Contrave and Lisinopril Drug Interactions: Safe Combo?
Dr. Matthew Olesiak, MD, is the Chief Medical Director at SANESolution, a renowned wellness technology company dedicated to providing evidence-based solutions for optimal living. Dr. Olesiak earned his medical degree from the prestigious Jagiellonian University Medical College in Kraków, Poland, where he developed a strong foundation in medicine.
Contrave and Lisinopril are two widely prescribed medications with different therapeutic uses. What does Contrave do? Contrave is commonly used for weight loss, while Lisinopril is a medication that helps treat high blood pressure and other cardiovascular conditions.
However, like many other drugs, there is a need to understand how these medications interact to ensure patient safety. Drug interactions can lead to unwanted side effects, reduced effectiveness, or increased risks associated with certain health conditions.
This article explores the potential Contrave and Lisinopril Drug Interactions, their effects on blood pressure, and what patients should know before taking them together.
Key Takeaways
- Contrave and Lisinopril may interact in ways that affect blood pressure regulation, requiring medical supervision.
- Patients should be aware of potential side effects, including nausea, vomiting, and dizziness, which may be heightened by combining these drugs.
- Consulting a doctor before starting Contrave while on Lisinopril is essential to minimize health risks and ensure safe use.
What Are Contrave and Lisinopril?
Contrave is a combination of bupropion and naltrexone that is prescribed to assist with weight loss by reducing appetite and affecting brain pathways involved in hunger and cravings. Naltrexone belongs to the drug class known as opioid antagonists, while bupropion is categorized as an antidepressant.
It is often recommended for certain individuals struggling with obesity or those with a high body mass index (BMI) who have related health conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor frequently prescribed for managing high blood pressure, treating heart failure, and enhancing survival rates following a heart attack. By relaxing blood vessels, it helps lower blood pressure and reduces the strain on the heart.
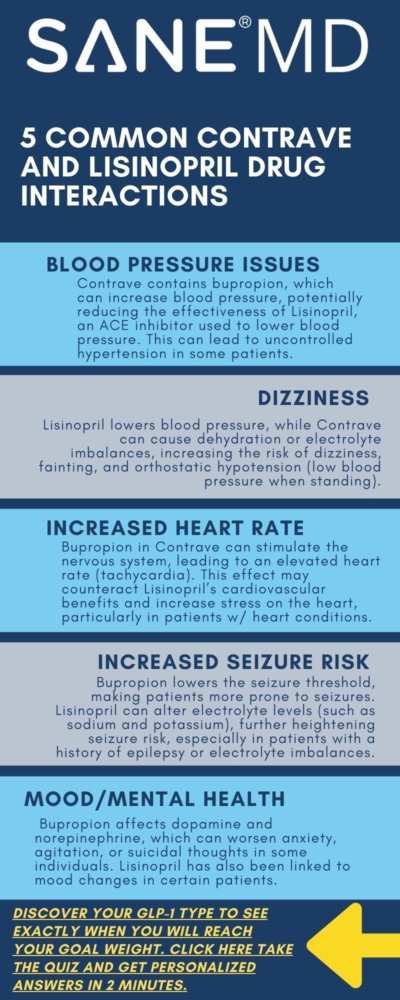
Potential Risks and Interactions Between Contrave and Lisinopril
| Interaction Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Blood Pressure Effects | Contrave (bupropion) can increase blood pressure, potentially counteracting Lisinopril’s effects. Monitoring is required. |
| Risk of Dizziness & Lightheadedness | Both drugs can cause dizziness, especially when standing quickly. Lisinopril lowers blood pressure, while Contrave may lead to dehydration. |
| Potential for Increased Heart Rate | Bupropion in Contrave may raise heart rate, counteracting Lisinopril’s cardiovascular benefits. Patients with heart conditions should be cautious. |
| Increased Risk of Seizures | Bupropion increases seizure risk, while Lisinopril can alter electrolyte levels, potentially worsening the risk. |
| Gastrointestinal Effects | Both drugs can cause nausea, vomiting, and digestive discomfort. Symptoms may be heightened when combined. |
| Mood & Mental Health Considerations | Bupropion can impact mood and increase suicidal thoughts. Lisinopril may also contribute to mood changes. |
| Alcohol Interaction | Alcohol can amplify side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and increased blood pressure. It also raises seizure risk with Contrave. |
| Other Drug Interactions | Contrave should not be combined with opioids, beta-blockers, or certain antidepressants. Lisinopril may interact with NSAIDs, lithium, and potassium supplements. |
How Do These Medications Interact?
