sunscreen daily, while a concerning 28% admitted to never using it[12]. This gap between scientific evidence and public practice highlights a critical area for public health intervention. The slight decline in daily usage from the previous year, possibly influenced by cost concerns or safety misconceptions around sunscreen, further emphasizes the need for renewed and evidence-based public education campaigns[14]. The success of Australia’s decades-long “Slip-Slop-Slap” campaign, which has been credited with stabilizing or even declining melanoma incidence rates in Australians under 40[16], provides a powerful testament to the effectiveness of sustained public health messaging. This campaign directly translates into measurable health outcomes, with epidemiologists estimating it has prevented about 10-15% of potential skin cancer cases in that population[17].
7.1.3 Public Health Campaigns and Early Detection
Building on successful models like “Slip-Slop-Slap,” public health campaigns in 2026 are increasingly sophisticated, leveraging digital platforms and community outreach. The goal is not only to educate but to instill sun-safe behaviors from an early age, making them habitual and culturally ingrained. Governments and health organizations globally are expanding initiatives, ranging from promoting UV Index alerts and school programs to advocating for regular skin self-exams.
One notable example demonstrating a progressive approach to public health intervention is the initiative by Cork City Council in Ireland. In the summer of 2025, in partnership with health authorities, the council launched a pilot program installing free SPF 50 sunscreen dispensers in four popular public parks[19]. This simple yet impactful measure directly addresses the barrier of accessibility, encouraging sun protection by making it readily available. Early usage data showed strong uptake, confirming that convenience significantly boosts protective behaviors. This initiative, costing only a few thousand euros, serves as a model for how basic infrastructure changes can translate into meaningful public health benefits, framing skin protection as a public amenity akin to clean water or shade in parks.
Early detection of skin conditions, particularly skin cancer, is another cornerstone of preventive public health strategy. Dermatologists consistently promote monthly self-examinations and regular professional screenings. Some regions, like Germany, have even implemented national skin cancer screening programs, which have been shown to increase early diagnoses[20]. For common conditions like acne and eczema, early intervention is emphasized to prevent progression to more severe states that can lead to scarring, infection, or significant psychological distress. This preventive mindset is increasingly being woven into routine healthcare check-ups and corporate wellness programs in 2026.
### 7.2 Lifestyle Integration for Holistic Skin Wellness
Beyond targeted public health campaigns, a broader trend in 2026 is the seamless integration of skincare practices into daily lifestyle and overall wellness routines. This holistic approach recognizes that skin health is a reflection of internal health and external environmental factors.
7.2.1 Diet, Sleep, and Stress: The Internal Factors
The interconnectedness of internal health with external skin appearance is gaining scientific and public recognition. There is growing evidence linking diet, sleep quality, and stress levels to various skin conditions. Dermatologists in 2026 adopt a more holistic view, often advising patients on nutritional choices—such as diets rich in antioxidants and low in processed sugars—to support healthier skin. For example, research increasingly points to the impact of gut health on skin conditions like acne and eczema. Cessation of smoking, a notorious accelerator of skin aging and wrinkling, is also a common recommendation.
Stress management is another critical, integrated component. Chronic stress can trigger flare-ups of conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and acne. Therefore, mindfulness practices, adequate sleep, and other stress-reduction techniques are often recommended alongside topical treatments. This alignment with the broader “wellness” movement sees consumers embracing skincare not just for aesthetic improvement but as a ritualistic component of self-care, contributing to mental well-being and stress relief. The act of maintaining one’s skin, through routines and rituals, is tied to a meditative and calming experience for many.
7.2.2 Environmental Factors and Protective Routines
In 2026, environmental factors such as pollution and climate change are increasingly linked to skin issues. Rising pollution levels, including smoke from wildfires, are associated with flare-ups of eczema and other inflammatory skin conditions[18]. This awareness has fueled demand for protective skincare routines that include antioxidant-rich creams and “pollution shields.” Urban consumers, in particular, are seeking products that offer a barrier against environmental aggressors.
Beyond daily pollution, increased UV exposure due to lifestyle changes (more outdoor activities, travel) and potential ozone depletion necessitate rigorous sun protection. Despite known benefits, public adherence to sun-protective behaviors is still developing. Preventive skincare now focuses on making sun protection not just a seasonal activity but a year-round habit. The daily application of broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade are foundational practices. The emerging market for innovative sunscreens, including nanoparticle-based formulations that are less greasy and leave no white cast[2], is aimed at improving user compliance, especially for daily, year-round use.
| Preventive Skincare: Key Lifestyle Integration Points in 2026 | Details | Impact on Skin Health |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Sun Protection | Consistent use of broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen, protective clothing, seeking shade. | Reduces skin cancer risk by 35-40%[11], prevents premature aging and hyperpigmentation. |
| Holistic Nutrition | Diets rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, probiotics; reduced sugar and inflammatory foods. | Supports skin barrier function, reduces inflammation (e.g., in acne, eczema), promotes healthy glow. |
| Adequate Sleep | 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. | Facilitates skin repair and regeneration, reduces signs of fatigue (dark circles, dullness). |
| Stress Management | Mindfulness, exercise, meditation. | Mitigates stress-induced flare-ups of conditions like acne, psoriasis, and eczema. |
| Environmental Protection | Antioxidant serums, anti-pollution skincare, regular cleansing. | Protects against free radical damage from urban pollution, smoke, and other environmental aggressors. |
| Regular Skin Assessment | Monthly self-checks for moles, early detection of changes. | Crucial for early detection of skin cancers and other serious dermatological conditions. |
7.2.3 The “Skin-First” Mindset and Self-Care
The booming global skincare market, valued at approximately $155 billion in 2023 and projected to exceed $220 billion by 2029 (a 6.1% CAGR), is a clear reflection of this “skin-first” mindset. Skincare has outpaced many other beauty segments, driven by consumer demand for products that support health and daily care routines. This is particularly evident in the anti-aging product sector, which is forecast to nearly double from $55.8 billion in 2023 to $108.5 billion by 2033[18], largely due to demographic shifts like aging populations and a growing preventive outlook among younger consumers.
The concept of skincare as self-care resonates deeply, especially post-pandemic. Consumers view their skincare routines as an investment in both health and confidence, a dedicated time for personal well-being. This trend encourages consistent spending on quality products and routines, moving skincare beyond superficiality towards a deeper engagement with personal health. The rise of “skinimalism” – simplifying routines for gentler, less stressful care – further illustrates this connection to overall wellness, aligning effective care with mental tranquility.
### 7.3 Technology and Innovation: Empowering Prevention and Personalization
Technological advancements are playing an increasingly pivotal role in preventive skincare, making care more tailored, accessible, and data-driven.
7.3.1 AI-Driven Diagnostics and Personalized Formulations
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing how individuals monitor and improve their skin health. AI-powered skin analyzers are entering the market, capable of scanning skin for hydration levels, pigmentation irregularities, wrinkles, and even early signs of certain conditions. Brands like L’Oréal have launched AI-driven devices that integrate facial scanning to recommend custom regimens[19]. These tools move skincare from a generic approach to one that is highly personalized, providing specific ingredient and product recommendations based on individual needs and environmental factors.
