Can You Take Contrave and Qsymia Together: Understanding Drug Interactions

Contrave and Qsymia are both weight loss drugs prescribed for chronic weight management in adults struggling with obesity or weight-related conditions. While both medications have shown efficacy in promoting weight loss for compatible individuals, they contain different active ingredients that could interact negatively when taken together.
Clinical trials have shown the safety and effects of these medications, including observed visual field defects, which were found to be reversible after discontinuing the treatment.
In other words, in taking Contrave and Qsymia together, drug interactions can occur. Understanding the drug interactions, possible side effects, and potential risks of combining Contrave and Qsymia is crucial for patients considering these treatments.
Key Takeaways
- Combining Contrave and Qsymia may increase the risk of serious drug interactions, including high blood pressure, seizures, and mood changes.
- Both medications have different active ingredients that can affect the central nervous system, potentially leading to dizziness, blurred vision, and difficulty concentrating.
- Patients should consult their doctor or pharmacist before taking these weight loss drugs to minimize risks and closely monitor side effects.
Comparison of Contrave and Qsymia
| Category | Contrave | Qsymia |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredients | Bupropion, Naltrexone | Phentermine, Topiramate |
| Mechanism of Action | Reduces cravings, alters neural responses to food stimuli | Suppresses appetite, increases satiety |
| Common Side Effects | Dizziness, dry mouth, insomnia, mood changes, increased blood pressure, nausea | Increased heart rate, blurred vision, mood changes, dizziness, insomnia |
| Key Warnings | Not recommended for individuals with seizure disorders, eating disorders, or those on MAOIs | Not recommended for individuals with heart disease, seizures, or substance abuse hist |
What Are Contrave and Qsymia?
Contrave
Contrave is a prescription weight loss drug designed for chronic weight management in certain adults with obesity or overweight individuals who have weight-related conditions such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, or high cholesterol. It combines two active ingredients:
- Bupropion: A medication commonly used to treat depression and aid in smoking cessation. It also acts on the central nervous system, influencing dopamine and norepinephrine levels, which play a role in appetite regulation and mood changes. When used to treat depression, it is important to monitor for suicidal thoughts and behaviors during treatment, especially among young adults.
- Naltrexone: An opioid antagonist often prescribed to help individuals with alcohol or opioid dependence. In the context of weight loss, it affects brain reward pathways, reducing food cravings and reinforcing healthy eating habits.
How Contrave Works
By targeting both hunger signals and food cravings, Contrave helps patients reduce calorie intake while following a reduced-calorie diet and engaging in increased physical activity. Unlike stimulant-based weight loss drugs, it does not directly suppress appetite but instead alters neural responses to food-related stimuli.
Possible Side Effects of Contrave
Like many weight loss medications, taking Contrave may lead to adverse reactions.
Some common Contrave side effects include:
- Dizziness and difficulty concentrating
- Dry mouth and insomnia
- Mood changes, including depression, anxiety, and in rare cases, suicidal thoughts
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate
- Stomach pain, abdominal pain, and nausea
- Constipation: this side effect is so common that it’s often called Contrave constipation.
Do side effects of Contrave go away? You’ll be pleased to know that most of the minor side effects diminish after your body adjusts to the medication.
Patients with eating disorders, seizure disorders, or those taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) should avoid the weight management drug due to increased risks of Contrave drug interactions and severe side effects. Consulting a doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment is essential.
Qsymia
Qsymia is another prescription weight loss drug that combines two active ingredients:
- Phentermine: A stimulant that belongs to the sympathomimetic amine class. It works by increasing norepinephrine release, reducing appetite, and boosting energy levels, making it easier for patients to follow a reduced-calorie diet.
- Topiramate: Originally an anti-seizure medication, it also promotes weight loss by enhancing satiety, making food less appealing, and reducing binge eating behaviors.
How Qsymia Works
Qsymia affects multiple pathways, leading to a dual-action approach to weight loss:
- Phentermine’s stimulant effects reduce hunger and increase metabolism.
- Topiramate’s neurological impact helps patients feel fuller sooner and for longer periods.
Because phentermine topiramate influences both brain chemistry and metabolic function, Qsymia is considered one of the more effective weight loss drugs for chronic weight management for compatible individuals.
However, it requires careful monitoring due to potential drug interactions and side effects.
Possible Side Effects of Qsymia
Patients taking Qsymia may experience various side effects, including:
- Increased heart rate and high blood pressure
- Blurred vision, eye pain, and difficulty operating hazardous machinery
- Abdominal pain and stomach pain
- Mood changes, including depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts
- Dizziness, insomnia, and dry mouth
Due to its stimulant component, Qsymia is not recommended for individuals with a history of heart disease, seizures, or substance abuse. Patients should work closely with their doctor to determine the recommended dose and assess any adverse reactions.
Can You Take Contrave and Qsymia Together?
While both Qsymia and Contrave treatment are used for weight loss, taking them together can increase the risk of severe drug interactions.

These medications work on different pathways but share overlapping side effects, potentially leading to:
- Increased blood pressure and heart disease risks
- Mood changes, including depression, suicidal thoughts, and anxiety
- Risk of seizures, especially in patients with a history of epilepsy
- Dizziness, blurred vision, and difficulty concentrating, increasing the risk when operating hazardous machinery
How These Medications Interact
When considering Contrave and Qsymia together, it is essential to understand how their active ingredients interact within the body.
Since both medications influence different physiological pathways, they can create compounding effects that may lead to significant health risks.
These interactions primarily affect three major areas: cardiovascular health, the central nervous system (CNS), and the risk of seizures. Patients who have pre-existing conditions related to high blood pressure, heart disease, depression, or neurological disorders should be especially cautious.
Consulting a doctor before combining these weight loss drugs is crucial to minimize the risk of severe adverse reactions.
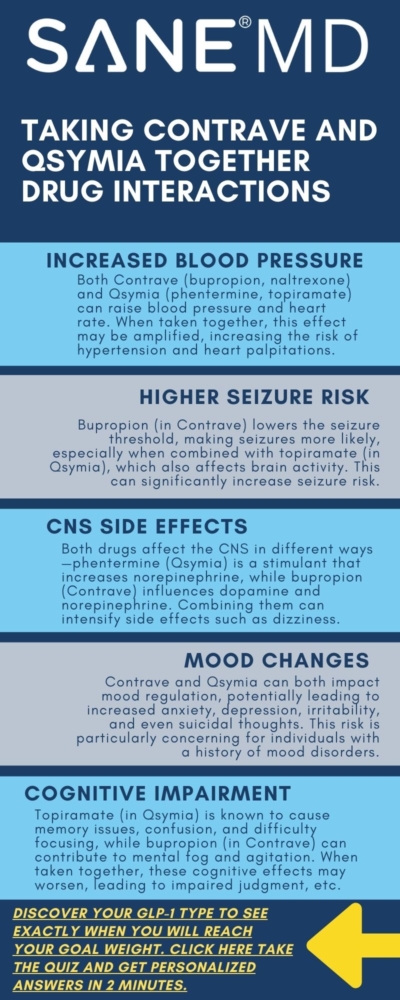
Effects on Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
One of the most concerning risks of combining Contrave treatment with phentermine topiramate in Qsymia is the impact on blood pressure and heart rate.