Blood Pressure Considerations
Taking Contrave and Lisinopril together may result in fluctuations in blood pressure. Contrave, due to its bupropion component, can increase blood pressure, which may counteract the effects of Lisinopril. This can be particularly concerning for patients taking Lisinopril to treat high blood pressure.
Additionally, Lisinopril lowers blood pressure by dilating blood vessels, while bupropion can cause mild hypertensive effects. Patients with pre-existing high blood pressure should have their blood pressure closely monitored to ensure that the combination does not lead to dangerous fluctuations.
The renin-angiotensin system, which Lisinopril influences, plays a key role in blood pressure regulation by helping blood vessels contract or relax. On the other hand, bupropion, which affects dopamine and norepinephrine systems, can indirectly stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, potentially leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure.
This opposing mechanism makes it essential for patients taking both medications to have their blood pressure monitored regularly to prevent hypertensive crises or hypotensive episodes.
Risk of Dizziness and Lightheadedness
Patients combining these medications may experience dizziness or lightheadedness, particularly when standing up quickly. This is due to Lisinopril’s blood pressure-lowering effects, which may be exacerbated by Contrave’s potential to cause dehydration or electrolyte imbalances.
Dehydration can lead to a drop in blood pressure, which in turn increases the likelihood of dizziness and fainting. Patients are advised to stay well-hydrated and to avoid sudden movements when standing.
Furthermore, bupropion’s stimulant-like effects may contribute to dizziness, as it increases activity in the central nervous system, affecting balance and coordination. Patients who experience persistent dizziness should consult their doctor to adjust dosages or explore alternative medications that do not cause severe fluctuations in blood pressure.
Potential for Increased Heart Rate
Bupropion, a key ingredient in Contrave, can increase heart rate, potentially placing extra strain on the cardiovascular system when combined with Lisinopril. Since Lisinopril is meant to ease the burden on the heart by reducing blood pressure, the stimulating effects of bupropion on heart rate may counteract its benefits.
Patients with a history of heart conditions should consult their doctor before using these medications together to prevent cardiovascular complications.
Individuals with pre-existing tachycardia or arrhythmias should be particularly cautious, as bupropion can lead to palpitations and rapid heart rate. Medical attention should be sought immediately if a patient experiences an abnormally high heart rate or chest discomfort.
Deciding if Contrave is right for you demands careful consideration of these potential drug interactions.
Risks and Side Effects
Contrave drug interactions are many, including the following:
Increased Risk of Seizures
Bupropion has been linked to an increased risk of seizures, especially in patients with a history of seizure disorder. Since Lisinopril may alter electrolyte levels, particularly sodium and potassium, it could further predispose some patients to seizures.
Low sodium levels, also known as hyponatremia, can increase seizure risk, making it essential for patients to have their electrolyte levels monitored regularly.
Gastrointestinal Effects
Both medications may cause nausea, vomiting, and stomach discomfort. This combination could heighten the risk of severe stomach upset, especially when starting Contrave. Bupropion and naltrexone both act on the central nervous system, which can lead to nausea, while Lisinopril can cause digestive disturbances.
Patients experiencing persistent gastrointestinal side effects should consult their doctor to determine if dosage adjustments or alternative medications are necessary.