Coupled with AI diagnostics, the ability to create customized skincare formulations is becoming more widespread. Services and devices are emerging that can dispense bespoke moisturizers and serums based on a user’s unique skin profile, adjusted in real time for factors like local weather or pollution. L’Oréal’s innovative device, Perso, introduced in 2020, exemplifies this trend by mixing personalized creams and cosmetics on demand[20]. This level of customization dramatically enhances product efficacy and consumer satisfaction, fostering a feeling of “made just for me” care.
7.3.2 High-Tech Devices and Advanced Ingredients
The market is flooded with high-tech at-home skincare devices that replicate professional treatments, empowering consumers to take more active roles in their preventive care. Smart LED light therapy masks, for instance, utilize specific wavelengths (blue for acne, red for collagen stimulation) to address various skin concerns over time. Microcurrent and radiofrequency (RF) devices allow users to tone muscles and tighten skin at home. These Bluetooth-enabled gadgets often integrate with apps to guide users and track progress, effectively gamifying and optimizing skincare routines[19].
Furthermore, ingredient science is continually pushing boundaries. Nanotechnology is yielding advanced sunscreen filters that offer superior UV protection without the aesthetic drawbacks (white cast, greasiness) of traditional formulas, encouraging better daily compliance. Encapsulated active ingredients like retinol and vitamins improve penetration and reduce irritation, maximizing anti-aging and therapeutic benefits. The blurring lines between cosmetics and medicine, driven by “cosmeceuticals,” means products in 2026 deliver clinically tested benefits for specific skin conditions, aiding in prevention and early management.
7.3.3 The Rise of Teledermatology
Teledermatology has emerged as a transformative force, making expert dermatological care more accessible than ever before. The market for online and virtual skin consultations was estimated at $12.7 billion in 2025 and is projected to soar to $57.4 billion by 2035, representing an annual growth of approximately 16%[21]. This accelerated growth is largely a legacy of the COVID-19 pandemic, which normalized telehealth.
Patients can now obtain remote consultations for a wide range of concerns, from checking moles for suspicious changes to managing chronic conditions like acne and eczema, often by sending high-resolution images to dermatologists. This expansion of access is particularly crucial for underserved and rural populations that historically face barriers to specialist care. AI is also assisting dermatologists through algorithms that analyze mole images for potential skin cancer with high sensitivity, or by triaging cases to ensure urgent ones are addressed promptly. In the near future, AI could even predict flare-ups for chronic conditions, such as an app alerting an eczema patient to adjust their routine based on local weather and pollen levels, facilitating proactive management.
### 7.4 Consumer Demands: Clean, Sustainable, and Inclusive Skincare
Consumer expectations in 2026 are increasingly shaping the skincare industry, driving demands for products that are not only effective but also aligned with ethical, environmental, and inclusive values.
7.4.1 Clean and Transparent Beauty
The “clean beauty” movement underscores a heightened consumer awareness of product ingredients. In a late-2023 global survey, 63% of respondents stated that the “clean” formulation (i.e., non-toxic ingredients) of a cosmetic product was extremely or very important in their purchasing decisions[22]. This trend has led to a proliferation of “free-from” labels (e.g., paraben-free, sulfate-free, fragrance-free) and a strong emphasis on dermatologist-tested formulations. Consumers demand transparency, seeking comprehensive ingredient lists and explanations of their functions. Brands that openly share their formulations and provide scientific backing for their claims are garnering significant consumer trust and loyalty. Regulatory bodies are also catching up, with increasing pressure to standardize definitions of “clean” and ensure product claims are substantiated.
7.4.2 Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Environmental consciousness is now a mainstream expectation. Approximately 81% of consumers believe beauty brands should actively reduce plastic packaging[23], prompting significant innovation in sustainable packaging solutions, including biodegradable materials, refillable containers, and concentrated product formats (e.g., bar cleansers). “Cruelty-free” status is a baseline expectation, and many consumers prioritize vegan formulations. Companies are increasingly integrating sustainability into their core business strategies, setting ambitious goals for reducing carbon footprints and using recycled materials. Furthermore, there is a growing demand for ethical sourcing of ingredients, supporting fair trade practices and community development. This holistic ethical stance reflects a broader consumer desire to support brands that demonstrate social responsibility alongside product quality.
7.4.3 Inclusivity and Diversity
The skincare market in 2026 is rapidly becoming more inclusive and diverse. The historical Euro-centric bias in product development and research is being actively dismantled. Brands are now formulating products with a broader range of skin tones and types in mind, ensuring sunscreens do not leave a white cast on darker skin tones or that tinted products offer a comprehensive shade range. There’s also increased attention to conditions disproportionately affecting certain populations, such as hyperpigmentation in skin of color or specific concerns for aging skin across different ethnic groups.
The expansion of skincare demographics is particularly notable in the men’s skincare segment, projected to grow from $17.6 billion in 2025 to $37.3 billion by 2035 (a 10.5% CAGR)[24]. This growth is driven by increasing societal acceptance of men’s grooming and targeted product lines. Younger consumers (Gen Z and millennials) are driving trends through social media, starting skincare routines earlier, and demanding inclusivity across all product offerings and marketing campaigns. Viral social media phenomena, such as CeraVe’s 2020 sales surge of 82% thanks to TikTok endorsements[25], demonstrate the power of digitally empowered, diverse consumer communities in shaping market success. This dynamic environment encourages brands to be authentic and responsive, moving beyond superficial gestures to genuinely cater to the diverse needs of a global clientele.
The integration of preventive skincare into public health and everyday lifestyles, supported by technological advancements and driven by evolving consumer values, marks a critical juncture in the approach to dermatological well-being. This comprehensive strategy, moving from reactive treatment to proactive prevention, is essential for addressing the escalating burden of skin diseases and fostering healthier, more resilient skin for populations worldwide.
The increasing role of public health and lifestyle integration in preventive skincare naturally leads to a deeper look at global variations and cultural nuances that influence skin health practices and market dynamics. The subsequent section will explore these aspects further.
8. Regional Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends
The global skincare market, projected to reach over $220 billion by 2029 from its $155 billion valuation in 2023 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6% [8], is a vibrant and ever-evolving landscape. This robust growth is not uniformly distributed but rather defined by distinct regional dynamics and emerging trends that reflect diverse cultural preferences, economic developments, dermatological needs, and technological adoption rates. As we approach 2026, understanding these regional nuances becomes paramount for stakeholders seeking to navigate and capitalize on the burgeoning opportunities within the skin health sector. This section will delve into the market leadership, particularly that of Asia-Pacific, and explore the unique forces shaping skincare consumption across different parts of the world, highlighting key statistics and examples that underscore these global disparities and convergence points.
Asia-Pacific: The Global Skincare Powerhouse
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region stands as the undisputed leader in the global skincare market, commanding the largest revenue share as of 2024 [9]. This dominance is a multifaceted phenomenon, rooted in a blend of deep-seated cultural emphasis on skin health, rapid economic growth, a burgeoning middle class, and an insatiable appetite for innovation. Countries within this region, such as South Korea, Japan, and China, are not just major consumers but also significant trendsetters, influencing global beauty standards and product development.