Both medications can stimulate the cardiovascular system, leading to:
- Increased blood pressure, which can elevate the risk of hypertension
- Chest pain, potentially signaling underlying heart disease
- Increased heart rate, which may contribute to cardiovascular complications
Patients with high blood pressure, heart disease, or those taking beta-blockers should avoid taking these medications together, as the combination may increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events.
Close monitoring of blood pressure and heart function is essential for anyone taking Contrave and Qsymia simultaneously.
Impact on the Central Nervous System
Both bupropion (from Contrave) and phentermine (from Qsymia) target the central nervous system, which can lead to neurological side effects when combined.
The simultaneous stimulation of the CNS may result in:
- Insomnia, making it difficult to fall or stay asleep
- Dizziness, which can impair physical activity and increase risks when operating hazardous machinery
- Mood changes, including increased anxiety, irritability, and depression
- Suicidal thoughts, particularly in patients with a history of mental health conditions
- Difficulty concentrating, which may affect work and daily activities
Because these drugs both affect neurotransmitter levels, they may also increase the risk of blurred vision and eye pain, further impacting day-to-day function.
If a patient experiences any of these symptoms, they should contact their doctor immediately.
Risk of Seizures
Combining Contrave and Qsymia may significantly increase the risk of seizures, especially in individuals with a personal or family history of epilepsy.
The following factors contribute to this increased risk:
- Bupropion in Contrave lowers the seizure threshold, making seizures more likely
- Phentermine topiramate in Qsymia also affects brain activity, which may compound the risk of seizures
- Patients using other drugs that influence neural function (such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications) may be at even greater risk
Those who have experienced seizures in the past should not take Contrave treatment and Qsymia together unless specifically approved and closely monitored by a doctor.
Possible Side Effects of Taking Contrave and Qsymia Together
The combined use of Contrave and Qsymia may lead to numerous adverse reactions.
Some of the most common side effects include:
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate, elevating the risk of heart disease
- Seizures, particularly in individuals with a history of neurological conditions
- Mood changes, including depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts
- Dizziness and blurred vision, which may interfere with daily activities
- Dry mouth and stomach pain, common among weight loss drugs
- Abdominal pain and joint pain, which may indicate an allergic reaction
- Eye pain and unusual changes in vision, potentially signaling a serious adverse reaction
Since these side effects can be severe, patients should carefully monitor their health and report any unusual symptoms to their doctor.
Proper medical supervision and periodic health checkups are essential when taking these medications for chronic weight management.
Contraindications and Warnings
When considering Contrave and Qsymia together, it is crucial to understand that not all patients are suitable candidates for these medications. Certain pre-existing medical conditions and other drugs can lead to severe adverse reactions, increasing the risk of heart complications, seizures, and mood changes.
Some individuals may face increased risks of high blood pressure, liver damage, or neurological issues when using these weight loss drugs.
Before starting treatment, patients should consult their doctor or pharmacist to assess whether these medications are safe for their specific health profile.
Below are the key groups of patients who should avoid taking Contrave and Qsymia together due to heightened health risks.
Who Should Avoid Taking These Drugs Together?
Patients with High Blood Pressure or Heart Disease
Since both Contrave and Qsymia can increase blood pressure and heart rate, individuals with hypertension or a history of heart disease should avoid combining these medications.
Taking Contrave and Qsymia together may elevate the risk of:
- Chest pain and heart palpitations
- Increased heart rate, which may worsen cardiovascular conditions
- High blood pressure, leading to a greater risk of stroke or heart attack
Patients with a history of heart disease should work closely with their doctor to determine safer alternatives for chronic weight management.
Individuals with a History of Seizures
People with a history of epilepsy or those at risk for seizures should avoid Contrave treatment, especially when combined with phentermine topiramate in Qsymia. Bupropion, one of the active ingredients in Contrave, is known to lower the seizure threshold, increasing the risk of seizures.
Additionally, topiramate in Qsymia can also impact neurological function, compounding the potential for seizure activity.
If a patient has previously experienced seizures, their doctor should explore alternative weight loss drugs that do not interfere with neurological stability.
Those Diagnosed with Eating Disorders (Such as Anorexia or Bulimia)
Patients with a history of eating disorders, particularly anorexia nervosa or bulimia nervosa, should not take Contrave. This is because bupropion has been shown to increase the risk of seizures in individuals with a history of disordered eating behaviors.
Additionally, using phentermine topiramate in Qsymia may suppress appetite to a dangerous extent, leading to malnutrition or worsening of disordered eating patterns.
For those with eating disorders, a doctor should be consulted for alternative treatments that support chronic weight management without increasing health risks.
Patients Currently Taking Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of antidepressant medications that interact dangerously with Contrave and Qsymia. Patients taking MAOIs, such as phenelzine or tranylcypromine, should avoid these weight loss drugs because the combination can cause:
- Dangerous spikes in blood pressure (hypertensive crisis)
- Severe mood changes, including increased risk of suicidal thoughts
- Increased heart rate, leading to cardiovascular complications
Patients should wait at least 14 days after stopping MAOIs before starting treatment with Contrave or Qsymia to prevent adverse reactions.
Those with Liver Damage or Severe Kidney Disease
Both Contrave and Qsymia are metabolized through the liver and kidneys, meaning patients with liver damage or severe kidney disease may be at increased risk of toxicity or impaired drug clearance.
These individuals may experience:
- Worsening liver function, increasing the risk of liver damage
- Reduced kidney function, leading to potential drug accumulation in the body
- Heightened side effects, including abdominal pain, joint pain, and blurred vision
Patients with liver disease or severe kidney impairment should speak with their doctor to find safer options for chronic weight management.
Final Considerations
For patients with any of the conditions above, the combination of Contrave and Qsymia may pose serious health risks.
A doctor should assess each individual’s medical history before prescribing weight loss drugs and consider alternative treatment plans that minimize drug interactions and adverse reactions.
Recommended Dose and Safety Precautions
Proper Dosage
Patients should follow the recommended dose for each medication and avoid self-medicating or combining low-dose forms without medical supervision.
Monitoring for Adverse Reactions
Patients should watch for adverse reactions, including chest pain, difficulty concentrating, blurred vision, and mood changes. If any of these occur, they should contact their doctor immediately.
Interactions with Other Drugs
When considering weight loss drugs like Contrave and Qsymia, it’s crucial to be aware of potential interactions with other medications. These interactions can lead to serious adverse reactions, including high blood pressure, seizures, and mood changes. Here are some key drug interactions to be mindful of:
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Combining Contrave with MAOIs can result in dangerous spikes in blood pressure, seizures, and severe mood changes. Patients should wait at least 14 days after stopping MAOIs before starting Contrave.
- Other Antidepressants: Taking Contrave with other antidepressants can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by high fever, agitation, and rapid heart rate.
- Antipsychotics: Combining Contrave with antipsychotic medications can heighten the risk of seizures and other adverse reactions, making it essential to consult a doctor before combining these drugs.
- Beta-Blockers: Using Contrave alongside beta-blockers can lead to increased blood pressure and other cardiovascular issues, necessitating close monitoring by a healthcare provider.