Mood and Mental Health Considerations
Patients with mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety should be cautious when taking Contrave and Lisinopril together. Bupropion, a component of Contrave, can interfere with mood regulation and may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts in some individuals.
Those with a history of depression should be closely monitored, particularly during the initial weeks of treatment. Lisinopril has also been reported to cause mood changes in some patients, further emphasizing the need for medical supervision.
Can You Drink Alcohol While Taking Contrave and Lisinopril?
Alcohol consumption while taking Contrave and Lisinopril is not recommended. Alcohol can interfere with the effectiveness of both drugs and increase the risk of side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and increased blood pressure.
Furthermore, alcohol use may increase the risk of seizures in patients taking Contrave. Since both medications affect blood pressure regulation, alcohol can compound these effects, leading to unpredictable fluctuations in blood pressure.
Patients are strongly advised to avoid alcohol or consume it in moderation only after discussing it with their healthcare provider.
Other Drugs That May Interact
Below are certain medicines that may also interact with Contrave:
Beta Blockers
Patients taking beta blockers alongside Lisinopril and Contrave should be cautious, as these medications affect heart rate and blood pressure regulation.
Beta blockers slow the heart rate, while Contrave can increase it, potentially leading to irregular heartbeat or cardiovascular stress.
Other Antidepressants
Taking Contrave with other antidepressants, including Wellbutrin SR, may increase the risk of side effects, including seizures and mood disturbances.
Certain antidepressants may also amplify the blood pressure-increasing effects of bupropion.
Opioid Medications
Since Contrave contains naltrexone, it blocks the effects of opioid-based medications, making them ineffective. This is especially relevant for individuals using opioids for pain management or opioid withdrawal treatment.
Patients currently on opioid therapy should not take Contrave without consulting their doctor, as this combination can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
Who Should Avoid This Drug Combination?
Patients with a history of liver problems, kidney disease, seizures, or heart conditions should consult a doctor before starting Contrave while on Lisinopril. The combination may also not be suitable for pregnant or breastfeeding individuals, as naltrexone and bupropion can pass into breast milk.
Individuals with uncontrolled high blood pressure or those at risk of cardiovascular events should be particularly cautious, as Contrave can elevate blood pressure.
Patients with a history of stroke, severe migraines, or metabolic disorders should also avoid combining these medications unless absolutely necessary.
Electrolyte imbalances caused by Lisinopril can heighten the risk of seizures, especially in patients predisposed to them due to bupropion’s effects.
A full assessment by a healthcare professional is essential before initiating this combination.
Alternative Weight Loss Options for Patients on Lisinopril
For patients who cannot take Contrave due to its interactions with Lisinopril, alternative weight loss treatments may be a safer option.
Several FDA-approved weight loss medications do not contain bupropion or naltrexone, making them more suitable for individuals with hypertension or heart-related conditions.
Other Prescription Medications
- Orlistat (Alli, Xenical): A lipase inhibitor that prevents fat absorption in the intestines, reducing overall caloric intake without affecting blood pressure or heart rate. Alli is an over-the-counter version of Orlistat.
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): A GLP-1 receptor agonist that promotes weight loss in certain individuals by regulating appetite and slowing digestion. It has been shown to lower blood pressure rather than increase it.
- Phentermine-Topiramate (Qsymia): A combination drug that suppresses appetite but must be used with caution in patients with hypertension.
Non-Prescription and Lifestyle Approaches
Patients on Lisinopril who wish to lose weight safely can benefit from lifestyle modifications, such as:
- Nutritional counseling: Reducing sodium intake can help control blood pressure while supporting weight loss.
- Regular physical activity: Moderate aerobic exercise, like brisk walking or swimming, can aid weight loss without putting excess strain on the cardiovascular system.
- Behavioral therapy: Working with a psychologist or dietitian to develop sustainable eating habits can improve long-term weight management.
Choosing a weight loss treatment tailored to individual medical needs ensures both safety and effectiveness.
Consulting a doctor before making changes to a medication regimen or diet plan is always recommended.