Cultural Imperatives and Skincare Rituals
In several East Asian cultures, particularly in South Korea and Japan, skincare is not merely a routine but a deeply ingrained cultural practice and a vital aspect of self-care and social presentation. This cultural reverence translates into elaborate, multi-step skincare regimens, often incorporating a wide array of products like cleansers, toners, essences, serums, ampoules, masks, and moisturizers [9]. The concept of “glass skin” or “mochi skin” originating from these regions exemplifies the pursuit of a luminous, smooth, and poreless complexion, driving demand for innovative and highly efficacious products. For instance, the K-beauty (Korean beauty) phenomenon, characterized by its focus on natural ingredients, innovative formulations (e.g., snail mucin, fermented extracts), and aesthetically pleasing packaging, has globalized these elaborate routines, significantly influencing consumer behavior in Western markets as well.
Economic Growth and Disposable Income
The rapid economic expansion and the rise of a substantial middle class across several APAC nations, especially China, have been pivotal in fueling skincare market growth. As disposable incomes increase, consumers are more willing to invest in premium and specialized skincare products, often viewing them as indicators of status and personal well-being. China, in particular, represents a massive growth engine, with its consumers demonstrating a strong demand for high-end skincare and anti-aging solutions. This economic transformation contributes significantly to the projected increase in the global anti-aging products market from $55.8 billion in 2023 to $108.5 billion by 2033, driven by a greater preventive mindset among consumers [10].
Innovation Hub and Fast Adoption Cycles
The APAC region is a hotbed of skincare innovation. South Korea, for example, is renowned for its rapid product development cycles, with new ingredients, technologies, and formats constantly emerging. This competitive environment fosters continuous innovation, pushing brands to deliver novel solutions that cater to increasingly sophisticated consumer demands. From hydrogel masks and cushion compacts to advanced serums incorporating cutting-edge ingredients, APAC innovation frequently sets the pace for the global industry [9]. The region’s consumers are also early adopters of new technologies, whether in formulations or in beauty devices, facilitating a dynamic market where trends evolve quickly.
North America and Europe: Mature Markets with Evolving Demands
While the APAC region exhibits the highest growth rates, North America and Europe remain substantial markets, albeit with different primary drivers and trends. These regions represent a significant portion of the global skincare market, characterized by mature consumer bases and a strong focus on “clean beauty,” sustainability, inclusivity, and techno-dermatology.
Focus on “Clean Beauty” and Sustainability
In North America and Europe, there is a pronounced shift towards “clean beauty” and sustainable practices. Consumers are increasingly scrutinizing ingredient lists, demanding products that are free from parabens, sulfates, phthalates, and other potentially harmful chemicals [13]. A survey revealed that 63% of consumers consider “clean beauty” (safe, natural ingredients) to be very important when selecting products [13]. This demand extends to the environmental footprint of products, with 81% of consumers believing that brands should reduce plastic packaging [13]. Consequently, brands in these regions are investing heavily in eco-friendly formulations, recyclable or refillable packaging, and ethical sourcing, aligning with broader consumer values around health and environmental responsibility.
Advanced Technology and Medical-Grade Skincare
The Western markets exhibit a high demand for technologically advanced skincare and professional-grade products. This includes interest in cosmeceuticals that bridge the gap between cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, offering clinically tested benefits for specific skin concerns such as hyperpigmentation, rosacea, and anti-aging. The integration of AI for personalized diagnostics and at-home smart devices (e.g., LED masks, microcurrent tools) is also gaining traction [11]. These technologies offer consumers unprecedented control and customization over their routines, bringing professional-level treatments into the home.
Demographic Shifts and Anti-Aging Focus
Similar to APAC, aging populations in North America and Europe contribute significantly to the anti-aging segment. With longer lifespans and increased awareness, older consumers are keen to maintain youthful skin, driving demand for products incorporating ingredients like retinol, collagen, and antioxidants [10]. However, younger generations are also adopting preventive anti-aging strategies earlier, recognizing the importance of consistent care to forestall visible signs of aging.
Emerging Markets: Rapid Expansion and Unique Needs
Beyond the established giants, emerging markets in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa are experiencing double-digit growth rates, positioning them as critical future drivers of the global skincare market. These regions often present unique demand patterns influenced by local environmental conditions, cultural practices, and evolving beauty standards.
Southeast Asia: Digital Growth and Local Adaptations
Countries such as Indonesia, Thailand, and Vietnam are witnessing booming skincare markets, propelled by increasing internet penetration, a young, digitally-savvy population, and rising disposable incomes. E-commerce platforms and social media play a crucial role in product discovery and sales. Brands often need to adapt their offerings to cater to specific local needs, such as products for humid climates, skin brightening, or solutions addressing pollution-related skin concerns. The influence of K-beauty and J-beauty is also strongly felt in this region, contributing to a diverse and dynamic market.
Latin America: Natural Ingredients and Strong Brand Loyalty
Latin American consumers show a high preference for natural ingredients and products with health benefits, often drawing on traditional botanical knowledge. This region’s market is characterized by strong brand loyalty and a growing interest in sustainable and ethically sourced products. Brazil, for instance, is a major beauty market, with a focus on body care and sun protection due to its sunny climate. Rising awareness of healthy skin maintenance, combined with increased purchasing power, is fueling growth in this diverse region.
Africa: Untapped Potential and Tailored Solutions
The African continent, while still an emerging consumer market compared to others, holds immense untapped potential. A young, rapidly urbanizing population, combined with greater access to information and products, is driving increased interest in skincare. Products tailored to specific skin types and concerns prevalent in African communities (e.g., hyperpigmentation, protection against harsh environmental elements) are gaining traction. International brands are recognizing this potential and beginning to customize their offerings and marketing strategies to resonate with local consumers.
Beyond Geography: Cross-Cutting Trends Shaping Global Skincare in 2026
While regional variations are significant, several overarching trends are shaping the entire global skincare market in 2026, regardless of geography. These reflect fundamental shifts in consumer mindset, technological capabilities, and societal values.
The Rise of Men’s Skincare
Skincare is no longer a female-centric domain. The men’s skincare segment is experiencing robust growth, projected to more than double from $17.6 billion in 2025 to $37.3 billion by 2035, representing an approximate 10.5% annual growth rate [11]. This growth is driven by increased societal acceptance of male grooming, targeted product lines addressing men’s specific skin concerns (e.g., post-shave irritation, oil control, anti-aging), and marketing efforts that normalize and encourage men to adopt comprehensive skincare routines. Brands are developing gender-neutral packaging and formulations, and men are increasingly investing in facial cleansers, sunscreens, and moisturizers as part of their daily regimen.
Technology as a Fundamental Pillar
Technology is profoundly transforming skincare. AI-powered diagnostics, personalized product formulations, and advanced at-home devices are becoming mainstream. L’Oréal, for example, has launched AI-powered skin analyzers that scan for hydration, pigmentation, and other indicators to recommend customized regimens [11]. Smart LED masks, nanotech-infused sunscreens, and wearable sensors are empowering consumers to monitor and improve their skin health with precision [11]. The teledermatology market is also skyrocketing, expected to reach $57.4 billion by 2035 from $12.7 billion in 2025 – a more than four-fold increase [12]. This allows for remote consultations and increased accessibility to expert dermatological advice, particularly in underserved areas.