- Antiarrhythmics: The combination of Contrave with antiarrhythmic drugs can elevate the risk of seizures and other serious side effects.
- Ticlopidine and Clopidogrel: These medications, when taken with Contrave, can increase the risk of bleeding, requiring careful medical supervision.
- Ritonavir and Lopinavir: Combining these antiviral drugs with Contrave can lead to elevated blood pressure and cardiovascular complications.
- Efavirenz: This medication can increase the risk of seizures and other adverse reactions when taken with Contrave.
- Theophylline: The risk of seizures and other adverse reactions is heightened when Contrave is combined with theophylline.
- Corticosteroids: Using corticosteroids with Contrave can lead to increased blood pressure and other cardiovascular problems.
- Levodopa and Amantadine: These medications can increase the risk of seizures and other adverse reactions when taken with Contrave.
- Alcohol: Combining alcohol with Contrave can exacerbate high blood pressure, seizures, and other adverse reactions, making it important to avoid alcohol while on this medication.
Understanding these interactions is vital for safe and effective chronic weight management. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting or combining weight loss drugs with other medications.
Alternative Weight Loss Treatments
For those who cannot take Contrave or Qsymia due to interactions with other medications, there are several alternative weight loss treatments available. These options can help you achieve your weight loss goals while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): Originally used to treat type 2 diabetes, Liraglutide has been shown to aid in weight loss by regulating appetite and food intake.
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): Another medication initially developed for type 2 diabetes, Semaglutide helps with weight loss by mimicking a hormone that targets areas of the brain involved in appetite regulation.
- Phentermine/Topiramate (Qsymia): While Qsymia may not be suitable for everyone due to potential interactions, it remains an effective option for some patients under careful medical supervision.
- Orlistat (Alli, Xenical): This medication works by reducing the absorption of fat in the digestive system, helping patients lose weight when combined with a reduced-calorie diet.
- Bariatric Surgery: For those with severe obesity, bariatric surgery can be a highly effective option. This surgical procedure reduces the size of the stomach, limiting food intake and promoting significant weight loss.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthier lifestyle is a cornerstone of weight loss. This includes following a reduced-calorie diet, increasing physical activity, and making sustainable changes to eating habits.
It’s essential to discuss these alternative treatments with your doctor to understand the potential risks and benefits. Your healthcare provider can help you determine the best weight loss strategy tailored to your individual health needs and medical history.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
As patients explore weight loss medications like Contrave and Qsymia, many have concerns about potential drug interactions and safety risks.
Below are answers to some of the most common questions regarding the use of Contrave treatment, phentermine-topiramate, and other medications.
Understanding these interactions is essential for chronic weight management and minimizing potential side effects.
1. Can you take Qsymia and Contrave together?
It is not recommended to take Qsymia and Contrave together due to their overlapping effects on blood pressure, heart rate, and the central nervous system. Both medications influence appetite suppression and cravings through different mechanisms, but when combined, they can increase the risk of severe side effects, such as high blood pressure, seizures, mood changes, and suicidal thoughts.
Additionally, both drugs can cause dizziness, blurred vision, and difficulty concentrating, making it dangerous to engage in activities like operating hazardous machinery.
Patients considering combining these drugs should consult their doctor immediately to discuss safer alternatives.
2. Can I take topiramate and Contrave together?
Taking topiramate (an ingredient in Qsymia) and Contrave together is generally not advised unless under strict medical supervision. Topiramate is known to affect cognitive function, which, when combined with bupropion in Contrave, could increase the risk of difficulty concentrating, dizziness, and mood changes.
Additionally, both medications have been linked to increased blood pressure and seizures, particularly in patients with pre-existing neurological conditions. If a doctor prescribes both medications, they may start with a low dose and closely monitor for adverse reactions.
3. Can you take phentermine and Contrave together?
Combining phentermine (the stimulant in Qsymia) with Contrave is generally not recommended due to its effects on the central nervous system and cardiovascular system.
Phentermine increases heart rate and blood pressure, which, when taken alongside bupropion and naltrexone in Contrave, could significantly increase the risk of chest pain, hypertension, and seizures. Furthermore, both drugs can contribute to insomnia, anxiety, and mood changes, potentially leading to suicidal thoughts in vulnerable patients.
Those interested in using both medications should consult a doctor to explore safer chronic weight management options.
4. What medications should not be taken with Contrave?
Several other medications can negatively interact with Contrave, leading to potentially serious adverse reactions.
Patients should avoid taking Contrave with:
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) – Can lead to dangerous spikes in blood pressure and severe drug interactions.
- Opioid medications – Since Contrave contains naltrexone (an opioid antagonist), it can block the effects of opioids and trigger withdrawal symptoms.
- Beta-blockers and blood pressure medications – Combining these drugs may lead to increased blood pressure or reduced effectiveness of blood pressure control.
- Seizure medications – Since bupropion lowers the seizure threshold, it should not be taken with drugs like phenytoin or carbamazepine, which also affect neurological stability.
- Alcohol – Consuming alcohol while taking Contrave can worsen dizziness, depression, and mood changes, increasing the risk of suicidal thoughts.
To prevent severe interactions, patients should discuss their current medications with a doctor or pharmacist before starting Contrave treatment.
Conclusion
Taking Contrave and Qsymia together is not typically recommended due to increased risks of high blood pressure, seizures, and drug interactions. Patients should discuss their weight loss options with a doctor or pharmacist before combining these medications.
Proper medical supervision and lifestyle changes are key to safe and effective chronic weight management.

Can You Take Gabapentin and Contrave Together? Risks & Warnings

Contrave (a combination of bupropion and naltrexone) is a prescription weight-loss drug used to help compatible individuals with obesity or weight-related medical conditions. Gabapentin, on the other hand, is commonly prescribed to treat seizures and nerve pain. While both medications have their respective uses, there are possible Contrave and Gabapentin drug interactions when taken together.
Patients should also be aware that Contrave may cause severe allergic reactions. If any symptoms of a severe allergic reaction occur, they should stop taking Contrave and seek immediate medical help.
Patients considering taking Contrave alongside gabapentin should be aware of the risks, side effects, and necessary precautions to avoid severe health complications.
Key Takeaways
- Contrave and Gabapentin Drug Interactions: Combining these medications may increase the risk of seizures, dizziness, and other serious side effects.
- Potential Health Risks: Patients with high blood pressure, liver damage, or a history of eating disorders should consult a doctor before taking Contrave.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Dose adjustment may be required, especially for patients with preexisting conditions or those taking other medications.
Understanding Contrave and Gabapentin
What is Contrave?
Contrave is a prescription weight loss medication designed to aid certain individuals struggling with obesity or weight-related medical conditions.
Contrave is prescribed for adults with an initial body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater, or those with a BMI of 27 or more if they have additional weight-related health issues.
It contains two active ingredients, bupropion and naltrexone, which work synergistically to help control appetite and reduce food cravings.
How Bupropion Works
Bupropion is an atypical antidepressant used to treat depression and aid smoking cessation. It influences the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can help improve mood, reduce cravings, and increase energy levels. As a stimulant-like antidepressant, bupropion may also enhance motivation and alertness, factors that can contribute to a more active lifestyle during a weight loss regimen.