Monitoring and Safety Tips
- Regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial for patients taking both medications to detect any concerning changes early.
- Discuss any side effects with a doctor, particularly dizziness, nausea, or heart palpitations, to determine whether dosage adjustments are needed.
- Stop taking Contrave and seek medical advice if severe side effects such as irregular heartbeat, persistent vomiting, or suicidal thoughts occur.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When taking prescription medications such as Contrave and Lisinopril, it’s important to understand how they interact with other drugs.
Many patients wonder whether they can safely combine these medications, as both can affect blood pressure and other bodily functions.
Below are answers to some of the most common questions regarding Contrave, Lisinopril, and potential drug interactions.
1. Can you take Contrave with blood pressure medicine?
Contrave can be taken with blood pressure medication, but it requires careful monitoring. Contrave contains bupropion, which can increase blood pressure in some patients, potentially counteracting the effects of antihypertensive medications like Lisinopril.
Doctors typically assess a patient’s baseline blood pressure before prescribing Contrave, especially if they are already taking medication to treat high blood pressure.
If the combination is deemed necessary, regular blood pressure monitoring is advised to ensure safe use. Patients with uncontrolled hypertension may need an alternative weight-loss treatment to minimize cardiovascular risks.
2. Can Lisinopril be taken with bupropion?
Lisinopril can generally be taken with bupropion, but caution is required due to the potential for blood pressure fluctuations and increased heart rate. Bupropion can lead to mild increases in blood pressure and heart rate, while Lisinopril works to lower blood pressure. In some individuals, this can create a balancing effect, but in others, it may cause unpredictable cardiovascular responses.
Additionally, Lisinopril can alter electrolyte levels, which may heighten the risk of seizures in patients taking bupropion, particularly those with a seizure disorder or a history of brain injuries. A doctor should evaluate the risks versus benefits before prescribing these medications together.
3. What medications should I avoid with Contrave?
Certain medications should be avoided while taking Contrave due to the risk of dangerous interactions. Opioid medications, such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, or morphine, should not be taken with Contrave, as its naltrexone component blocks opioid effects, potentially leading to sudden withdrawal symptoms.
Other antidepressants, particularly monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) like phenelzine or tranylcypromine, should also be avoided due to the risk of hypertensive crisis and serotonin syndrome. Stimulants, such as amphetamine-based ADHD medications, may further increase heart rate and blood pressure, posing additional risks.
Patients should also be cautious with other drugs that affect mood or seizure threshold, including some antipsychotics and corticosteroids. Also, though not confirmed, Contrave and birth control drug interactions may occur, so you’ll need to be aware of this potential risk. Always consult a doctor before combining Contrave with other medications.
4. What medications should you avoid while taking Lisinopril?
Several medications should be avoided while taking Lisinopril to prevent potentially dangerous interactions. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen or naproxen, can reduce Lisinopril’s effectiveness and may increase the risk of kidney damage.
Potassium supplements and potassium-sparing diuretics, such as spironolactone, should also be used cautiously, as Lisinopril can lead to high potassium levels, which may cause heart complications. Lithium, a medication used for mood disorders, can become toxic when taken with Lisinopril, as the drug affects lithium’s clearance from the body.
Additionally, other blood pressure medications, particularly angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) or direct renin inhibitors, may cause excessive blood pressure drops or kidney dysfunction when combined with Lisinopril. Patients should always inform their doctor about all the medications they are taking to avoid adverse effects.
Conclusion
Understanding Contrave and Lisinopril drug interactions is essential for patients considering taking these medications together. While they can be prescribed together under medical supervision, patients must be mindful of potential risks, including increased blood pressure, gastrointestinal side effects, and mood changes.
Consulting a doctor or pharmacist before starting Contrave is necessary to ensure safe and effective treatment, particularly for individuals managing high blood pressure, seizures, or other conditions. Always follow the prescribed dosage and be aware of potential interactions with other medications to minimize health risks.