Wellness and Holistic Health Integration
Skincare in 2026 is increasingly viewed as an integral part of holistic wellness and self-care. Consumers are connecting skin health to overall lifestyle factors like diet, sleep, stress management, and environmental exposure. The demand for protective routines against pollution and climate factors (e.g., antioxidant creams, pollution shields) is growing [12]. Furthermore, the act of maintaining one’s skin through routines and rituals is often linked to mental well-being and stress relief, embodying a “skin-first” mindset that prioritizes health and intrinsic radiance over mere superficial coverage. This holistic approach encourages brands to innovate with ingredients and messaging that support overall health, including nutricosmetics like collagen peptides.
Influence of Social Media and Informed Consumers
Social media platforms, particularly TikTok and Instagram, have become powerful drivers of skincare trends and consumer education. Viral content from “skinfluencers” and dermatologists can rapidly propel products to global fame, as evidenced by CeraVe’s 82% sales jump in the first nine months of 2020 after gaining traction on TikTok [14]. This digital landscape creates a highly informed, yet sometimes vulnerable, consumer base. Consumers are savvier about ingredients and product efficacy but are also susceptible to misinformation. This dynamic compels brands to be transparent, scientifically rigorous, and responsive to consumer dialogue across digital channels.
The Imperative of Inclusivity
The global skincare market is shedding its historical Euro-centric biases, embracing inclusivity and catering to a wider range of skin tones, types, and concerns. Brands are focusing on formulations that do not leave a white cast on darker skin tones, addressing issues like hyperpigmentation which are more prevalent in skin of color, and acknowledging hormonal fluctuations that impact skin health across different demographics. Marketing campaigns increasingly feature diverse models, reflecting the broad user base for skincare products globally and emphasizing that effective skincare solutions should be accessible and appropriate for everyone.
Summary Table of Regional Dynamics and Trends
To summarize the diverse regional dynamics, the following table outlines key characteristics and emerging trends:
| Region | Market Status & Size (2023-2025) | Key Drivers & Cultural Influences | Dominant Trends & Innovation Focus | Selected Examples/Data Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific (APAC) | Largest global market (highest revenue share). Strongest growth rates. | Cultural emphasis on elaborate skincare routines (e.g., K-beauty, J-beauty). Rapid economic growth and rising middle class in China. | Elaborate multi-step routines, innovative ingredients (fermented extracts, snail mucin), fast product adoption. Anti-aging, skin brightening. | K-beauty/J-beauty influence globally [9]. Anti-aging market to reach $108.5B by 2033 globally [10]. |
| North America & Europe | Sizable, mature markets with steady growth rates. | High consumer awareness of ingredients and sustainability. Aging populations driving anti-aging demand. | “Clean beauty” (63% importance) [13], sustainable packaging (81% demand) [13], advanced tech/med-grade skincare, personalized diagnostics. | AI-powered skin analyzers (L’Oréal) [11]. Teledermatology projected to reach $57.4B by 2035 [12]. |
| Emerging Markets (Southeast Asia, Latin America, Africa) | Double-digit growth, significant untapped potential. | Increasing disposable income, urbanization, rising digital access. Local environmental factors and specific skin concerns. | E-commerce boom, influence of global trends (e.g., K-beauty in SEA), focus on natural ingredients (LatAm), tailored solutions for diverse skin types (Africa). | Men’s skincare growing ~10.5% annually [11]. Brands adapting to humid climates, skin brightening needs. |
| Global Cross-Cutting Trends | All markets | Increased health awareness, digitalization, consumer empowerment, societal shifts. | Men’s skincare growth, personalized tech (AI, devices), holistic wellness, sustainability, transparency, inclusivity (diverse skin tones), social media influence. | CeraVe’s 82% sales jump due to TikTok [14]. Sunscreen usage in US only 12% daily, but awareness rising [6]. |
The intricate web of regional dynamics and emerging trends underscores a global consumer base that is increasingly informed, discerning, and proactive about skin health. While Asia-Pacific continues to lead with its cultural embeddedness and innovation, Western markets drive demand for ethical and technologically advanced solutions, and emerging economies represent vast new frontiers for growth. The convergence of these forces, enhanced by digital transformation and a global shift towards wellness, means that the skincare landscape in 2026 is one of unparalleled opportunity and complexity, requiring brands to be agile, authentic, and globally-aware to succeed.
This comprehensive overview of regional market dynamics and emerging trends sets the stage for a deeper dive into the specific technological advancements that are reshaping the skincare industry, which will be explored in the subsequent section.
9. Frequently Asked Questions
In an era where personal well-being is increasingly prioritized and technological advancements reshape consumer habits, the realm of skin health has emerged as a critical focus. From the profound public health implications of widespread skin diseases to the burgeoning, innovation-driven skincare market, understanding the nuances of skin care in 2026 requires a comprehensive approach. This section addresses common inquiries surrounding skin health, offering detailed insights into prevalent conditions, preventive strategies, market dynamics, and the future outlook, all underpinned by the latest research and data. It aims to clarify why maintaining skin health is not merely a cosmetic concern but a vital component of overall health and quality of life, both for individuals and global populations. By dissecting the multifaceted aspects of this topic, we can better appreciate the importance of proactive skin care practices and the exciting trajectory of the industry.
What is the global health burden of skin diseases, and why should it be a concern in 2026?
The global health burden of skin diseases in 2026 remains a significant, often underestimated, public health challenge. Skin conditions are not merely superficial aesthetic issues; they represent a major source of morbidity and disability worldwide. The human skin, being the largest organ, acts as the body’s primary protective barrier, and its compromise can lead to substantial physical, psychological, and economic consequences. The data unequivocally highlight this growing concern:
- Significant Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs): Skin and subcutaneous diseases accounted for an alarming 44.84 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) globally in 2021[1]. This figure signifies the total number of healthy years lost due to illness, disability, or early death caused by skin conditions. This represents a substantial increase from approximately 41.6 million DALYs reported in 2013[2], underscoring a worsening trend in the global impact of skin health issues. In 2013, skin diseases were already ranked as the 4th leading cause of non-fatal global health loss[3], demonstrating their persistent and considerable contribution to worldwide disability.
- High Prevalence Among Common Ailments: Skin diseases are incredibly ubiquitous, with several conditions consistently ranking among the most prevalent health issues globally. For instance, global health studies affirm that three skin diseases rank among the 10 most prevalent diseases worldwide[4]. Conditions such as dermatitis (eczema), which affected roughly 230 million people in 2019, acne, and various fungal infections are widespread, impacting hundreds of millions globally. While often not life-threatening, these conditions can be chronic, causing discomfort, impairing quality of life, and reducing productivity.