However, bupropion has been associated with an increased risk of seizures, especially at high doses or in individuals with a history of seizure disorder, eating disorders, or excessive alcohol consumption. Because of this, it is crucial for patients taking Contrave to follow prescribed dosage instructions carefully.
How Naltrexone Works
Naltrexone is primarily used for opioid withdrawal and alcohol dependence treatment. It works by blocking opioid receptors in the brain, reducing the pleasurable effects of alcohol and opioids. In Contrave, naltrexone is believed to modify reward pathways associated with food consumption, helping individuals curb cravings for high-calorie foods.
Naltrexone also affects appetite regulation by interacting with the hypothalamus, the part of the brain responsible for hunger and satiety. Decreasing the brain’s reward response to food helps reinforce long-term eating behavior changes for compatible individuals.
How Contrave Supports Weight Loss Compared to Other Weight Loss Drugs
By combining bupropion and naltrexone, Contrave helps manage appetite, cravings, and emotional eating. However, its effectiveness depends on adherence to a reduced-calorie diet and physical activity. Clinical trial data has shown that patients taking Contrave lose more weight compared to those in the placebo group, though side effects such as nausea, dizziness, and insomnia are common.
Additionally, Contrave drug interactions are common, including medications for high blood pressure, heart disease, and seizures, necessitating caution for individuals with preexisting health conditions. Because of the presence of bupropion, individuals with bipolar disorder should also consult their doctor before starting Contrave to assess the risk of mood disturbances.
Contrave and Gabapentin Drug Interactions: Risks & Effects
Medication Overview
| Category | Contrave | Gabapentin | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medication Type | Weight loss drug containing bupropion & naltrexone | Anticonvulsant used for seizures, nerve pain, and anxiety | Increased risk of neurological side effects |
| Primary Use | Aids weight loss by controlling appetite | Treats seizures, nerve pain, and anxiety | Can cause overlapping effects on the nervous system |
| Seizure Risk | Bupropion lowers seizure threshold | Helps prevent seizures but sudden withdrawal may trigger them | Higher seizure risk, especially in those with neurological disorders |
| CNS Effects | May cause restlessness, insomnia, or agitation | Can cause drowsiness and dizziness | May result in confusion, cognitive impairment, and slowed reflexes |
| Liver & Kidney Impact | Metabolized in the liver, affects enzyme activity | Excreted through the kidneys, caution in renal impairment | Possible drug accumulation, increasing toxicity risk |
| Mood & Mental Health Risks | May contribute to mood swings, suicidal thoughts | Linked to depression, suicidal ideation | Combined use may worsen mental health symptoms |
| Dizziness & Motor Impairment | Increases alertness but can cause anxiety | May cause dizziness, slowed reflexes | Risk of falls, impaired motor coordination |
| Drug Absorption & Metabolism | Affected by high-fat meals and liver enzymes | Absorption reduced by antacids | Timing of doses and food intake may affect drug effectiveness |
| Alcohol & Sedative Interactions | Should not be taken with alcohol or sedatives | Increases sedative effects when combined with alcohol | High risk of excessive sedation and respiratory depression |
| Who Should Avoid? | Those with seizure disorders, eating disorders, or uncontrolled hypertension | Patients with kidney disease, history of substance misuse | Individuals with existing neurological or metabolic conditions should consult a doctor |
What is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication primarily prescribed to treat seizures and nerve pain. It is also used for treating insomnia, bipolar disorder, and anxiety, as it has sedative effects that can help calm an overactive nervous system. Although it is not classified as a controlled substance, it has the potential for misuse due to its calming and pain-relieving properties.
How Gabapentin Works
Gabapentin affects the brain by altering calcium channel activity in nerve cells, helping to stabilize electrical signals and prevent seizures. While it does not interact with the brain’s major neurotransmitters in the same way as traditional psychiatric medications, it has been found to reduce nerve excitability, making it useful for treating conditions like neuropathic pain and anxiety.
Gabapentin also enhances the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and reduces nerve pain. Because of this, it is sometimes prescribed off-label to treat insomnia and anxiety disorders.
Common Uses of Gabapentin
- Seizure control: Often used in combination with other medications to prevent seizures in patients with epilepsy or other seizure disorders.
- Neuropathic pain relief: Frequently prescribed for nerve pain caused by diabetes, shingles, or spinal cord injuries.
- Bipolar disorder and mood stabilization: While not a first-line treatment, some doctors prescribe gabapentin off-label to help treat depression and bipolar disorder, particularly when mood instability is a concern.
- Anxiety and sleep disorders: Gabapentin’s sedative effects make it beneficial for individuals experiencing insomnia, stress, or anxiety.
Risks and Side Effects
Although gabapentin is widely used and generally considered safe, it can affect brain function and lead to side effects such as:
- Dizziness and drowsiness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Skin rash
- Memory problems and difficulty concentrating
- Suicidal thoughts (a rare but serious risk that requires monitoring). If you experience any concerning symptoms, contact the Suicide and Crisis Lifeline.
Because gabapentin can increase the risk of central nervous system depression, it should be used cautiously alongside other drugs that cause sedation, such as opioids, benzodiazepines, or alcohol. Patients should also be aware of possible interactions with over-the-counter medications and discuss all other medications they are taking with their healthcare provider.
Gabapentin is not recommended for individuals with liver damage or significant liver problems, as it is metabolized in the kidneys and requires careful dose adjustment in those with kidney disease. Additionally, abrupt discontinuation of gabapentin can increase the risk of withdrawal symptoms, including anxiety, insomnia, and, in severe cases, seizures.
Possible Interactions Between Contrave and Gabapentin
When taken together, Contrave and gabapentin can result in several possible interactions that may increase health risks. Since both medications affect brain activity, the central nervous system (CNS), mood, and organ function, their combination requires careful monitoring.
While Contrave is primarily prescribed for weight loss, its active ingredient bupropion is known to increase the risk of seizures and alter mood. Similarly, gabapentin, used to treat seizures and nerve pain, impacts nerve signaling and can contribute to drowsiness, cognitive impairment, and dizziness.
Because of these overlapping effects, patients should be aware of how Contrave interacts with gabapentin and the potential for serious side effects, including seizures, mood disturbances, and liver damage. Clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Contrave and Gabapentin, highlighting the importance of controlled studies in understanding their interactions.
Below is a breakdown of the most significant concerns when combining these two medications.
Increased Risk of Seizures in Patients with Seizure Disorder
One of the most serious risks of Contrave and gabapentin drug interactions is an increased risk of seizures.
- Bupropion, an ingredient in Contrave, is known to lower the seizure threshold, meaning that it makes the brain more prone to experiencing seizure activity.
- Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant, often used to treat seizures, but it also alters nerve activity and neurotransmitter function. In some cases, gabapentin withdrawal or abrupt dose changes can trigger seizures in individuals without a prior seizure disorder.
- When taking Contrave and gabapentin together, there may be a higher risk of seizures, especially in patients with preexisting neurological conditions, bipolar disorder, eating disorders, or those who suddenly stop drinking alcohol.
- Increased risk is also noted in patients who take other medications that affect the brain’s electrical activity, such as nicotine replacement therapies, opioid withdrawal treatments, or mood stabilizers.