- Impact on Quality of Life and Productivity: Beyond the DALYs metric, the chronic nature and visible symptoms of many skin conditions have profound impacts on individuals’ daily lives. They can lead to physical discomfort (e.g., itching, pain, disfigurement), psychological distress (e.g., anxiety, depression, low self-esteem), and social stigma. For example, severe acne or psoriasis has been linked to higher rates of anxiety and depression[5]. This not only affects personal well-being but also translates into economic costs through lost workdays and increased healthcare utilization.
- Gateway to Other Health Problems: Compromised skin health can serve as a gateway for other, more serious health complications. Breaches in the skin barrier due to conditions like chronic ulcers or dermatitis can facilitate the entry of pathogenic infections. Persistent systemic inflammation associated with certain skin conditions, such as psoriasis, has been linked to an increased risk of other health issues, including arthritis and cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, accumulated UV damage, often manifesting as sunspots or actinic keratoses on the skin, can progress to life-threatening skin cancers. Therefore, maintaining skin integrity is crucial for preventing a cascade of downstream health problems.
- Global Inequities: The burden of skin diseases is not equally distributed. Developing countries often face higher prevalence rates for certain infectious skin diseases (e.g., fungal infections, leprosy) and frequently lack adequate access to dermatological care. Even within developed nations, disparities exist. Underserved communities may experience worse outcomes due to delayed diagnoses or environmental factors. For example, higher melanoma mortality rates are observed in rural areas due to later detection, and conditions like eczema can be exacerbated in polluted urban centers[6][7]. Stigma can further impede individuals from seeking timely help, highlighting the need for culturally sensitive public health interventions.
In summary, the global burden of skin diseases in 2026 is a compelling concern due to its widespread prevalence, significant contribution to disability, detrimental impact on physical and mental well-being, potential to lead to more severe health issues, and existing inequities in care. Recognizing skin health as a critical public health issue is paramount for developing effective preventive strategies and ensuring equitable access to care worldwide.
What are the critical facts about skin cancer, and what risk reduction strategies are effective but underutilized in 2026?
Skin cancer represents a rapidly escalating global health crisis, constituting the most frequent form of cancer worldwide. Despite advances in detection and treatment, incidence rates continue to rise, necessitating a greater emphasis on preventive measures. In 2026, several critical facts about skin cancer underscore the urgency of improved prevention and early detection strategies:
- World’s Most Frequent Cancer and Rising Incidence: Skin cancers (which include melanoma and non-melanoma types like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) are now the world’s most common malignancy[8]. In 2022 alone, more than 1.5 million new skin cancer cases were estimated worldwide[9]. The total annual incidence (melanoma and non-melanoma combined) reached 6.64 million cases globally in 2021[10]. This reflects a consistent upward trend, with the age-standardized incidence rate increasing by approximately 1.94% per year from 1990 to 2021[11]. Drivers for this increase include an aging global population, increased UV exposure due to lifestyle habits and ozone depletion, and improved detection methods.
- Melanoma: The Deadliest Form: Within skin cancers, cutaneous melanoma is the most aggressive and deadly form. In 2022, there were an estimated 330,000 new melanoma cases and nearly 60,000 melanoma deaths globally[12]. Projections indicate that by 2040, annual melanoma cases could increase by 50% due to demographic shifts and behavioral factors, unless significant improvements are made in prevention[13].
Risk Reduction Strategies: Effective but Underutilized
Despite clear evidence of effective prevention strategies, public adherence remains a considerable challenge in 2026.
- Sunscreen Use: Proven Effectiveness, Low Adherence:The consistent use of sunscreen is a powerful tool in reducing skin cancer risk. Long-term studies have demonstrated its efficacy:
- A 2018 Australian study found that young adults who regularly used sunscreen from childhood had a 35–40% lower risk of developing melanoma by age 40 compared to those who rarely used it[14].
- A landmark randomized trial in Queensland showcased that daily sunscreen application could halve the incidence of squamous cell carcinoma[15].
However, despite these compelling benefits, daily sunscreen use is far from routine for most people. In the U.S., as of 2025, only 12% of adults reported using sunscreen daily, while a substantial 28% stated they never use it at all[16]. This even marked a slight decline in regular use from the previous year, possibly attributable to misconceptions about sunscreen safety or cost[17]. Similar patterns are observed globally, with a Statista survey revealing that over 40% of men in the UK never use sunscreen[18]. This disparity between knowledge and practice highlights a critical gap in public health messaging and behavior.
- Comprehensive Sun Protection Habits:Beyond sunscreen, a holistic approach to sun protection is vital, yet often underemphasized or inconsistent:
- Protective Clothing: Wearing long-sleeved shirts, pants, and wide-brimmed hats offers physical barriers against UV radiation, but these habits are not universally adopted, particularly in warmer climates or during recreational activities.
- Seeking Shade: Avoiding peak sun hours (typically 10 AM to 4 PM) and seeking shade is a simple yet effective strategy that many overlook.
- Avoiding Tanning Beds: Despite widespread warnings, indoor tanning remains a habit for a segment of the population, significantly increasing skin cancer risk.
- Early Detection: Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are critical for early detection of suspicious lesions. Many people are unaware of the warning signs of skin cancer or neglect self-checks.
The success of initiatives like Australia’s “Slip-Slop-Slap” campaign[19] provides a powerful case study. After decades of consistent public health efforts, melanoma incidence rates in Australians under 40 have begun to stabilize or decline[20]. This demonstrates that sustained, community-wide educational and behavioral interventions can effectively “bend the curve” of skin cancer incidence over time. In 2026, greater emphasis on accessible education, innovative public health campaigns, and making sun protection convenient (e.g., free sunscreen dispensers in public spaces) are crucial to bridge the gap between known effective strategies and public adherence.
How large is the global skincare market, and what key demographic and technological trends are driving its growth in 2026?
The global skincare market is experiencing robust growth in 2026, transforming into a powerhouse segment within the broader beauty industry. This booming market reflects a fundamental shift in consumer priorities, increasingly viewing skin care as an essential aspect of health, wellness, and self-expression rather than merely a cosmetic indulgence. The market’s trajectory is remarkable:
- Market Valuation and Growth Projection: The global skincare products market was valued at approximately $154.9 billion USD in 2023[21]. It is projected to reach an impressive $220.8 billion by 2029, demonstrating a substantial 6.1% compound annual growth rate (CAGR)[22]. This growth rate outpaces many other beauty segments, signaling significant investment and consumer demand.
Key Demographic and Technological Trends Driving Growth:
Several interconnected trends are fueling this expansion:
Demographic Shifts:
- Aging Global Population:The world is aging rapidly, particularly in regions like Asia, where 414 million people were aged 65 or older in 2020, a figure expected to triple to 1.2 billion by 2060[23]. As lifespans extend, the desire to maintain a youthful appearance and healthy skin drives significant demand for anti-aging products. The global anti-aging products market alone was valued at around $55.8 billion in 2023 and is forecast to reach $108.5 billion by 2033[24]. This near-doubling in a decade (approximately 6.9% CAGR) underscores the impact of this demographic trend.
- Broadening Skincare Demographics (Men & Gen Z):Skincare is moving beyond its traditional female-centric and Western-centric consumer base:
- Men’s Skincare: The men’s skincare market is burgeoning, projected to grow from $17.6 billion in 2025 to $37.3 billion by 2035, reflecting a robust ~10.5% annual growth rate[25]. Increased societal acceptance of male grooming, targeted product development, and sophisticated marketing are motivating men to adopt daily skincare routines that include cleansers, moisturizers, and sunscreens.
- Younger Generations (Gen Z & Millennials): Younger consumers are initiating skincare routines at an earlier age, often in their teens or early twenties, with a focus on preventative care (e.g., daily SPF, antioxidant serums) and addressing specific concerns like acne. Social media platforms, particularly TikTok, play a significant role in educating and influencing these demographics, turning skincare into a viral topic and driving trends.
- Rising Consumer Awareness and “Skin-First” Mindset:There’s a heightened awareness of skin health as integral to overall wellness. Consumers are increasingly informed, ingredient-savvy, and proactive about their skin’s condition, leading to a “skin-first” approach where they invest in products and routines that promise both immediate benefits and long-term health. This mindset is amplified by dermatologists and influencers leveraging social media to educate the public.
- Regional Leadership: Asia-Pacific:The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is the largest skincare market globally, holding the highest revenue share as of 2024[26]. This dominance is driven by factors such as a strong cultural emphasis on elaborate skincare routines (e.g., K-beauty, J-beauty with their multi-step regimens and innovative products like essences), a rapidly expanding middle class with increasing disposable income, and continuous innovation in product development within countries like South Korea and Japan. China also remains a significant growth engine.
Technological Innovations:
- AI-Powered Personalized Diagnostics and Skincare:Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how consumers receive skincare recommendations and products. Major brands like L’Oréal have launched AI-powered skin analyzers that scan for specific skin concerns (e.g., hydration, pigmentation, wrinkles) to recommend custom regimens[27]. L’Oréal’s *Perso* device, for example, combines AI analysis with a bespoke dispensing system to provide freshly mixed, personalized serums or moisturizers based on real-time data and environmental factors.This data-driven personalization eliminates guesswork, enhancing product efficacy and consumer satisfaction. By 2026, many consumers will have access to virtual skin assessments via apps or in-store kiosks, democratizing expert-level advice.
- At-Home Beauty Devices and Wearable Tech:The market is seeing an explosion of high-tech at-home devices that bring professional-grade treatments into consumers’ hands. This includes:
- LED Light Therapy Masks: Once confined to clinics, these devices use specific light wavelengths (e.g., blue for acne, red for collagen stimulation) for targeted skin improvements.
- Microcurrent and Radiofrequency (RF) Devices: Used for facial toning and skin tightening.
- Smart Skincare Tools: Bluetooth-enabled micro-needling devices with app guidance and progress tracking.
These gadgets empower consumers to monitor and improve their skin health with precision, offering convenience and potentially significant cost savings compared to frequent professional treatments.
- Advanced Ingredients and Nanotechnology:Innovation extends to the very formulations of skincare products. Nanotechnology is enabling the development of advanced ingredients:
- Nanoparticle-based Sunscreens: Offering superior UV protection without the traditional white cast or greasiness, improving user compliance[28].
- Encapsulated Actives: Retinol and vitamins are encapsulated in nano-carriers to improve penetration, enhance stability, and reduce irritation.
- Biotechnology: Lab-grown collagen, stem-cell conditioned media, and other bio-engineered compounds are being incorporated to boost skin repair and anti-aging benefits.
This blurring of lines between cosmetics and pharmaceuticals (cosmeceuticals) signifies a drive towards scientifically validated, high-performance products.
- Digital Dermatology (Teledermatology):Teledermatology, leveraging video consultations and image-based assessments, has expanded significantly, driven by the push for accessible healthcare. The global teledermatology market, valued at approximately $12.7 billion in 2025, is projected to soar to $57.4 billion by 2035, representing a four-fold increase and ~16% annual growth[29]. This makes dermatological expertise available to underserved populations and offers greater convenience for routine check-ups and prescription refills, further integrating technology into skin health management.
In conclusion, the global skincare market’s robust expansion in 2026 is a dynamic interplay of demographic shifts toward an older, more diverse, and more health-conscious consumer base, coupled with relentless technological innovation that offers personalized, precise, and accessible skincare solutions.
What are consumers demanding beyond product efficacy in 2026, and how is the skincare industry responding?
In 2026, consumer demands in the skincare industry have evolved significantly beyond mere product efficacy. A new era of conscious consumption dictates that brands must also align with values centered on environmental responsibility, ethical practices, transparency, and inclusivity. The industry is responding with a multifaceted strategy encompassing product formulation, packaging, marketing, and corporate social responsibility.
Evolving Consumer Demands:
- Clean Beauty and Ingredient Transparency:Consumers are increasingly wary of potentially harmful chemicals and seek “clean” formulations. A late-2023 global survey indicated that 63% of respondents considered “clean beauty” (safe, non-toxic ingredients) as extremely or very important in their purchasing decisions[30]. This drives demand for products free from parabens, sulfates, phthalates, synthetic fragrances, and other controversial ingredients. Transparency about ingredient sourcing, manufacturing processes, and the scientific rationale behind formulations is crucial for building trust. Consumers want to understand what they are putting on their skin.
- Sustainability and Eco-Consciousness:Environmental impact is a top concern. Consumers expect brands to demonstrate genuine commitment to sustainability:
- Reduced Plastic Packaging: A substantial 81% of consumers believe beauty brands should actively reduce plastic packaging[31]. This pushes for innovations like recyclable, refillable, or biodegradable packaging, and the introduction of solid formats (e.g., bar cleansers) to minimize waste.
- Cruelty-Free and Vegan: “Cruelty-free” status (no animal testing) is a baseline expectation for many, and there’s a growing preference for vegan formulations.
- Ethical Sourcing and Carbon Footprint: Demand for ingredients sourced ethically, with fair labor practices, and for brands to minimize their carbon footprint (e.g., through energy-efficient manufacturing or carbon-offsetting initiatives).
- Inclusivity and Diversity:The call for skincare that truly serves “all” skin types, tones, and demographics is louder than ever:
- Diversity in Formulations: Products are expected to perform effectively across a wide spectrum of skin tones, addressing concerns like hyperpigmentation which is more prevalent in skin of color, or ensuring sunscreens do not leave a white cast.
- Gender Neutrality and Men’s Skincare: The market is becoming less gender-specific, with a significant rise in men’s skincare. The global men’s skincare segment is growing at approximately 10.5% annually[32], driven by increased acceptance and tailored product offerings.
- Representation in Marketing: Advertising and branding are increasingly expected to feature diverse age groups, ethnicities, body types, and genders, reflecting the true breadth of the consumer base.
- Wellness and Self-Care Connection:Skincare routines are increasingly perceived as acts of self-care and moments for mental well-being. Consumers seek products and brands that offer not just physiological benefits but also a sense of ritual, relaxation, and emotional uplift. This ties into the broader “wellness” movement, where healthy skin is seen as an outcome of a healthy lifestyle.