To minimize this risk, patients should consult their healthcare provider about potential dose adjustments, particularly if they have a history of seizure disorder or liver damage or are using over-the-counter supplements that may further affect neurological stability.
Central Nervous System (CNS) Effects
Both Contrave and gabapentin influence the central nervous system, and taking them together may increase the risk of severe side effects such as:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Cognitive impairment (difficulty concentrating, confusion, and memory issues)
- Slower reflexes and motor impairment
Because of these effects, patients taking Contrave and gabapentin should avoid driving or operating heavy machinery, as the combination can affect coordination and mental alertness. Contrave and Oxycodone drug interactions can also occur. Basically, any drug that affects the central nervous system may interact with Contrave, and this should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
Additionally, these medications may intensify the effects of alcohol, leading to more significant sedation, increased dizziness, and a higher risk of falls or accidents. Patients should not drink alcohol while taking these medications to avoid compounding their CNS effects.

Liver and Kidney Health Risks
Patients with liver problems or kidney disease should use caution when taking Contrave and gabapentin together.
- Contrave interacts with liver enzymes, which play a key role in metabolizing bupropion and naltrexone.
- Gabapentin is primarily excreted through the kidneys, meaning patients with kidney impairment may experience a toxic buildup of the drug in their system.
- Liver damage or liver problems can slow drug metabolism, leading to higher concentrations of both Contrave and gabapentin in the bloodstream. This can increase the risk of serious side effects, such as nausea, dizziness, skin rash, and confusion.
- Patients should undergo regular lab tests to assess liver function, and doctors may recommend a dose adjustment to prevent dangerous drug accumulation.
Those with a history of high-fat meals should also be cautious, as consuming excessive fat while taking Contrave may increase the risk of adverse effects by altering drug absorption rates.
Mood and Mental Health Effects
Patients with depression, bipolar disorder, or anxiety should be aware that Contrave and gabapentin may contribute to mood changes, including:
- Suicidal thoughts (especially in young adults)
- Increased risk of depression
- Mood swings and irritability
- Anxiety or panic attacks
Since bupropion is an antidepressant, it affects dopamine and norepinephrine levels, which can increase the risk of agitation or emotional instability. Similarly, gabapentin has been linked to depression and suicidal thoughts, particularly in patients with underlying mental health conditions.
Young adults taking these medications should be closely monitored for changes in mood or behavior, and patients with a history of bipolar disorder should consult a doctor before starting Contrave to evaluate the risk of mood destabilization.
Additionally, those taking methylene blue (used for certain medical conditions) may experience possible interactions affecting serotonin levels, potentially leading to serious side effects such as confusion, rapid heart rate, and excessive sweating.
Interaction with Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Contrave may interact with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), a class of antidepressants commonly prescribed to treat depression and anxiety. Examples of SSRIs include fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), paroxetine (Paxil), and fluvoxamine (Luvox).
When taken together, Contrave and SSRIs can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition caused by excessive levels of serotonin in the body.
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include agitation, confusion, rapid heart rate, changes in blood pressure, dilated pupils, loss of muscle coordination or twitching muscles, muscle rigidity, heavy sweating, diarrhea, headache, shivering or shaking, and goosebumps.
If you are taking Contrave and an SSRI, your doctor may need to monitor you closely for signs of serotonin syndrome to ensure your safety.
Interaction with Certain Beta-Blockers
Contrave may interact with certain beta-blockers, which are medications used to treat high blood pressure and other heart conditions. Examples of beta-blockers that may interact with Contrave include propranolol (Inderal), metoprolol (Lopressor), atenolol (Tenormin), and nadolol (Corgard). Combining Contrave with these beta-blockers can raise the risk of side effects such as low blood pressure, slow heart rate, fatigue, dizziness, and lightheadedness.
If you are taking Contrave and a beta-blocker, your doctor may need to monitor you closely for signs of these side effects. Regular check-ups and communication with your healthcare provider are essential for effectively managing your blood pressure and overall health.
Interaction with Supplements
Contrave may interact with certain supplements, including St. John’s Wort, ginseng, guarana, and yerba mate. These supplements can increase the risk of side effects from Contrave, such as increased heart rate, high blood pressure, anxiety, and insomnia.
If you are taking Contrave and any supplements, it is crucial to inform your doctor or pharmacist. They can help you understand the potential interactions and adjust your treatment plan accordingly to ensure your safety and well-being.
Interaction with Food
Contrave may interact with certain foods, particularly high-fat foods and grapefruit or grapefruit juice. Consuming high-fat foods while taking Contrave can increase the level of the drug in your body, raising the risk of side effects. Similarly, grapefruit and grapefruit juice can also elevate the levels of Contrave in your system, leading to an increased likelihood of adverse effects.
To minimize these risks, it is advisable to follow your healthcare provider’s dietary recommendations and avoid high-fat meals and grapefruit products while taking Contrave.
Interaction with Vaccines
Currently, there are no reports of Contrave interacting with vaccines. However, it is always a good practice to inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the medications and supplements you are taking before receiving a vaccine.
This ensures that your healthcare provider can make informed decisions about your treatment and vaccination plan, minimizing the risk of any potential interactions.
Interaction with Lab Tests
Bupropion, one of the active ingredients in Contrave, may cause a false-positive result for amphetamines on a urine drug test. A false-positive means the test shows a positive result for a drug that is not actually present. Before having a urine drug test for amphetamines, be sure to tell your doctor that you are taking Contrave.
This information can help prevent misinterpretation of your test results and ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Risks and Warnings
Who Should Avoid This Combination?
Patients with the following health conditions may be at higher risk when taking both medications:
- Seizure disorder
- Eating disorders (as bupropion increases seizure risk)
- Severely high blood pressure
- Liver damage or liver problems
- Bipolar disorder
- Heart disease or a history of heart attack
Interactions with Other Medications
Patients taking Contrave should inform their healthcare provider about all other medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Some possible interactions include:
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): Combining these with bupropion can lead to dangerously high blood pressure.
- Methylene blue: May interact with Contrave, leading to serotonin syndrome.
- Nicotine replacement therapies: May increase the risk of seizures.
- Other drugs that affect liver function, increasing toxicity risks.
Common Side Effects
Side Effects of Contrave
Contrave side effects may include:
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Insomnia
- High blood pressure
- Increased risk of seizures
- Suicidal thoughts
Side Effects of Gabapentin
Patients taking gabapentin may experience:
- Drowsiness
- Skin rash
- Dizziness
- Other side effects affecting coordination
- Increased risk of suicidal ideation
Stopping the Medication
Patients should not stop taking either Contrave or gabapentin suddenly. Doing so may lead to withdrawal symptoms, including seizures, nausea, and suicidal thoughts.
A healthcare provider should oversee the treatment transition to prevent adverse effects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When taking Contrave, bupropion, gabapentin, and naltrexone, it is important to understand their potential drug interactions, side effects, and how they can impact treatment.
Below are comprehensive answers to commonly asked questions regarding these medications and their safety.
1. Can I take bupropion and gabapentin together?
Bupropion and gabapentin can be taken together, but this combination requires caution due to the potential increased risk of seizures. Bupropion, an active ingredient in Contrave, is known to lower the seizure threshold, making individuals more susceptible to seizure activity, particularly those with a history of eating disorders, bipolar disorder, or excessive alcohol consumption.
Gabapentin, while used to treat seizures, can also affect nerve signaling and brain activity in a way that may increase the risk of neurological side effects when combined with bupropion. These effects include dizziness, confusion, drowsiness, and cognitive impairment, which can interfere with daily activities.
Anyone considering using these medications together should consult their doctor for proper dose adjustment and risk assessment.
2. What medications should not be taken with Contrave?
Several medications should not be taken with Contrave, as they can lead to severe interactions or reduce their effectiveness. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), such as phenelzine and isocarboxazid, should be avoided, as they can cause dangerously high blood pressure when combined with bupropion. Opioid-containing medications should also not be used, as naltrexone in Contrave blocks opioid effects and can trigger sudden opioid withdrawal symptoms.
Certain antidepressants, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), may interact with Contrave and increase the risk of serotonin syndrome and suicidal thoughts, especially in young adults.
Additionally, blood pressure medications and other drugs that affect the central nervous system, such as seizure medications, require careful consideration to avoid increased risk of side effects. For example, Contrave and Losartan drug interactions can seriously impact blood pressure.
To prevent potential complications, patients should inform their healthcare provider about all other medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs. They should also consult their healthcare provider about other weight loss drugs that may be suitable alternatives to Contrave.
3. Can naltrexone and gabapentin be used together?
Naltrexone and gabapentin can be used together, but patients should be closely monitored for potential side effects. Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, does not have a direct interaction with gabapentin, but their combined use may increase the risk of dizziness, drowsiness, and cognitive impairment.
Individuals with a history of liver damage should use caution, as both medications can affect liver metabolism, potentially leading to toxicity or reduced drug clearance.
Additionally, naltrexone’s effect on the brain’s reward system may impact the mood-stabilizing properties of gabapentin, which is sometimes used off-label for anxiety and bipolar disorder. Patients taking both medications should follow their prescribed dosages carefully and report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider.
4. What cannot be mixed with gabapentin?
Gabapentin should not be combined with alcohol, opioids, sedatives, benzodiazepines, or certain over-the-counter medications, as these combinations can lead to dangerous central nervous system depression. Alcohol intensifies the sedative effects of gabapentin, increasing the likelihood of drowsiness, dizziness, and cognitive impairment, which may impair coordination and reaction time.
Opioids such as oxycodone and hydrocodone should also be avoided, as their interaction with gabapentin can result in respiratory depression and potentially fatal overdose. Sedatives and benzodiazepines, including lorazepam and diazepam, may amplify gabapentin’s effects, making users excessively drowsy or confused.
Over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine can further contribute to sedation, leading to an increased risk of falls and accidents. Patients should also be aware that taking antacids within two hours of gabapentin can reduce its effectiveness by interfering with absorption.
5. Does naltrexone interact with gabapentin?
Naltrexone does not have a direct pharmacological interaction with gabapentin, but both medications can cause similar side effects, such as dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea. Individuals taking both drugs should be cautious when performing tasks that require alertness, as cognitive impairment may occur.
In rare cases, naltrexone has been associated with mood changes, including depression and suicidal thoughts, which may be exacerbated by gabapentin in certain individuals. This is particularly relevant for patients with a history of bipolar disorder, anxiety, or severe depression.
Those taking both medications should notify their doctor if they experience worsening mood symptoms, unusual fatigue, or excessive sedation.
If you have any further questions regarding Contrave, gabapentin, naltrexone, or bupropion, consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Final Thoughts
Patients considering taking Contrave alongside gabapentin should consult their healthcare provider to assess the risks and possible interactions. Given the increased risk of seizures, dizziness, and liver damage, close monitoring is essential.
Always follow the medication guide, undergo necessary lab tests, and stay informed about potential side effects.

Contrave and Topamax Together Drug Interactions: Dangerous?

Contrave and Topamax together are two prescription drugs used to treat obesity and other health conditions. Some patients seek to combine these weight loss drugs for enhanced results, but drug interactions can increase the risk of severe side effects.
Contrave drug interactions are common with hundreds of medications, including Topamax. Understanding how taking Contrave and Topamax Together can lead to drug interactions is crucial for patient safety.
Key Takeaways
Taking Contrave and Topamax together may lead to serious drug interactions, requiring medical supervision:
- Potential Risks: Combining these medications can increase the risk of seizures, mood changes, and metabolic imbalances.
- Mechanism of Interaction: Both drugs influence the central nervous system, potentially amplifying neurological effects and altering drug metabolism.
- Medical Supervision Needed: Patients should tell their doctor before taking these medications together to ensure safety and appropriate monitoring.
What is Contrave?
Contrave is a prescription drug designed to treat obesity by helping compatible individuals manage body weight. Body mass index (BMI) is a critical factor in determining treatment dosages for weight management medications like Contrave. It contains two active ingredients: bupropion and naltrexone.
Bupropion, also marketed as Wellbutrin XL, is an antidepressant that can treat depression by affecting dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, which also helps decrease appetite. Naltrexone, originally used for opioid and alcohol dependence, can reduce food cravings.
To maximize the weight loss benefits of Contrave, patients must follow a reduced-calorie diet and engage in regular exercise. However, Contrave interacts with other drugs, so it is essential to tell your doctor about all medications taken.
What is Topamax?
Topamax (topiramate) is a combination drug primarily used for seizure disorder and migraine prevention. It is also prescribed off-label for weight loss for certain individuals due to its appetite-suppressing effects.
Topamax works by influencing neurotransmitters like gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate, which regulate brain activity and appetite control. However, Topamax can interact with other medications, leading to serious drug interactions, including an increased risk of seizures.
Because Topamax affects brain function, its interaction with Contrave raises concerns about possible interactions and potential health risks.
Potential Risks and Recommendations for Taking Contrave and Topamax Together
| Interaction Type | Effect When Combined | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Seizure Risk | Increased seizure risk due to bupropion lowering seizure threshold and Topamax altering brain chemistry. | Avoid use if history of seizures; medical supervision required. |
| Cognitive and Psychiatric Effects | Mood instability, depression, anxiety, cognitive dulling, memory issues, and increased risk of suicidal thoughts. | Monitor mood and cognitive changes; consult healthcare provider for worsening symptoms. |
| Metabolic and Electrolyte Imbalances | Dehydration, kidney stones, metabolic acidosis, electrolyte imbalances, and low blood sugar levels. | Stay hydrated, monitor blood sugar and electrolytes, and follow dietary recommendations. |
| Drug Metabolism and Liver Function | Potential liver damage, altered metabolism leading to increased drug concentration, and toxicity risks. | Liver function tests recommended; monitor for symptoms like dark urine and fatigue. |
| Cardiovascular Risks | Increased blood pressure, risk of chest pain, and possible cardiovascular complications. | Regular blood pressure monitoring; avoid in patients with cardiovascular conditions. |
Taking Contrave and Topamax Together: How Contrave and Topamax Interact
When taken together, Contrave and Topamax can lead to drug interactions affecting neurological functions, metabolic processes, and cardiovascular health. The two drugs require careful consideration before use.