- Social Media Influence and Educated Buyers:Social media has created a highly informed and discerning consumer base. Platforms like TikTok have popularized ingredient deep-dives, dermatologist recommendations, and peer reviews. Viral trends can rapidly elevate a brand’s status (e.g., CeraVe’s 82% sales jump in 9 months due to TikTok[33]) or, conversely, swiftly expose greenwashing or product failures. Consumers look for genuine endorsements and evidence-based claims.
Industry Response:
The skincare industry is adapting to these elevated demands in several ways:
- Reformulation and Certification: Brands are investing heavily in R&D to reformulate products, eliminating undesirable ingredients and seeking certifications (e.g., Ecocert, Leaping Bunny) to validate their clean and ethical claims. Many now offer detailed ingredient glossaries on their websites.
- Sustainable Packaging and Circular Economy Initiatives: Companies are introducing refillable packaging systems, using post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics, exploring alternative materials like glass or aluminum, and offering recycling programs for empties. Some are implementing “waterless” formulations or concentrates to reduce packaging and shipping weight.
- Broadening Product Lines and Inclusive Marketing: New product development now considers diverse skin concerns from inception. Brands are expanding shade ranges for tinted products, developing solutions for common issues in various skin tones (e.g., keloid scarring, specific hyperpigmentation patterns), and ensuring marketing campaigns authentically represent their global customer base.
- Emphasis on Holistic Wellness: Many brands now frame their products within a broader wellness narrative, highlighting rituals over rapid fixes. They may promote ingredients with adaptogenic properties, emphasize sensorial experiences, and even venture into “nutricosmetics” (supplements for skin health) to address beauty from within.
- Direct Engagement and Scientific Communication: Brands are actively engaging on social media, collaborating with dermatologists, cosmetic chemists, and credible influencers. They’re investing in educational content to explain ingredients and scientific benefits, and participating in real-time Q&A sessions to address consumer questions directly and transparently.
In essence, the skincare industry in 2026 is navigating a landscape where ethical, environmental, and inclusive practices are as crucial as product performance. Brands that successfully integrate these values into their core identity and operations are the ones poised for sustained success.
What notable examples illustrate the success of prevention and innovation in skin health?
Several notable examples from recent years highlight the significant impact of both preventive public health initiatives and technological innovation in shaping skin health outcomes and the industry’s landscape:
Successes in Prevention:
- Australia’s “Slip-Slop-Slap” Sun Safety Campaign (1981–Present):
- Initiative: Launched in 1981, the iconic “Slip-Slop-Slap” campaign (slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen, slap on a hat) was Australia’s response to its alarmingly high skin cancer rates. Over time, it expanded to include “Seek” shade and “Slide” on sunglasses. It became a deeply embedded cultural message.
- Outcome: This sustained, multi-decade public health effort is strongly associated with a demonstrable change in behavior and health outcomes. Epidemiologists have linked the campaign to a stabilization or decline in melanoma incidence rates among younger age groups in Australia[34]. Consistent sun-safe habits instilled through generations have effectively reduced the long-term risk of skin cancer. This exemplifies how consistent, accessible public health messaging can lead to cultural shifts and measurable improvements in population health.
- Cork City’s Free Sunscreen Dispensers Initiative (2025):
- Initiative: In the summer of 2025, Cork City Council in Ireland, in collaboration with health authorities, launched a pilot program installing free SPF 50 sunscreen dispensers in four popular public parks[35]. This proactive measure aimed to address rising skin cancer rates by making sun protection easily accessible and free for park visitors.
- Outcome: Though a recent initiative, initial reports indicated strong public uptake, particularly on sunny days. The program was praised for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness (only a few thousand euros to implement), especially when compared to the societal cost of treating skin cancers. Its success has spurred plans for expansion and inspired other municipalities. This case illustrates that innovative public health doesn’t always require high-tech solutions; sometimes, simply removing barriers to prevention (like cost or convenience) can have a significant impact on community health, positioning sun protection as a public amenity.
Triumphs in Innovation and Market Adaptation:
- L’Oréal’s AI-Powered Personalized Skincare Device (*Perso*):
- Initiative: Unveiled in 2020, L’Oréal’s *Perso* represents the cutting edge of AI and personalization in skincare. This smartphone-sized device uses artificial intelligence to analyze a user’s skin (via a selfie) to assess hydration, wrinkles, dark spots, and even environmental factors like local weather. It then dispenses a freshly mixed, customized dose of skincare (e.g., a moisturizer or serum) tailored to the individual’s specific, real-time needs[36].
- Outcome: While still evolving, *Perso* and similar AI-driven analysis tools have significantly enhanced customer engagement and satisfaction. L’Oréal reports that its AI-powered services have boosted online sales conversions for its brands[37]. This demonstrates how merging sophisticated technology with skincare fulfills a strong consumer desire for highly personalized and data-driven solutions, moving beyond generic products towards bespoke formulations.
- CeraVe’s TikTok-Fueled Rise to Global Prominence (2020):
- Initiative: CeraVe, a drugstore brand known for its ceramide-infused formulas, experienced an unprecedented surge in popularity largely due to viral content on TikTok and YouTube during the COVID-19 lockdowns. Influencers and dermatologists lauded its affordable, science-backed efficacy, leading to a grassroots social media phenomenon.
- Outcome: CeraVe’s sales surged by 82% in the first nine months of 2020 (year-over-year), leading to global sell-outs and significant expansion into new markets[38]. This case highlights the immense power of digital word-of-mouth and social media in disrupting the traditional beauty market. It proved that authenticity, scientific backing, and affordability, when amplified by credible online voices, can turn an unassuming brand into a global blockbuster, forcing established brands to rethink their digital engagement strategies.
These examples collectively demonstrate that both sustained public health efforts and rapid technological and market innovation are crucial drivers in the ongoing evolution of skin health, shaping consumer behavior, industry offerings, and ultimately, individual well-being.
| Trend Category | Specific Trend | Impact on Skin Health / Industry | Supporting Data / Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Health Burden | Rising DALYs from Skin Diseases | Increased recognition of skin conditions as a major non-fatal health loss. | 44.84 million DALYs globally in 2021 (up from ~41.6M in 2013)[1]. |
| Skin Cancer Epidemic | Increasing Incidence of Skin Cancer | Urgent need for effective prevention and early detection strategies. | 6.64 million global skin cancer cases in 2021, 1.94% annual increase since 1990[10]. |
| Prevention Gap | Insufficient Sun Protection Habits | Missed opportunities for significant risk reduction. | Only 12% of U.S. adults use sunscreen daily in 2025; 28% never use it[16]. |
| Market Growth | Booming Global Skincare Market | Driven by increased consumer awareness and prioritization of skin health. | Valued at ~$155 billion in 2023, projected to reach >$220 billion by 2029 (6% CAGR)[21]. |
| Demographic Drivers | Aging Population & Anti-Aging Demand | Significant investment in products to maintain youthful appearance. | Anti-aging market: $55.8B in 2023 to $108.5B by 2033[24]. |
| Demographic Drivers | Rise of Men’s Skincare | Expansion of consumer base beyond traditional demographics. | Men’s skincare market: $17.6B in 2025 to $37.3B by 2035 (10.5% CAGR)[25]. |
| Technological Innovation | AI & Personalized Skincare | More tailored and data-driven solutions for individual skin needs. | L’Oréal’s AI-powered skin analyzers; *Perso* device for custom formulations[27]. |
| Technological Innovation | Expansion of Teledermatology | Increased accessibility to expert dermatological care. | Market valued at ~$12.7B in 2025, forecast to reach $57.4B by 2035 (~16% annual growth)[29]. |
| Consumer Values | Demand for Clean & Sustainable Beauty | Brands must meet higher ethical and environmental standards. | 63% of consumers value “clean beauty”; 81% want reduced plastic packaging[30]. |
| Social Influence | Social Media’s Impact | Rapid trend adoption and increased consumer knowledge. | CeraVe’s sales jumped 82% post-TikTok virality[33]. |
This comprehensive overview of frequently asked questions underscores the dynamic landscape of skin health in 2026. The information presented here will serve as a foundational understanding as we transition to exploring specific preventive measures and future outlook in greater detail in the subsequent sections of this report.