Increased Risk of Seizures
Both Contrave and Topamax affect neurotransmitter activity. Taking bupropion, one of the active ingredients in Contrave, can increase the risk of seizures, particularly in those with a seizure disorder. Topamax, while an anticonvulsant, may not prevent seizures when combined with Contrave.
Patients with a history of seizures or other neurological health conditions face a higher risk when combining these medications.
Cognitive and Psychiatric Side Effects
Both Contrave and Topamax impact brain chemistry, which can lead to significant mood changes and cognitive side effects. When taken together, they may increase the likelihood of developing psychiatric complications such as depression, anxiety, emotional instability, and even suicidal thoughts.
These effects can range from mild mood fluctuations to severe psychiatric disturbances, which may require immediate medical attention.
Bupropion’s Role
Bupropion, one of the active ingredients in Contrave, is an atypical antidepressant that primarily affects dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain. It is commonly used to treat depression and assist with smoking cessation, but it can also cause agitation, restlessness, irritability, and insomnia in some individuals. Additionally, bupropion is associated with an increased risk of suicidal ideation, particularly in young adults and individuals with a history of mood disorders.
For those sensitive to its stimulating effects, it may contribute to heightened anxiety, panic attacks, or even manic episodes in individuals with bipolar disorder.
Topamax’s Contribution
Topamax (topiramate) has a direct impact on cognitive function, as it alters neurotransmitter activity in the brain. While it is primarily used to treat seizure disorders and migraines, it is known to cause cognitive dulling, making it harder to focus, process information, or recall memories. Patients have reported feeling as though they are in a “fog” or struggling with word retrieval, leading to difficulty with daily tasks and work-related performance.
Furthermore, emotional instability is a well-documented side effect, as Topamax can lead to sudden mood swings, increased depression, or a blunted emotional response. Some individuals may feel emotionally detached or have difficulty experiencing joy and motivation.
Combined Effect
When taken together, Contrave and Topamax may have a compounding effect on mental health, potentially leading to severe psychiatric symptoms. The risk of suicidal thoughts and mood instability may be heightened, particularly in those who have a history of depression, anxiety, or other psychiatric conditions.
Cognitive impairment may become more pronounced, affecting problem-solving skills, reaction times, and emotional processing. Some individuals may experience confusion, disorientation, or feelings of depersonalization, making it challenging to engage in routine activities.
Patients taking both medications should be closely monitored for changes in mood, behavior, or cognitive function. If symptoms such as severe depression, intrusive suicidal thoughts, or significant cognitive decline occur, medical intervention is necessary.
If you or someone close to you notices these changes while taking Contrave and Topamax together, tell your doctor immediately.
Metabolic and Electrolyte Imbalances
Contrave and Topamax together can significantly impact metabolic processes, including hydration, electrolyte balance, and blood pressure regulation. Both medications influence how the body processes nutrients, retains fluids, and maintains essential minerals like sodium and potassium.
If not carefully managed, these imbalances can lead to fatigue, confusion, muscle weakness, irregular heart rhythms, and severe dehydration.

Dehydration Risk
Topamax has diuretic-like properties, meaning it can cause the body to lose excess fluid. This can lead to dehydration and an increased risk of kidney stones. Dehydration can also result in dry mouth, dizziness, headaches, and lightheadedness, which may worsen when combined with Contrave.
Additionally, Contrave can cause nausea, excessive sweating, and gastrointestinal upset, all of which may further contribute to fluid loss. Dehydration can also affect blood pressure, potentially leading to fluctuations that increase the risk of dizziness, fainting, or heart complications.
To minimize dehydration risk:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain hydration levels.
- Avoid alcohol and caffeinated beverages, as they can further dehydrate the body.
- Monitor urine color—dark yellow or amber-colored urine may indicate dehydration.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Topamax is known to cause metabolic acidosis, a condition in which blood becomes too acidic due to a buildup of acid or loss of bicarbonate. Contrave can exacerbate this effect, leading to an increased risk of fatigue, confusion, shortness of breath, and muscle weakness.
Additionally, metabolic acidosis can result in bone density loss over time, increasing the risk of fractures in individuals who are already prone to bone-related conditions.
Certain symptoms, such as irregular heartbeat, muscle cramps, and excessive fatigue, may indicate a serious electrolyte imbalance. Tell your doctor if you experience persistent weakness, numbness, tingling, or muscle pain while on these medications.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
Both Contrave and Topamax can contribute to low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia), especially in patients with diabetes or those on a reduced-calorie diet. Since Topamax suppresses appetite and Contrave affects metabolism, some individuals may not consume enough calories, leading to dizziness, shakiness, confusion, and irritability.
If left untreated, severe hypoglycemia can result in seizures, loss of consciousness, or even coma.
To prevent dangerously low blood sugar levels:
- Eat balanced meals at regular intervals to maintain stable blood glucose.
- Monitor blood sugar if you have diabetes or take insulin or other glucose-lowering medications.
- Avoid skipping meals, even if you experience appetite suppression from these medications.
Weight Loss Drugs Complications
While both Contrave and Topamax aid in weight loss, excessive or rapid weight loss can lead to malnutrition and muscle wasting. Monitoring body mass index (BMI) is essential to ensure weight loss occurs at a healthy rate and to avoid complications. Individuals who lose weight too quickly may develop weakness, brittle nails, hair loss, and immune system deficiencies.
Additionally, drastic weight loss can stress the heart and other organs, increasing the risk of low blood pressure, dizziness, and irregular heart rhythms.
Patients combining Contrave and Topamax should aim for gradual, sustainable weight loss under medical supervision rather than extreme caloric restriction. Tell your doctor if you experience unintentional rapid weight loss, persistent weakness, or signs of malnutrition while on these medications.
Drug Metabolism and Liver Function
Both Contrave and Topamax are metabolized in the liver, increasing the risk of liver damage. Patients with liver problems must discuss taking Contrave with their healthcare provider before starting treatment.
- Increased Topamax Levels: Contrave may slow the breakdown of Topamax, increasing the risk of side effects.
- Altered Contrave Metabolism: Topamax may change how Contrave interacts with other medications, reducing its effectiveness.
- Liver Problems: Patients should monitor for dark urine, pale stools, and unusual tiredness, which may indicate liver damage.
Cardiovascular Risks
Combining these drugs can lead to increased blood pressure and chest pain. Since bupropion can increase the risk of high blood pressure, patients with cardiovascular issues should avoid taking Contrave and Topamax together.
Managing Side Effects and Risks
Patients taking Contrave and Topamax together must follow medical guidance to prevent interactions and manage side effects.
- Tell Your Doctor: Disclose all medications, including over-the-counter drugs.
- Monitor Blood Pressure: Regularly check for high blood pressure and report chest pain immediately.
- Prevent Dehydration: Stay hydrated to avoid kidney stones and electrolyte imbalances.
- Watch for Mood Changes: Suicidal thoughts and emotional instability should be reported immediately.
- Follow a Reduced Calorie Diet: Combining medications with proper nutrition can reduce health risks.