References
- Skin Diseases Among Top Global Causes of Disability
- Global Burden of Skin Disease Representation in the Literature: Bibliometric Analysis – PMC
- Factors affecting health-related quality of life in patients with skin disease: cross-sectional results from 8,789 patients with 16 skin diseases | Health and Quality of Life Outcomes | Full Text
- Skin cancer – IARC
- Global, regional, and national trends in the burden of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer: insights from the global burden of disease study 1990–2021 | Scientific Reports
- Sunscreen reduces melanoma risk by 40 percent in young people – The University of Sydney
- Sunscreen Usage in 2025: Skepticism and Skincare Interest Shift Usage and Growth – CivicScience
- Skincare Market Global Outlook & Forecast 2024-2029: Global Skincare Market Projected to Reach USD 220.75 Billion by 2029 – ResearchAndMarkets.com
- Anti Aging Products Market Size & Share, Trends | Forecast 2033
- Anti Aging Products Market Size & Share, Trends | Forecast 2033
- Future of Skin Care: Innovations Transforming Health | Skin Inc.
- The Burden of Air Pollution on Skin Health: a Brief Report and Call to Action – PMC
- Clean Beauty Survey | Statistics & Insights | CleanHub
- Men’s Skincare Products Market Size & Share 2025-2035
- Inside Cerave’s marketing strategy, post-TikTok fame | Vogue
- Skin Diseases Among Top Global Causes of Disability
- Global Skin Disease Morbidity and Mortality: An Update From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 – PMC
- Global Burden of Skin Disease Representation in the Literature: Bibliometric Analysis – PMC
- Factors affecting health-related quality of life in patients with skin disease: cross-sectional results from 8,789 patients with 16 skin diseases | Health and Quality of Life Outcomes | Full Text
- Global, regional, and national trends in the burden of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer: insights from the global burden of disease study 1990–2021 | Scientific Reports
- Global, regional, and national trends in the burden of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer: insights from the global burden of disease study 1990–2021 | Scientific Reports
- Global, regional, and national trends in the burden of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer: insights from the global burden of disease study 1990–2021 | Scientific Reports
- Skin cancer – IARC
- Skin cancer – IARC
- Skin cancer – IARC
- Global burden of cutaneous melanoma in 2020 and projections to 2040 – IARC
- Sunscreen reduces melanoma risk by 40 percent in young people – The University of Sydney
- Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up – PubMed
- Sunscreen Usage in 2025: Skepticism and Skincare Interest Shift Usage and Growth – CivicScience
- Sunscreen Usage in 2025: Skepticism and Skincare Interest Shift Usage and Growth – CivicScience
- U.S.: attitudes towards sunscreen by gender 2024| Statista
- State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now – PMC
- State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now – PMC
- Skincare Market Global Outlook & Forecast 2024-2029: Global Skincare Market Projected to Reach USD 220.75 Billion by 2029 – ResearchAndMarkets.com
- Skincare Market Global Outlook & Forecast 2024-2029: Global Skincare Market Projected to Reach USD 220.75 Billion by 2029 – ResearchAndMarkets.com
- Skincare Market Outlook & Forecast Report 2024-2029 –
- Skincare Market Outlook & Forecast Report 2024-2029 –
- Anti Aging Products Market Size & Share, Trends | Forecast 2033
- Men’s Skincare Products Market Size & Share 2025-2035
- Teledermatology Market | Global Market Analysis Report – 2035
- Clean Beauty Survey | Statistics & Insights | CleanHub
- Clean Beauty Survey | Statistics & Insights | CleanHub
- Inside Cerave’s marketing strategy, post-TikTok fame | Vogue
- Global Burden of Skin Disease Representation in the Literature: Bibliometric Analysis – PMC
- Skin Diseases Among Top Global Causes of Disability
- Factors affecting health-related quality of life in patients with skin disease: cross-sectional results from 8,789 patients with 16 skin diseases | Health and Quality of Life Outcomes | Full Text
- Factors affecting health-related quality of life in patients with skin disease: cross-sectional results from 8,789 patients with 16 skin diseases | Health and Quality of Life Outcomes | Full Text
- The Burden of Air Pollution on Skin Health: a Brief Report and Call to Action – PMC
- The Burden of Air Pollution on Skin Health: a Brief Report and Call to Action – PMC
- Skincare Market Global Outlook & Forecast 2024-2029: Global Skincare Market Projected to Reach USD 220.75 Billion by 2029 – ResearchAndMarkets.com
- Skincare Market Global Outlook & Forecast 2024-2029: Global Skincare Market Projected to Reach USD 220.75 Billion by 2029 – ResearchAndMarkets.com
- Anti Aging Products Market Size & Share, Trends | Forecast 2033
- Anti Aging Products Market Size & Share, Trends | Forecast 2033
- Skincare Market Outlook & Forecast Report 2024-2029 –
- Future of Skin Care: Innovations Transforming Health | Skin Inc.
- Unveil Perso, The World’s First AI-Powered Device For Skincare And Cosmetics
- Future of Skin Care: Innovations Transforming Health | Skin Inc.
- Future of Skin Care: Innovations Transforming Health | Skin Inc.
- Teledermatology Market | Global Market Analysis Report – 2035
- State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now – PMC
- The effectiveness of a population-based skin cancer screening program: evidence from Germany – PubMed
- State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now – PMC
- Cork City Council and HSE Southwest Launch Free Sunscreen Dispensers in City Parks – Cork City Council
- Clean Beauty Survey | Statistics & Insights | CleanHub
- Clean Beauty Survey | Statistics & Insights | CleanHub
- Men’s Skincare Products Market Size & Share 2025-2035
- Inside Cerave’s marketing strategy, post-TikTok fame | Vogue
- State of the Science on Prevention and Screening to Reduce Melanoma Incidence and Mortality: The Time is Now – PMC
- Future of Skin Care: Innovations Transforming Health | Skin Inc.
- Future of Skin Care: Innovations Transforming Health | Skin Inc.
- Cork City Council and HSE Southwest Launch Free Sunscreen Dispensers in City Parks – Cork City Council
- Inside Cerave’s marketing strategy, post-TikTok fame | Vogue