Monitoring and Testing
To minimize the risk of drug interactions, it’s essential to take proactive steps:
- Tell your doctor: Always inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you’re taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements. This helps your doctor identify potential interactions and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
- Monitor your body weight: Regularly check your body weight to ensure that you’re not experiencing any significant changes that could be related to a drug interaction. Sudden weight changes can be a sign of an adverse reaction.
- Check your blood pressure: Regularly monitor your blood pressure to ensure it remains within a healthy range. Some drug interactions can cause fluctuations in blood pressure, which can be dangerous if not managed properly.
- Report any side effects: If you experience any side effects, such as abdominal pain, chest pain, or panic attacks, inform your healthcare provider immediately. Early detection of side effects can prevent more serious complications.
Dose Adjustments and Alternative Medications
If a drug interaction is suspected, your healthcare provider may take several steps to manage the situation:
- Adjust the dose: Your doctor might change the dose of one or both medications to minimize the risk of a drug interaction. This can help maintain the effectiveness of your treatment while reducing side effects.
- Switch to an alternative medication: If the interaction risk is too high, your healthcare provider may replace one medication with another that is less likely to interact with your other medications. This ensures you continue to receive effective treatment without the added risk.
- Monitor you closely: Your healthcare provider may decide to closely monitor you for any signs of a drug interaction, such as changes in body weight, blood pressure, or the appearance of side effects. Regular check-ups and tests can help catch any issues early.
Working closely with your healthcare provider is essential to minimize the risk of drug interactions and ensure you receive the best possible treatment for your condition. Always communicate openly about your medications and any changes in your health.
Long-Term Use Considerations
Long-term use of Contrave and Topamax together may lead to dependency, withdrawal symptoms, and adverse effects such as mood changes and metabolic imbalances. Patients should regularly reassess their treatment plan with their healthcare provider to avoid increased risk of complications.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Both drugs have FDA warnings. Contrave carries a black-box warning due to the risk of suicidal thoughts associated with bupropion. Topamax has warnings related to metabolic acidosis and congenital disabilities when used during pregnancy.
Additionally, the World Health Organization monitors the safety of weight loss drugs and advises against unsupervised use. Before starting treatment, patients must read the medication guide and patient package insert.
Should You Take Contrave and Topamax Together?
Given the potential risks, patients should only take Contrave and Topamax together under close medical supervision. They should also consult their healthcare provider to assess their health history and discuss possible interactions with other medications.
FAQ: Contrave and Topamax Drug Interactions
Combining medications can sometimes enhance therapeutic effects, but it can also lead to dangerous drug interactions. Below are answers to common questions regarding the use of Contrave and Topamax, as well as their interactions with other medications.
If you are considering taking these medications together, always consult your healthcare provider to ensure safety.
1. Can you take topiramate and Contrave?
Topiramate (Topamax) and Contrave are both used for weight loss but affect the body differently. While some healthcare providers may prescribe them together off-label, this combination can increase the risk of serious side effects, including seizures, mood changes, and metabolic imbalances. Since Contrave contains bupropion, which lowers the seizure threshold, adding Topamax could further alter brain chemistry and exacerbate neurological side effects.
Due to these risks, medical supervision is necessary to determine if this combination is appropriate for you.
2. Can you take bupropion and Topamax together?
Bupropion, one of the active ingredients in Contrave, is sometimes prescribed alongside Topamax for conditions such as depression, weight loss, or migraine prevention. However, this combination may lead to an increased risk of seizures, mood instability, and cognitive impairments such as brain fog or memory problems. While some patients tolerate the combination well, others may experience amplified side effects, making close monitoring by a healthcare provider essential.
If prescribed together, your doctor may recommend starting at a lower dose to reduce potential risks.
3. Can you take semaglutide and Topamax together?
Semaglutide (found in medications like Ozempic and Wegovy) is a GLP-1 receptor agonist used for weight loss and diabetes management, while Topamax is sometimes used off-label for appetite suppression. These medications do not have a well-documented direct interaction, but their combined use may lead to amplified appetite suppression, nausea, and gastrointestinal distress.
Additionally, Topamax can contribute to metabolic acidosis, and when combined with semaglutide, it could potentially worsen dehydration or electrolyte imbalances. Patients should consult their healthcare provider to assess the safety and efficacy of combining these two drugs.
4. Is Contrave or Topamax better?
Contrave and Topamax work differently for weight loss, and their effectiveness varies based on one’s weight loss drug type (quiz here), individual health conditions, and treatment goals. Contrave combines bupropion and naltrexone to target appetite and food cravings through neurotransmitter regulation, while Topamax, originally an anticonvulsant, suppresses appetite and alters taste perception.
Contrave may be more suitable for individuals struggling with cravings, while Topamax is sometimes prescribed off-label for patients who have not responded well to other weight loss drugs. The best choice depends on your medical history, existing conditions, and how your body reacts to each medication.
5. Can you take Contrave with Topamax?
While some doctors may prescribe Contrave and Topamax together for weight loss, this combination is not widely recommended due to potential risks. Both medications affect the central nervous system, increasing the risk of seizures, mood disturbances, and cognitive side effects such as confusion and memory issues.
Additionally, Contrave can raise blood pressure, while Topamax can contribute to dehydration and metabolic imbalances, further complicating their combined use. If your doctor prescribes both, they will likely recommend starting at low doses with careful monitoring to minimize risks.
6. Can Topamax and bupropion be taken together?
Topamax and bupropion (a key ingredient in Contrave) can be prescribed together, but this combination requires caution. Bupropion is known to lower the seizure threshold, while Topamax can alter brain activity, increasing the likelihood of seizures, mood swings, or cognitive impairment.
Patients with a history of seizures, bipolar disorder, or other neurological conditions may be at higher risk for adverse effects. If prescribed together, your healthcare provider will typically adjust dosages and monitor you for potential side effects.
7. What medications should I avoid with Contrave?
Several medications may interact negatively with Contrave, increasing the risk of dangerous side effects.
Some key medications to avoid include:
- MAO Inhibitors (e.g., Phenelzine, Tranylcypromine): Can cause severe blood pressure spikes and serotonin syndrome.
- Opioid Medications (e.g., Oxycodone, Morphine): Contrave contains naltrexone, which blocks opioid effects and may cause withdrawal symptoms in opioid users. If you’re interested in drug interactions between Contrave and specific opinion medications, please see our comprehensive guild on Contrave and Tramadol Drug Interactions.
- Other Bupropion-containing Drugs (e.g., Wellbutrin, Zyban): Increases the risk of seizures and overdose.
- Certain Antidepressants and Antipsychotics: May interact with bupropion and increase the risk of mood changes or serotonin syndrome.
- Stimulants (e.g., Adderall, Ritalin): Can raise blood pressure and heart rate when combined with Contrave.
To prevent interactions, tell your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and herbal supplements, before starting Contrave.
Conclusion
While Contrave and Topamax can aid in weight loss, their combination poses risks that outweigh the benefits for many individuals. Patients should be aware of increased risk factors such as high blood pressure, liver problems, and mental health complications. It is essential to tell your doctor about all medications taken, follow a reduced-calorie diet, and monitor for serious side effects, including dark urine, chest pain, and suicidal thoughts.
Understanding these drug interactions and working with a healthcare provider can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment plans.